Full Stack Vs MEAN Stack Development: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Business
Oct 25, 2025 5 Min Read 1018 Views
(Last Updated)
There are several ways to perform any specific task, and the quality of its result largely depends on the individual’s objective. Similarly, when it comes to designing and developing websites and web applications, there are multiple options in the market through which one can achieve the desired outcome.
Likewise, Full Stack and MEAN Stack are excellent examples of web development technologies that enable developers to create comprehensive software platforms and applications by integrating both front-end and back-end systems. While the development scope of Full Stack development is much broader in size, MEAN Stack development is limited to only four technologies, yet very effective in creating scalable and real-time apps. In simple terms, we can say MEAN Stack is a type of full-stack methodology.
In this blog, our primary purpose is to navigate through all the aspects of Full Stack Vs MEAN Stack development, so that one can make a pragmatic decision on which technology method to choose for their business.
Table of contents
- What is Full Stack Development?
- Core Components
- Advantages
- Real-World Applications
- What is MEAN Stack Development?
- Core Components
- Advantages
- Real-World Applications
- Full Stack vs MEAN Stack Development: A Comparative Analysis
- Which One to Choose for Your Business: Full Stack or MEAN Stack
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- What is the main difference between Full Stack and MEAN Stack?
- Which stack is better for small startups?
- Can both stacks handle large-scale applications?
What is Full Stack Development?
Full-stack development is the process of building scalable and complex websites and applications by blending both the frontend (client-side) and backend (server-side) systems. As there are no restrictions on choosing any particular set of technology, Full Stack offers developers the flexibility to build products with multiple tech components, meeting project requirements and goals. The frontend part is designed to enable users to interact with the visual interface, whereas the backend code is written to handle server-side operations and databases.
1. Core Components
- Front-end (Client Side)
Through programming languages (HTML, CSS, and JavaScript) and frameworks such as React, Angular, or Vue, interactive and engaging user interfaces are designed that consist of visually appealing design patterns and smooth navigational flow with minimal technical glitches.
- Back-end (Server Side)
The back-end is the part built to manage and handle business-specific logic, authentication processes, and server operations, ensuring the seamless internal workflow of the entire software architecture. Some popular backend technologies include Node.js, Python, Java, and PHP.
- Database
SQL (MySQL, PostgreSQL) or NoSQL (MongoDB) database management systems are implemented into the project to store and manage high volumes of data and business information. These tools are specifically connected to the systems to enable faster data accessibility, retrieval, and manipulation, which are beneficial for complex online processes such as concurrency control, online transactions, and data backup and recovery, while also providing robust security support.
- APIs & Web Services
To ensure smooth communication between the front-end and back-end systems, API (application programming interfaces) and web services are integrated into the codebases. The APIs are used to fetch data or request services from other programs, while Web Services are communication protocols (such as REST and SOAP) designed to exchange data over the network via the XML format.
Here, REST: Representational State Transfer, SOAP: Simple Object Access Protocol, and XML: Extensible Markup Language (this language is used for storing, transmitting, and reconstructing the data)
- Version Control & Deployment
Tools like Git/GitHub or GitLab are used for tracking and managing changes or modifications made to code files for production. The version control system (VCS) software also enhances the quality of team collaboration and the software development life cycle by allowing the developers to work on different elements and functionalities of the project in parallel without deviating from the core objective. In other words, it will enable all the team members to work on distinct assignments by staying on the same page, leading to faster product delivery.
2. Advantages
- End-to-End Expertise: The development life cycle process encompasses both the front-end and back-end of the applications, resulting in a complete, workable software product.
- Technology Flexibility: According to the business objectives or customer requirements, pick the best set of tools and technologies to build different layers.
- Faster Project Delivery: A full-stack developer is proficient in developing and managing multiple modular components of applications, eliminating the need to hire separate front-end and back-end engineers. This results in a significantly shorter project delivery timeframe, with no compromise on build quality and performance.
- Cost-Effective: The overall development cost is minimized due to optimal resource allocation and reduced dependency on multiple domain specialists.
- Broad Career Opportunities: Due to the capabilities and importance of Full Stack development, it is a widely accepted skill across the industry; top tech companies consistently prioritize Full Stack developers over candidates with single-domain specialization, such as front-end and back-end.
3. Real-World Applications
- E-commerce Platforms: Most popular e-commerce sites, such as Amazon, eBay, and Flipkart, which are scalable and complex from a development perspective, are excellent examples of full-stack projects. This development method is the ideal choice for managing a wide variety of products, payments, order systems, and user accounts.
- Social Media Apps: Interactive and user-friendly social media applications, such as Facebook and Instagram, can be crafted by considering all the intricacies and essential features, including handling feeds, a seamless messaging system, notifications, and pushing relevant and trending content based on an algorithm.
- Streaming Services: Smooth streaming platforms such as Netflix and Spotify can be built to provide a great user experience (UX). The front-end part of these applications can be designed using the latest frameworks such as Svelte, React, Vue, Material UI, and Tailwind CSS to enable users to search for their desired content without any hindrances. Backend tools like Django and Node.js are implemented for sophisticated backend operations, such as buffering control, database management, subscription & payment processing, and content delivery (audio, video) via leveraging Content Delivery Networks (CDNs).
What is MEAN Stack Development?
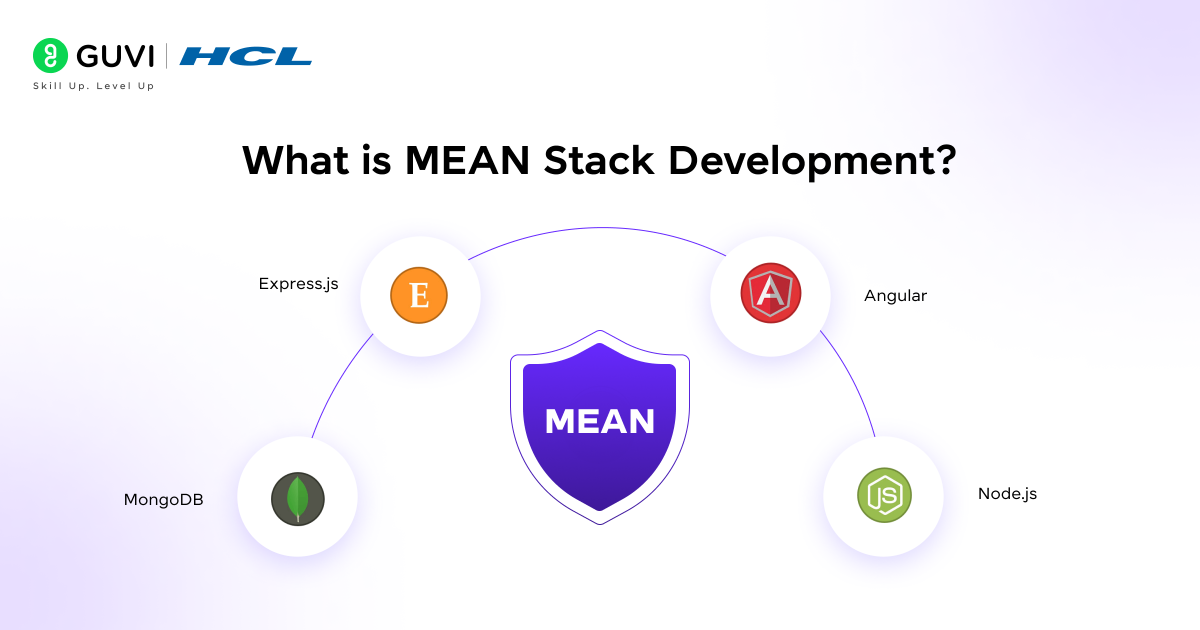
MEAN (MongoDB, Express.js, Angular, and Node.js) stack development is a type of full-stack development that utilizes a single programming language: JavaScript. This JavaScript-based framework is specifically designed to create applications that are flexible, scalable, and can be easily modified to accommodate changing business requirements and needs. Using a single language throughout the process makes the entire development cycle faster, modular, consistent, and simpler to handle and maintain. The MEAN stack is specifically designed for projects that prioritize real-time features and dynamic user interfaces.
1. Core Components
It is a NoSQL database that is used for storing and managing unstructured and rapidly changing data efficiently. This document-based data model is commonly employed in projects that adhere to an agile development methodology. MongoDB uses the BSON data format, which enables developers to store objects within a single main collection with different sets of parameters, making applications more flexible and scalable.
- Express.js
This is a Node.js framework used for managing and handling server-side logic and operations, as well as APIs. This specific tool simplifies the routing facility in the applications by dividing the project into multiple small modules, each having its own functionality. Apart from this, Express also helps with error handling and controlling the request-response cycle within the application.
It is an open-source front-end framework used for creating dynamic user interface (UI) components, which are rendered only when users interact or data is manipulated, rather than loading the entire page. Angular is one of the best choices, whether you’re developing small projects or enterprise-grade applications.
- Node.js
It is a JavaScript runtime environment that uses an asynchronous (non-blocking) programming approach, which means that in cases of heavy or slow functions, the entire program execution is not blocked or delayed. This means that complex tasks, such as file reading, making API calls (HTTP requests), and managing databases, can be handled simultaneously with ease. It is an ideal backend tool for creating fast and scalable network applications.
- RESTful APIs
These interfaces are implemented within the code to enable communication between the front-end and back-end parts of the application, making it a fully functional software product. Most of the class or functional components in the program require interaction with external or internal systems and third-party services to perform various tasks. With these APIs, it is possible. RESTful APIs are also implemented through HTTP methods (GET, PUT, DELETE, etc.) to pass user requests to the servers.
2. Advantages
- Single Language: JavaScript is used throughout the development, i.e, for front-end, back-end, and database operations. Due to this, the language complexity issue is eliminated, and developers can focus their primary attention on core engineering rather than being confused by switching languages.
- Faster Development: The unified technology model helps minimize the complexity involved in converting business ideas into software solutions, resulting in an increased pace of development.
- High Performance: Asynchronous operations can be performed, resulting in a drastic improvement in the overall performance of the applications.
- Scalable & Maintainable: As the business grows, its requirements and objectives also change. In this case, using the MEAN stack can be an ideal choice, as it can significantly contribute to scaling the application in response to evolving changes, while also maintaining it.
- Strong Community Support: The MEAN stack boasts a large and vibrant developer community, where tutorials, latest updates, optimization techniques, and valuable resources for full-stack development are shared. Develpopers can get tips from some of the best tech minds across the world in building projects that create real-world impact.
3. Real-World Applications
- Real-Time Chat Apps: Real-time messaging or chat web apps, such as WhatsApp Web and Slack, can be developed using the MEAN stack with all essential features, including instant messaging, typing indicators, end-to-end encryption, file and media sharing, and more. MEAN can be an excellent choice for creating this type of project, where user experience (UX) plays a crucial role.
- Single-Page Applications (SPA): Platforms such as Gmail and Google Docs can be created through this technology stack, with a smooth and fast internal workflow. Due to its asynchronous programming approach and two-way binding feature, it reduces page reloading time and supports dynamic content updates, as well as a seamless navigational flow.
- Task Management Tools: To design and develop high-quality software tools like Trello and Asana, MEAN can be the best option for developers. As this particular technology stack effectively supports real-time updates and team collaboration features, such as video conferencing, project dashboards, activity feeds, and many others, through asynchronous communication with WebSockets, event-driven architecture, and MongoDB access control.
Full Stack vs MEAN Stack Development: A Comparative Analysis
Full Stack
- Can mix multiple languages and frameworks
- Performance depends on chosen technologies
- Requires learning multiple languages
- Highly scalable with varied tech
- Suitable for large-scale, complex applications
MEAN Stack
- Limited to JavaScript across all layers
- High performance with Node.js and asynchronous operations
- Easier for developers familiar with JavaScript
- Scalable with a uniform stack
- Ideal for real-time apps, SPAs, and dynamic web apps
Which One to Choose for Your Business: Full Stack or MEAN Stack
Choosing between Full Stack and MEAN Stack for your business depends on your project requirements, team expertise, and long-term goals. Full-stack development is ideal if your project requires flexibility to use different technologies for the front-end, back-end, and database. It works well for large-scale or complex applications where you may want to mix and match frameworks and languages to achieve the best performance and functionality.
On the other hand, MEAN Stack is an excellent choice if you prefer a single-language (JavaScript) approach, which simplifies development, ensures faster deployment, and is particularly effective for real-time applications, dynamic websites, or single-page applications (SPAs). MEAN Stack also facilitates maintaining uniformity across the project and leveraging the benefits of asynchronous operations for improved performance.
Ultimately, the choice should be guided by your team’s skills, project complexity, budget, and scalability needs, ensuring that the stack you pick aligns with both current and future business goals.
If you are someone who is curious to delve deep into the full-stack development domain and wants to contribute to building industry-grade software applications, then join HCL GUVI’s IITM Pravartak Certified MERN Full Stack Development Course and master the in-demand tools Git, MongoDB, Express, React, Node.js, and more. Unlock the most prosperous tech careers by getting mentored by industry experts. Wait no further – talk to our expert team to learn more.
Conclusion
I hope this blog was meaningful for me in providing some valuable insights on Full Stack and MEAN stack development methodologies, along with their differences. The dilemma of choosing the optimal technology stack for your business ultimately depends on the type of project requirements and needs, as well as the long-term goals you want to achieve.
FAQs
What is the main difference between Full Stack and MEAN Stack?
Full Stack utilizes any technology for front-end and back-end development, while MEAN Stack consistently uses only JavaScript tools.
Which stack is better for small startups?
MEAN Stack is faster, simpler, and easier to maintain for small projects efficiently.
Can both stacks handle large-scale applications?
Yes, Full Stack is more flexible, while MEAN Stack is faster and uniform for scalability.




































Did you enjoy this article?