Generative AI vs AI Agents vs Agentic AI: Understanding the Evolution
Aug 19, 2025 3 Min Read 5219 Views
(Last Updated)
What’s the real difference between Generative AI, AI Agents, and Agentic AI, and why does it matter? As businesses and developers race to build smarter systems, understanding these distinctions isn’t just technical nitpicking.
It’s about knowing what each type of AI can do, where it fits, and how it scales with your ambitions. This article breaks down how these three AI paradigms evolved, what sets them apart, and how to choose the right one for the job.
Although these terms are often used interchangeably, they represent distinct levels of capability, autonomy, and task complexity. This article aims to break down their definitions, differences, and real-world implications, so you can better evaluate and build intelligent systems that suit your goals.
Table of contents
- I. What is Generative AI?
- Definition:
- Core Component:
- Capabilities:
- Limitations:
- II. What is an AI Agent?
- Definition:
- Key Components:
- Functionality:
- Limitations:
- III. What is Agentic AI?
- Definition:
- Key Characteristics:
- Security & Control Considerations:
- IV. Side-by-Side Comparison
- V. Key Takeaways
- VI. Tools and Frameworks to Build with
- Final Thoughts
I. What is Generative AI?
Generative AI refers to AI systems that are capable of creating new content based on the patterns they’ve learned from existing data.
Definition:
A model trained to produce outputs such as text, images, code, or even music, based on patterns from vast datasets.
Core Component:
- Large Language Models (LLMs) like GPT-4, Claude, and Gemini.
- These models are trained on large datasets including books, encyclopedias, web pages, and more.
Capabilities:
- Text generation (e.g., writing emails, stories, articles).
- Image and video synthesis (via multimodal models).
- Code generation based on user prompts.
Limitations:
- Knowledge Cutoff: LLMs cannot access real-time data or updates beyond their training date.
- Static Outputs: They generate content but cannot perform real-world tasks or interact with tools.
- Limited Autonomy: They only respond to prompts without the ability to reason or act independently.
II. What is an AI Agent?
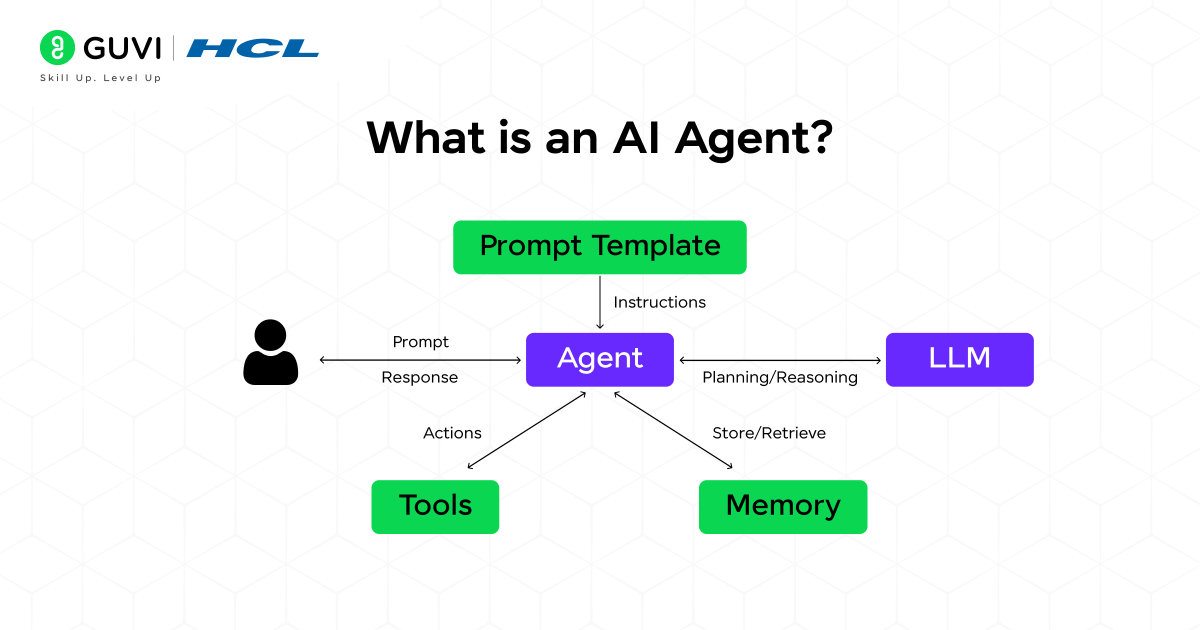
AI Agents bridge the gap between passive AI systems and interactive digital assistants. They take input, process it using AI, and take real actions to complete specific tasks.
Definition:
An AI-driven system that uses LLMs to analyze input and interact with tools or APIs to accomplish a defined objective.
Key Components:
- LLM: The reasoning engine or brain.
- Tools/APIs: External services the agent can interact with (e.g., flight booking APIs).
- Memory: Stores and recalls previous interactions for better contextual performance.
- Knowledge Base: Contains structured data the agent uses for informed decision-making.
Functionality:
- Goes beyond Q&A to perform tasks like searching for flights, submitting forms, or automating emails.
- Makes decisions autonomously (e.g., choosing the best flight option based on cost and time).
Limitations:
- Best suited for narrow or well-defined tasks.
- May struggle with tasks requiring high-level planning or unpredictable conditions.
III. What is Agentic AI?
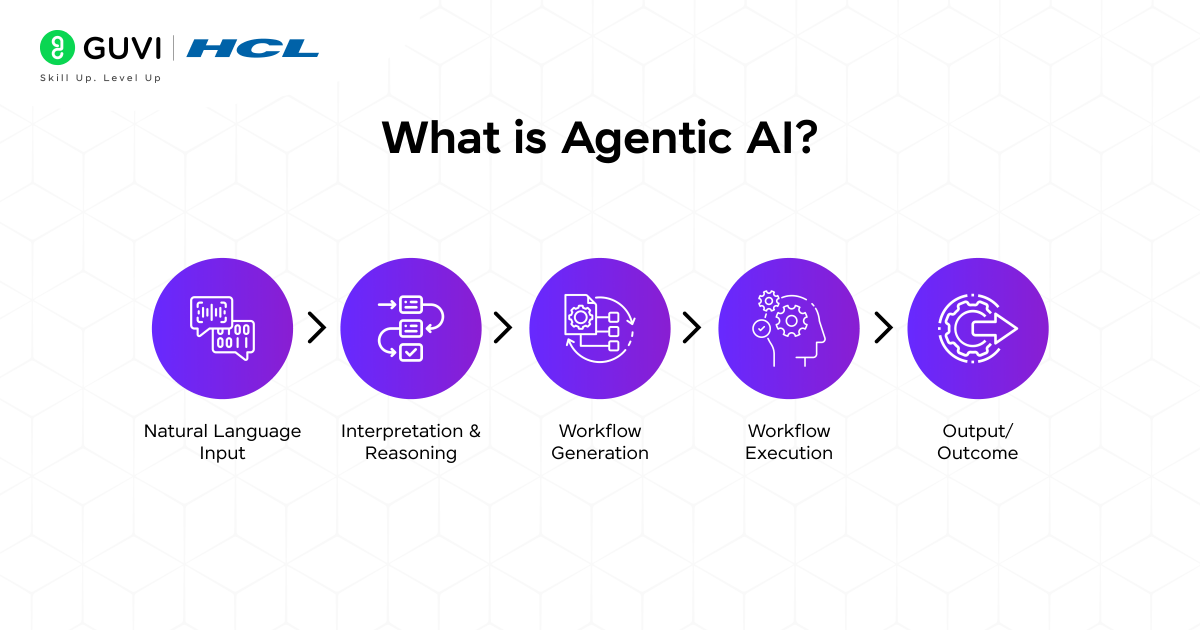
Agentic AI represents a more advanced form of AI agents. These systems work autonomously across multiple steps, use tools, and even coordinate with other AI agents to complete complex tasks.
Definition:
An intelligent, autonomous system composed of one or more agents capable of reasoning, planning, and executing multi-step operations to achieve a defined goal.
Key Characteristics:
- Multi-Step Reasoning and Planning: Handles tasks that involve several steps and dynamic decision-making.
- Example: Planning a multi-destination trip based on weather, budget, and visa constraints.
- Example: Planning a multi-destination trip based on weather, budget, and visa constraints.
- Tool Usage and Coordination: Can access multiple APIs or databases to gather and verify information.
- Example: Using a weather API and a flight API to plan the best travel day.
- Example: Using a weather API and a flight API to plan the best travel day.
- Collaboration Between Agents: Multiple agents can work together, each specializing in a part of the workflow.
- Example: A booking agent collaborates with a visa-checking agent before confirming an itinerary.
- Example: A booking agent collaborates with a visa-checking agent before confirming an itinerary.
- Goal-Oriented Autonomy: Designed to achieve complex, high-level objectives with minimal human intervention.
Security & Control Considerations:
- Due to their high autonomy, agentic AI systems must be controlled and sandboxed.
- Access to sensitive systems or data must be restricted to avoid unintended consequences.
IV. Side-by-Side Comparison
| Feature | Generative AI | AI Agent | Agentic AI |
| Core Function | Content Generation | Task Completion | Complex Goal Achievement |
| LLM | Required | Required | Required |
| Tool Usage | No | Yes | Yes |
| Takes Action | No | Yes | Yes |
| Autonomy | Limited | Moderate | High |
| Task Complexity | Low | Medium | High |
| Decision-Making | Limited | Moderate | High |
| Agent Collaboration | No | Rare | Common |
| Knowledge Cutoff | Present | Reduced (via tools) | Reduced (via tools) |
| Reasoning/Planning | Limited | Basic | Advanced, Multi-Step |
V. Key Takeaways
- Generative AI is powerful for creating content but cannot act or reason.
- AI Agents enhance generative AI by enabling real-world interactions through tools and APIs.
- Agentic AI builds on agents by introducing autonomy, multi-agent collaboration, and advanced task planning.
- As we move from Generative AI to Agentic AI, we see an increase in capability, autonomy, and complexity.
VI. Tools and Frameworks to Build with
If you’re looking to experiment or build AI-driven systems, consider the following tools:
- N8N: A visual, node-based tool for building agentic AI workflows.
- Agno: A flexible framework to define, manage, and deploy AI agents with varying autonomy levels.
- LangGraph: A powerful framework for building composable, multi-step AI agents with memory and tool access.
These frameworks help developers quickly move from experimentation to production with agentic AI systems.
In case, you want to explore more on Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning, consider enrolling for GUVI’S Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Course which teaches everything related to it with an industry-grade certificate!
Final Thoughts
The AI landscape is evolving from simple content generation to complex, autonomous task execution. Understanding the differences between Generative AI, AI Agents, and Agentic AI helps organizations and developers choose the right approach for their goals.
Whether you’re drafting emails with GPT-4, automating bookings with an AI agent, or building a self-managing assistant with agentic AI—these technologies are not just futuristic ideas. They’re here, and they’re reshaping how we work, build, and innovate.




























Did you enjoy this article?