
AI in IoT (Internet of Things) Explained
Oct 07, 2025 6 Min Read 2215 Views
(Last Updated)
Sundar Pichai once said, “AI is probably the most important thing humanity has ever worked on. I think of it as something more profound than electricity or fire.” This thought encapsulates the profound impact of the change AI is bringing.
Artificial Intelligence is reshaping every major industry, and its combination with the Internet of Things is one of the most powerful shifts in technology today. AI in IoT takes this promise and turns it into action. It allows connected devices to do more than collect and transmit information. Data moves through systems that can analyze it and make decisions without waiting for human intervention.
Read the full blog to explore top tools, benefits, unique applications, leading companies, and upcoming advancements that will define the next decade of AI in IoT.
- Forecasts project the number of IoT devices worldwide will reach around 40 billion by 2030.
- The global market size for IoT devices was estimated at USD 70.3 billion in 2024 and is expected to exceed USD 181 billion by 2030.
- IoT operations are predicted to save more than 8 times the energy they consume by 2030.
Table of contents
- What is AI in IoT?
- Top Tools for AI in IoT
- Azure IoT with AI and Machine Learning
- AWS IoT Greengrass
- Google Cloud IoT with Vertex AI
- ThingSpeak with MATLAB Analytics
- Edge Impulse
- IBM Watson IoT Platform
- Top Benefits of AI in IoT
- Improved Decision-Making
- Better Customer Experience
- Augmented Security
- Cost Reduction
- Best Use Cases of AI in IoT
- Predictive Maintenance in Manufacturing
- Personalized Healthcare Therapy
- Smart Energy Optimization
- Context-Aware Smart Farming
- Adaptive Traffic Management
- Top Companies Using AI in IoT
- Siemens
- General Electric (GE)
- Microsoft
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- IBM
- Challenges and Solutions
- Data Quality Issues
- Latency in Decision-Making
- Security Vulnerabilities
- Scalability Pressure
- Model Drift Over Time
- Future Advancements of AI in IoT
- Federated Learning and Privacy-Preserving Architectures
- Edge AI and Hybrid Learning Models
- Integration of Large Language Models with IoT Systems
- Intelligent Sensor Fusion and Contextual Adaptation
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- Can AI in IoT work without an internet connection?
- How does AI in IoT impact battery life of devices?
- Are open-source AIoT frameworks available?
- Can AI in IoT help with compliance reporting?
- What role does 5G play in AIoT?
- How can Generative AI be used in IoT?
What is AI in IoT?
Artificial Intelligence in the Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the integration of machine learning and other AI techniques into IoT ecosystems to make connected devices more intelligent and autonomous
Simultaneously, AI enables these systems to analyze data locally (edge AI) or in the cloud, making predictive or prescriptive decisions without constant human oversight. This convergence converts IoT from a passive data-collection framework into a proactive and self-learning system that can adapt to changing environments and scale efficiently.
Top Tools for AI in IoT
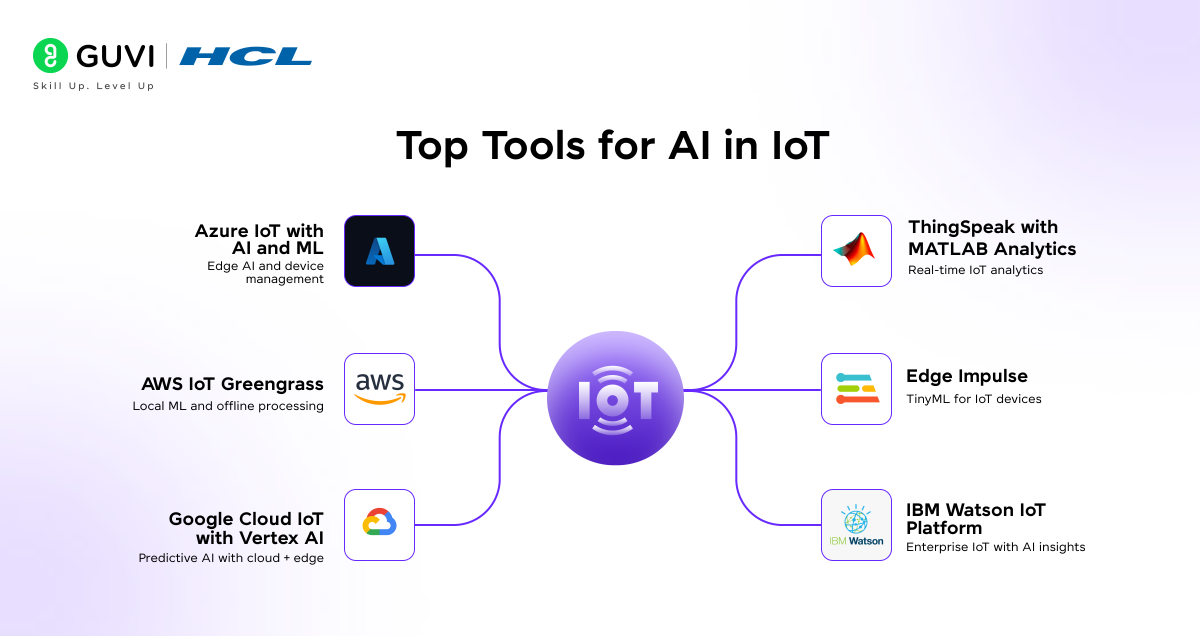
AI in IoT relies on specialized platforms and tools that process data from sensors and run machine learning models. These tools support model training and edge deployment. The following tools are widely adopted in the AIoT space:
1. Azure IoT with AI and Machine Learning
Top Features:
- Secure and bidirectional communication between devices and the cloud.
- Device provisioning, management, and firmware updates.
- Deploys AI and ML models at the edge using Azure IoT Edge.
- Integration with Azure Machine Learning and Cognitive Services.
Companies Using:
- Rockwell Automation
- General Motors
- B. Braun
- Lexmark
Price:
- Free tier: up to 8,000 messages/day with limited features.
- Paid tiers (Basic/Standard) with higher message limits and advanced features.
Key Insights:
- Edge intelligence reduces latency and bandwidth costs.
- Seamlessly integrates with the Microsoft ecosystem for analytics and cloud.
2. AWS IoT Greengrass
Top Features:
- Runs AWS Lambda functions and ML models locally on devices.
- Secure communication and synchronization with the AWS Cloud.
- Supports offline operation and syncs when connectivity returns.
- Extends AWS services to edge devices for low-latency decisions.
Companies Using:
- Widely adopted in manufacturing, logistics, and smart city deployments.
Price:
- Free tier: first 3 Greengrass Core devices free for 1 year.
- Paid: charged per connected core device per month, plus usage of AWS services.
Key Insights:
- Ideal for environments with intermittent connectivity.
- Reduces dependence on cloud latency by enabling local processing.
3. Google Cloud IoT with Vertex AI
Features:
- Connects and ingests IoT device data at scale.
- Trains and deploys ML models with Vertex AI.
- Supports real-time analytics and predictive decision-making.
- Can deploy workloads on edge or cloud infrastructure.
Companies Using:
- Adopted in smart city projects, industrial monitoring, and utilities.
Price:
- Pricing based on data ingestion, device management, and Vertex AI usage.
- Free trial credits available for new Google Cloud users.
Key Insights:
- IoT Core service was deprecated, but Vertex AI provides strong AI integration.
- Best suited for large-scale analytics and AI workloads.
4. ThingSpeak with MATLAB Analytics
Features:
- Collects and visualizes IoT data in real time.
- Provides MATLAB analytics directly on incoming data.
- Supports RESTful and MQTT APIs for device connectivity.
- Offers event-based triggers and alerts.
Companies Using:
- Cadmus (energy data monitoring)
- Academic and research institutions worldwide
Price:
- Free tier available for academic and prototyping use.
- Paid plans for commercial deployments with higher data limits.
Key Insights:
- Strong platform for prototyping and research.
- Powerful analytics due to MATLAB integration.
5. Edge Impulse
Features:
- End-to-end platform for Edge AI and TinyML development.
- Tools for data collection, training, optimization, and deployment.
- Supports sensor, audio, and vision data on resource-constrained devices.
- Low-code interface plus advanced customization.
Companies Using:
- Oura
- Know Labs
- NOWATCH
- Lexmark (Optra Edge)
Price:
- Free for developers and small projects.
- Enterprise pricing for large-scale deployments.
Key Insights:
- Recently acquired by Qualcomm, boosting hardware integration.
- Strong developer community with 170k+ users.
6. IBM Watson IoT Platform
Features:
- Connects, manages, and monitors IoT devices at scale.
- Real-time data ingestion, dashboards, and visualization.
- Integration with Watson AI services for analytics and anomaly detection.
- Supports secure device communication and authentication.
Companies Using:
- Enterprises in the manufacturing, automotive, and energy sectors.
Price:
- Plans start around $500 per instance/month.
- Additional charges for analytics and data services.
Key Insights:
- Designed for enterprise-scale IoT with strong AI integration.
- High reliability but complex setup and higher costs.
Top Benefits of AI in IoT
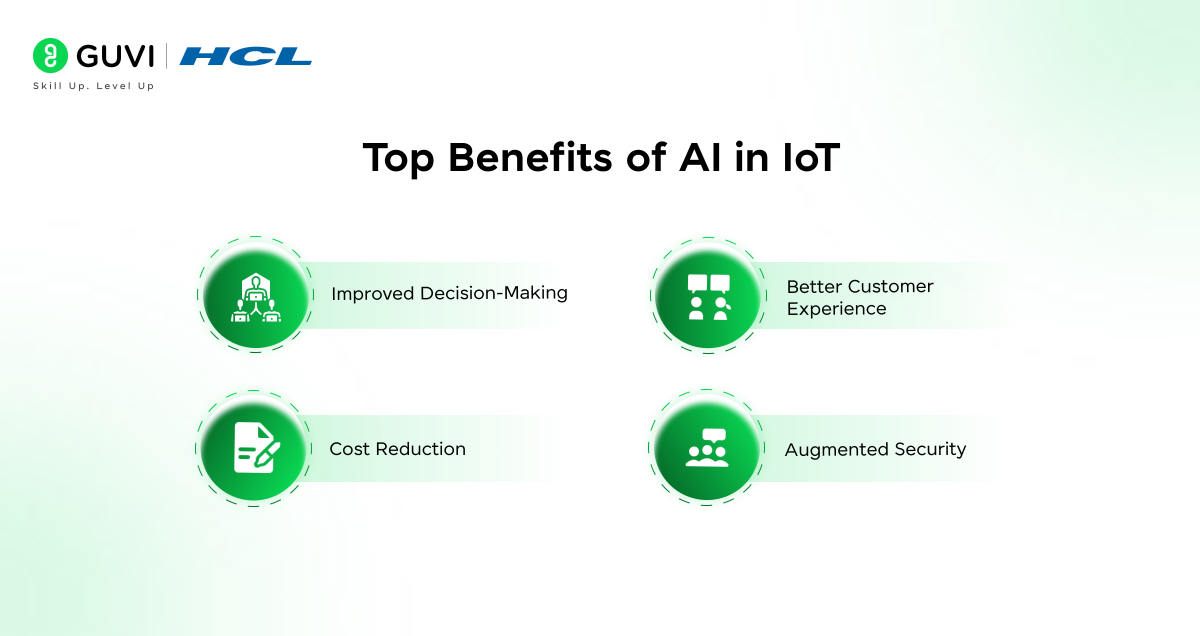
1. Improved Decision-Making
AI analyzes IoT data in real time and provides actionable insights that support better operational decisions. Predictive analytics help organizations forecast equipment failures before they occur and reduce downtime. These decisions become faster and more accurate as the AI model processes more data over time.
2. Better Customer Experience
AI in IoT personalizes user interactions based on real-time behavioral data. Smart home devices adjust temperature and lighting based on user preferences. This level of personalization improves user satisfaction and builds stronger brand loyalty.
3. Augmented Security
AI-powered IoT systems monitor connected devices for unusual activity and detect potential threats quickly. They flag irregular network traffic and stop attacks before they spread across the network. This creates a stronger and more resilient security posture for organizations.
Read: Top AI Use Cases Transforming Industries in 2025
4. Cost Reduction
AI helps lower operational costs by predicting maintenance needs and extending the life of assets. Manufacturers use AI-driven IoT solutions to reduce production downtime and avoid expensive emergency repairs. Cost savings grow as the system continues to refine its predictions.
Best Use Cases of AI in IoT
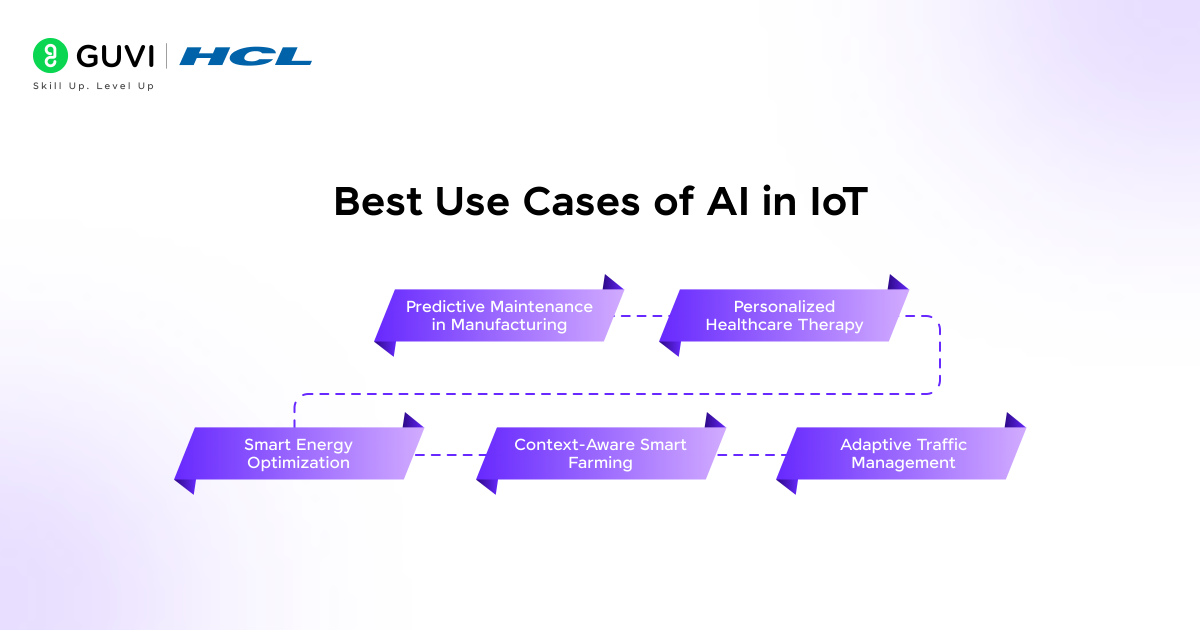
1. Predictive Maintenance in Manufacturing
AI models process IoT sensor data from machines to predict potential failures before they occur. Vibration readings and temperature fluctuations reveal early signs of wear in components. Maintenance teams receive precise alerts, which reduces unplanned downtime and keeps production lines running efficiently.
2. Personalized Healthcare Therapy
IoT devices track patient vitals, medication intake, and activity levels continuously. AI models recommend dosage adjustments or therapy changes based on the patient’s response over time. Doctors receive concise reports that improve treatment precision and reduce side effects.
3. Smart Energy Optimization
AI analyzes real-time energy consumption data from IoT-enabled meters and adjusts distribution across the grid. Load balancing algorithms respond to spikes in demand by redirecting power to priority areas. This approach prevents energy loss and lowers operational costs for utility companies.
4. Context-Aware Smart Farming
AI processes soil data from IoT sensors and adjusts irrigation schedules based on moisture levels and weather forecasts. The system changes nutrient delivery in real time based on crop growth stage and environmental stress indicators. Farmers see higher yield quality and lower water usage as a result.
5. Adaptive Traffic Management
IoT cameras and road sensors feed continuous traffic flow data to AI models. The system predicts congestion before it forms and adjusts signal timings in advance. Emergency vehicles receive priority routing instructions, which reduces response times.
Also, Read: Top 17 Best IoT Project Ideas
Transform your career with the future of technology! Enroll in our Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Course with Intel Certification and gain hands-on expertise in IoT, predictive analytics, edge AI, and real-world AI solutions. Build the skills to lead innovation in connected systems and intelligent automation. Start Your Journey Today.
Top Companies Using AI in IoT
Siemens
Siemens applies AI within its industrial IoT platform MindSphere, which connects machines and production lines. Data from connected equipment flows into analytics models that predict failures and optimize workflows. Their digital twin technology replicates physical systems and compares real sensor readings with simulated outputs to improve uptime and product quality.
General Electric (GE)
GE Digital uses its Predix platform to gather data from turbines and other heavy equipment. AI models process vibration and performance data to detect anomalies before breakdowns occur. Predictive AI and maintenance strategies based on this data reduce downtime and lower maintenance costs.
Microsoft
Microsoft provides Azure IoT along with AI services that allow enterprises to deploy machine learning models on connected devices and in the cloud. Their platform supports real time data processing. It additionally supports edge analytics and the creation of digital twins that reflect the state of factories and infrastructure. This gives operators clear insights into performance and areas that require adjustment.
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
AWS offers IoT services that help collect and process sensor data from industrial plants, smart cities, and supply chain systems. Machine learning models trained on this data run at the edge or in the cloud to optimize operations and detect issues early. Their IoT Greengrass service allows local devices to act on data even without constant internet connectivity.
IBM
IBM integrates IoT data with analytics through its Watson IoT platform. Organizations use it to monitor industrial assets and optimize production schedules. The platform supports integration with supply chain and enterprise resource systems, which helps align operations with business goals.
Challenges and Solutions
AI in IoT brings measurable value, but it also introduces technical and operational challenges. Each challenge has a clear solution that helps build reliable and scalable systems:
1. Data Quality Issues
Challenge: IoT data and big data often contain duplicates and missing values. They are also filled with uncertain and inconsistent formats.
Solution: Use automated data cleaning pipelines and enforce schema validation at the point of data ingestion.
2. Latency in Decision-Making
Challenge: Cloud-only processing increases delay for time-critical decisions.
Solution: Deploy AI models at the edge to process data locally and trigger immediate actions.
3. Security Vulnerabilities
Challenge: Large numbers of connected devices expand the attack surface.
Solution: Implement device authentication, encrypted communication, and anomaly detection models that run continuously.
4. Scalability Pressure
Challenge: Growth in connected devices increases network and compute load.
Solution: Use a distributed IoT architecture with load balancing and dynamically scalable cloud resources.
5. Model Drift Over Time
Challenge: AI models lose accuracy as operating conditions change.
Solution: Retrain models on recent data and use monitoring systems that flag performance degradation early.
Future Advancements of AI in IoT
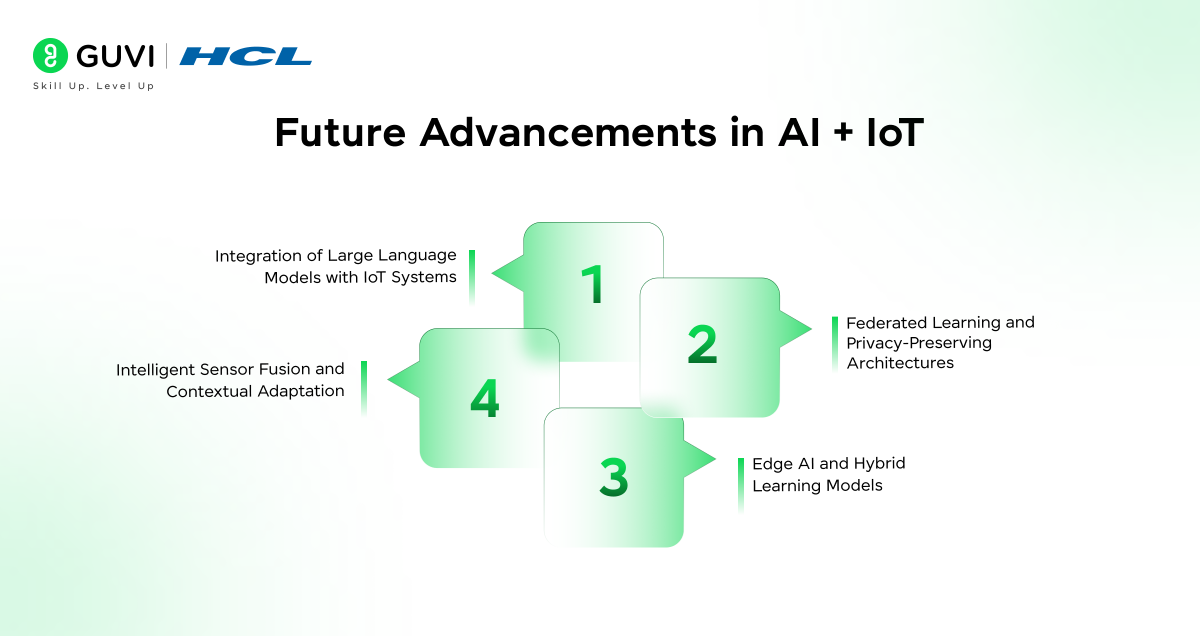
1. Federated Learning and Privacy-Preserving Architectures
Federated learning lets devices train shared models without sending raw data to central servers. Current research is solving challenges such as handling data that is not evenly distributed across devices and reducing communication overhead.
Privacy techniques like differential privacy and secure multi-party computation are combined with federated learning to protect sensitive IoT data while still improving model accuracy.
2. Edge AI and Hybrid Learning Models
New approaches split AI models across devices, edge nodes, and cloud infrastructure. The most latency-sensitive layers run close to the sensors, while heavy computation is offloaded to more capable systems.
Techniques such as model pruning and compression allow inference on resource-constrained IoT hardware, which keeps response times low and reduces bandwidth usage.
3. Integration of Large Language Models with IoT Systems
Large language models are beginning to work alongside IoT platforms to interpret commands, summarize events, and make contextual decisions. Researchers are combining them with federated and split learning frameworks so that LLMs can operate efficiently with distributed IoT data. This reduces unnecessary data transmission and improves energy efficiency across the network.
4. Intelligent Sensor Fusion and Contextual Adaptation
AI models will use multiple sensor types together with contextual data such as location and usage history to refine decisions. Seasonal changes and user preferences will influence system responses. Semi-supervised and self-supervised learning will allow anomaly detection even when labeled data is scarce, which is a common challenge in IoT environments.
Conclusion
AI in IoT has moved beyond theory and is now shaping how industries operate and how individuals interact with technology. It turns raw sensor data into meaningful actions that improve efficiency, safety, and reliability. The combination of edge intelligence and real-time response creates systems that adapt as conditions change.
The future of AI in IoT points toward more distributed intelligence and context-aware systems that work together seamlessly. Organizations that invest in this direction now position themselves to gain a clear advantage as AI and IoT continue to evolve.
FAQs
1. Can AI in IoT work without an internet connection?
Yes. Edge AI processes data locally on the device or gateway, which allows IoT systems to keep functioning even when cloud connectivity is unavailable.
2. How does AI in IoT impact battery life of devices?
Optimized models such as TinyML use low-power algorithms that run efficiently on microcontrollers. This reduces energy consumption and extends battery life.
3. Are open-source AIoT frameworks available?
Yes. Frameworks like TensorFlow Lite for Microcontrollers, EdgeX Foundry, and OpenHorizon allow developers to build AIoT solutions without vendor lock-in.
4. Can AI in IoT help with compliance reporting?
Yes. AI can automatically analyze sensor data, generate logs, and prepare reports that meet regulatory requirements in sectors like manufacturing and energy.
5. What role does 5G play in AIoT?
5G provides low-latency, high-bandwidth connectivity that allows IoT devices to send and receive data quickly. This improves the accuracy and timeliness of AI-driven decisions.
6. How can Generative AI be used in IoT?
Generative AI creates simulations and synthetic data that help train IoT models when real-world data is limited. It can also generate predictive maintenance scenarios and design suggestions for complex systems before they are built.




























Did you enjoy this article?