
Difference Between System Software and Application Software
Oct 28, 2025 6 Min Read 1787 Views
(Last Updated)
Computers and mobile devices have become an integral part of our lives. Exceptions still exist in every domain; however, the majority of the population relies heavily on these digital electronic devices to perform tasks, simplify processes, and make better decisions.
But there is only one thing without which these computers, tablets, and mobile phones would become futile and isolated, and that is System Software. These are programs that are required to establish a connection with the device’s hardware. Apart from this, there are Application Software that run and operate on top of the system software. These programs are designed to address specific tasks and problems, leveraging advanced features and functionalities integrated into their architecture.
Many of us often consider system and application software as a similar entity; they are related but not equivalent to each other. In this blog, we will explore the difference between System Software and Application Software and what sets them apart.
Table of contents
- System Software and Application Software: Know Their Definition
- A. System Software
- B. Application Software
- Key Differences Between System Software and Application Software
- Key Characteristics of System Software
- Key Characteristics of Application Software
- Functions of System Software
- Functions of Application Software
- Types and Examples of System Software
- Operating System (OS)
- Utility Software
- Device Drivers
- Firmware
- Language Translators
- Types and Examples of Application Software
- General-Purpose Application Software
- Special-Purpose Application Software
- Custom Application Software
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- What is the main difference between system software and application software?
- Can application software run without system software?
- What are some examples of system software?
System Software and Application Software: Know Their Definition
A. System Software
It is a type of software that acts as the foundational base of the entire computer system. It bridges the gap between software and hardware while ensuring seamless communication between them. This software is designed to enable users to operate computers and mobile devices without any hindrances.
These programs are primarily responsible for controlling and directing hardware resources, such as CPUs, memory, storage components, and firmware. Some of the most essential and complex low-level operations, like file management, security updates, system upgrades, memory management, and process scheduling, are all handled by system software.
These are the internal logic that runs on the backend and is not explicitly displayed to the users. The central focus behind developing and designing this software is to enhance the usability and effectiveness of the hardware, while creating an optimal digital environment or platform where the application software can run smoothly.
Brief Illustration
Think of an Operating System (OS) software that is primarily designed and developed for managing all the hardware components (CPU, memory space, keyboard, screen) and their operations. It provides an environment where other software programs, applications, and digital tools can run at peak efficiency.
B. Application Software
Application software is the functional programs that are developed and deployed for the end users (customers, business owners, enterprises, and organizations). With the help of this powerful software, users gain the ability to virtually perform daily tasks such as ordering food, sending funds, streaming videos and music, shopping, editing images, and creating presentations. Some of the best examples are WhatsApp, Zomato, Adobe Photoshop, PowerPoint, Netflix, and Spotify.
This software runs on top of system software, which means that without the technical support of the system programs, these applications are not self-sufficient to be active. The sole purpose behind crafting these apps is to meet the expectations and ongoing requirements of end users.
Developers typically implement the best tools and technologies to make these application software more user-friendly and interactive, ensuring connectivity between people and digital services.
Brief Illustration
Observe all the tasks and activities we perform regularly through digital media. For ordering food from restaurants and cloud kitchens, we use Zomato and Swiggy. For online transactions, we use Google Pay, Paytm, and Phone Pay. For booking train tickets, we use the IRCTC web platform. For shopping, we use Myntra, Amazon, and Flipkart. These are some popular and widely used application software that save our time and effort from redundancy and repetitive actions.
Key Differences Between System Software and Application Software
Based on certain key aspects, we will differentiate between these two software. So these are the following points:
- Purpose
- System software is developed by software engineers to manage computer hardware functions effectively. This software also ensures that these components are involved in performing only necessary tasks, meaning they should carry out the operation only when needed, and not otherwise.
- Application software, on the other hand, is designed and developed to facilitate users in simplifying their daily activities, such as writing and organizing documents, searching for desired products, or monitoring the real-time internal flow of operations.
- Dependency
- System software is much broader in scope and can operate independently without relying on any external sources. They run in the background of computers and mobile devices (such as Windows, macOS, Android, and iOS) and create an integrated environment to execute multiple sub-programs and applications.
- Whereas application software is dependent on system software because, without it, they are not capable of utilizing the computer’s resources. It is not possible and practical for any application software to run directly on hardware. To actively exist and operate, it requires the support of the operating systems (OS) and other utilities.
- Users
- System software communicates with the computer’s hardware and resources, rather than directly interacting with end users. All the processes associated with it run in the background, such as managing memory space, assessing average response time and active time, and many more.
- Application software is only concerned with delivering value to the end users. They are specifically designed to allow users to interact with engaging content, visual components, and multiple features and functionalities through a user-friendly interface.
- Installation
- From an installation perspective, System software generally comes pre-installed on mobile phones or computers. In most cases, users don’t need to install them manually; instead, they only need to update the software to ensure optimal performance.
- Application software is generally installed by the users. A user’s requirements and objectives are the primary factors in deciding which specific application software to install.
- Complexity
- Processes such as memory management, process synchronization and scheduling, and device coordination are complex mechanisms that are managed by system software. As these are not visible to the naked eye, users can’t form a relationship with them.
- In contrast, application software is generally accessible and more straightforward for users to interact with. The complex parts, such as the algorithm and backend operations, are hidden; users see only the interface and tools necessary to operate the application software.
Key Characteristics of System Software
- Foundational Computing: It provides the most basic and vital environment for the smooth functioning of all software programs.
- Resource Management: It provides the most basic and vital environment for the smooth functioning of all software programs. It controls the resources of a computer, which includes CPU, memory, storage, input, and output peripherals, efficiently without compromising their performance.
- Automatic Operation: All operations run in the background when the computer and mobile devices are in active mode, requiring minimal user interaction.
- Core Essentiality: Without the system software, all the computers in the world would be just pieces of stagnant machinery. To make computer devices workable machines, this software is installed in them.
- Less User-friendly: These advanced and complex software are designed for performance and stability, and as a result, they do not encourage interactivity and engagement with the system, making them less user-friendly.
Key Characteristics of Application Software
- Task-Specific: These applications are designed to perform specific tasks, such as shopping, editing, browsing, gaming, or activities required to streamline the workflow of any business or organization.
- Broad Range: Apart from general-purpose application software, there are numerous specialized apps, including healthcare platforms, online transaction apps, ed-tech apps, and e-commerce applications, which vary across different business verticals.
- User-Centric: Users can directly interact with the application software through simple and effective interfaces. The navigational flow enables end users to visit various sections and pages within the application without requiring external guidance.
- Customizable: As different users and businesses have their own sets of goals and requirements, applications are tailored to meet those diverse objectives with unique features and tools.
- Optional in Nature: These are not mandatory programs that the operating system in any device needs to run; instead, they are optional technologies designed to boost the productivity and efficiency levels of end users.
Functions of System Software
- Manages Hardware: Controls CPU, memory, and devices.
- Runs Applications: Provides a platform for apps to work.
- File Management: Organizes, stores, and retrieves data.
- System Security: Protects the system from errors and threats.
- Multitasking Support: Enables multiple programs to run simultaneously.
Functions of Application Software
- Performs User Tasks: Helps in writing, designing, gaming, or browsing.
- Data Processing: Creates, edits, and manages information.
- Communication: Enables email, chat, and video calls.
- Entertainment: Plays music, videos, and games.
- Productivity Boost: Enhances efficiency with tools such as spreadsheets, presentations, and project management apps.
Types and Examples of System Software
1. Operating System (OS)
The operating system of a computer device is the central brain of the computer; without it, the computer becomes dysfunctional and useless. It is responsible for controlling resources such as the CPU, memory, storage, and input/output devices connected to it. It also ensures the stability, usability, security, and reliability of the computer.
Examples: Windows, Linux, macOS, iOS, Android
2. Utility Software
Utility programs are like the support system for the operating system (OS). The core responsibility of this software is to maintain, safeguard, and optimize the quality and performance of computer or mobile models.
Technical tasks and operations such as managing files and folders, compressing data to prevent high memory consumption, data cleansing to maintain consistency and integrity of instructions, detecting viruses and unauthorized access, and many more, are all handled by utility software.
Examples: Norton Antivirus, McAfee Antivirus, CCleaner, WinRAR, Acronis True Image
3. Device Drivers
If we have to define device drivers in one word, it will be known as an interpreter. A device driver acts as an interpreter between the software and hardware of a computer system.
Each hardware device, when connected with computers, mobiles, or tablets, needs a driver attached with it so that the OS can decode the information regarding how to communicate with the device as well as use it through the system software. A device driver manages the log events, power requirements, and validates the input parameters.
Examples: HP Printer Driver, Canon Printer Driver, NVIDIA Graphics Driver, AMD Graphics Driver, Realtek Audio Driver
4. Firmware
Firmware is a type of system software that is stored permanently inside the hardware components (mainly installed in the motherboard of computers). It is responsible for providing low-level instructions that direct the devices to start and operate. To initialize the device, it uses non-volatile chips (these are memory chips that retain the stored data even when the device is not operating or is off).
Examples: BIOS/UEFI, TP-Link Router Firmware, Samsung Smart TV Firmware, Canon Camera Firmware, Apple iPhone Firmware
5. Language Translators
Computers are not capable of functioning and performing complex tasks solely by relying on hardware operations. That’s why programming languages are necessary for writing algorithms, rules, and instructions that humans can understand, enabling them to solve complex problems and complete specific tasks.
But computers understand only machine-level code. This is where language or program translators, such as compilers, interpreters, and assemblers, come into action, who translate or transform human-readable language into byte codes.
Examples: GCC Compiler, Java Compiler (javac), Python Interpreter, Ruby Interpreter, NASM Assembler
Types and Examples of Application Software
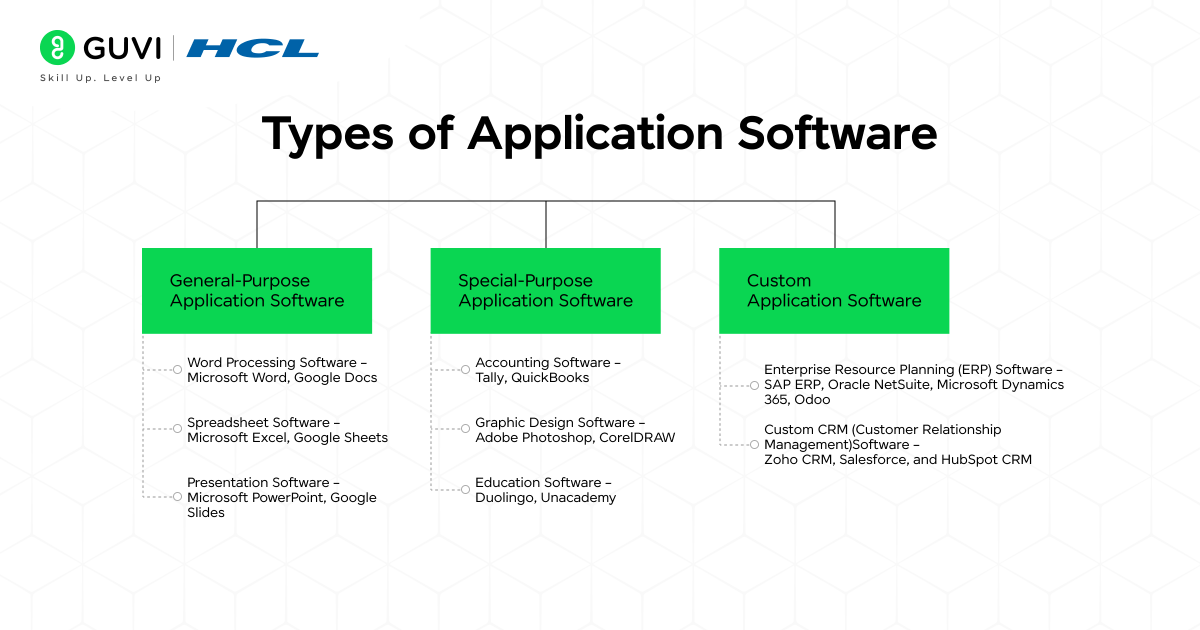
1. General-Purpose Application Software
As the name suggests, this software is designed for everyday tasks, offering a comparatively simple yet effective platform for writing and preparing documents, organizing information and data, and creating slides for both professional and personal purposes.
Examples:
Word Processing Software – Microsoft Word, Google Docs
Spreadsheet Software – Microsoft Excel, Google Sheets
Presentation Software – Microsoft PowerPoint, Google Slides
2. Special-Purpose Application Software
This software is built to serve a specific industry, profession, or audience. A certain level of competency and understanding is required to operate the application software. It is more concentrated on performing complex and advanced tasks rather than general utilities.
Examples:
Accounting Software – Tally, QuickBooks
Graphic Design Software – Adobe Photoshop, CorelDRAW
Education Software – Duolingo, Unacademy
3. Custom Application Software
There are many intricacies and customizations involved while developing these unique software applications. Developers follow the most optimal software development methodology to align with the unique needs of a particular organization or individual. These apps also provide personalized recommendations to enhance operational quality, and, similar to Special-Purpose application software, they are not intended for general use.
Examples:
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Software – SAP ERP, Oracle NetSuite, Microsoft Dynamics 365, Odoo
Custom CRM (Customer Relationship Management)Software – Zoho CRM, Salesforce, and HubSpot CRM
System software has existed since 1956, and today, over 2.5 billion devices run operating systems like Windows, macOS, iOS, or Android.
Application software is used by billions worldwide. Microsoft Word has been downloaded over 1.2 billion times, SAP ERP serves more than 437,000 companies in 180 countries, and Salesforce manages data for over 150,000 businesses.
Are you a software developer aspirant aiming to build a strong and future-ready tech career? In today’s AI-driven era, where artificial intelligence is transforming every domain and boosting the efficiency of software solutions, equipping yourself with AI-powered software development skills is the smartest move you can make. Take the leap with HCL GUVI’s IITM Pravartak & MongoDB certified AI Software Development course and gain the expertise you need to stand out and crack top product-based companies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, system software and application software work hand in hand to make computers and mobile devices functional and user-friendly. System software provides the essential foundation by managing hardware, resources, and core operations.
In contrast, application software runs on top of it to help users perform specific tasks, from productivity and learning to entertainment and business. Together, they transform complex hardware into accessible technology, streamlining daily activities and enhancing efficiency in both personal and professional life.
FAQs
What is the main difference between system software and application software?
System software manages hardware and core operations, while application software helps users perform specific tasks.
Can application software run without system software?
No, application software depends on system software to function because it cannot interact directly with hardware.
What are some examples of system software?
Examples include Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, device drivers, and utility programs like antivirus software.



































Did you enjoy this article?