
Agile Methodology Explained: Principles, Phases, and Benefits
Mar 11, 2026 5 Min Read 2442 Views
(Last Updated)
Software development has grown faster and more dynamically in our digital world. Companies want results, users expect even faster update cycles for products they use, and technology just keeps advancing. If companies want to continue to keep up with this trend, they have to take new approaches that are flexible and efficient. This is where Agile methodology in software development comes in.
So, what is Agile methodology? In simple terms, Agile is a way of building software in the 21st century that emphasizes flexibility, speed, teamwork, and continuous improvement. In short, where traditional methodology focuses on a rigid plan, Agile allows teams to embrace change, collaborate, and quickly deliver working software.
If you are unfamiliar with the subject, that’s okay. In this blog, we’ll break down what is Agile methodology in simple terms, explore its principles, phases, steps, pros and cons, as well as contrast Agile vs Waterfall methodology. In no time, you will understand why Agile software development has come to be the heart of modern-day software development.
Table of contents
- What is Agile Methodology?
- The Agile Model in SDLC
- Agile Methodology in Software Development
- Requirements Gathering
- Sprint Planning
- Development and Testing
- 4) Deployment
- 5) Maintenance in Agile
- Principles of Agile Methodology
- Agile Scrum Methodology
- Other Agile frameworks include:
- Benefits of Agile Methodology
- Agile Methodology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Advantages of Agile methodology:
- Disadvantages of Agile methodology:
- Difference between Agile vs Waterfall Methodology
- Final thoughts…
- FAQs
- What is Agile methodology in simple words?
- Is Agile better than Waterfall?
- What are the main types of Agile?
- How long is an Agile sprint?
- Why is Agile important for Software Development?
What is Agile Methodology?
Agile methodology is an approach to software development that focuses on flexibility, collaboration, and delivering value quickly. It encourages a progressive and collaborative approach by prioritizing incremental iterations over more linear traditional methods (e.g., Waterfall methodology). Most agile methodologies work within short iterations (also called sprints or iterations) instead of the more linear step-by-step development process.
Instead of waiting months (or even years) for a final product, Agile teams release smaller pieces of working software early and improve them continuously based on user feedback.
In short:
- Agile is primarily about responding to change, rather than following a detailed plan.
- It values individuals and interactions more than extensive documentation.
- It focuses on customer satisfaction by enabling customers to receive value early, and often.
Agile was born in 2001 when 17 software developers created the Agile Manifesto, introducing a new way of building software that prioritized flexibility, collaboration, and customer interaction over rigid planning. Fast forward to today, and more than 71% of companies worldwide use Agile practices not only in software development, but also in marketing, product design, and even education to deliver adaptability in fast-moving environments.
The Agile Model in SDLC
To get a better understanding of Agile, let’s place it into the software development life cycle (SDLC).
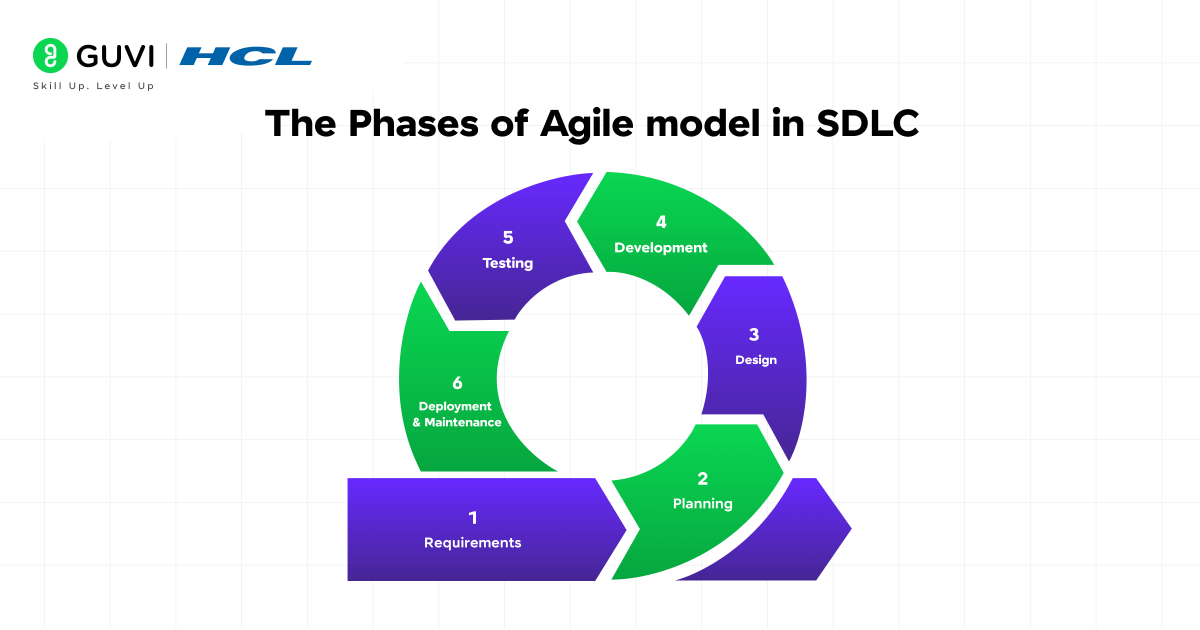
The SDLC typically has five phases:
- Requirements Gathering
- Planning
- Design
- Development
- Testing
- Deployment & Maintenance
In the Agile model in SDLC, these phases do not happen sequentially. Instead, they occur repetitively in shorter cycles. Each cycle will produce a version of the product that works, and that version will be tested and iterated on in the next cycle.
Agile Methodology in Software Development
The agile process in software development is iterative and incremental, meaning that software is built in smaller cycles rather than long timelines. These cycles are called sprints, and at the end of each sprint (typically lasting 1-4 weeks), the team has developed some working product or feature.
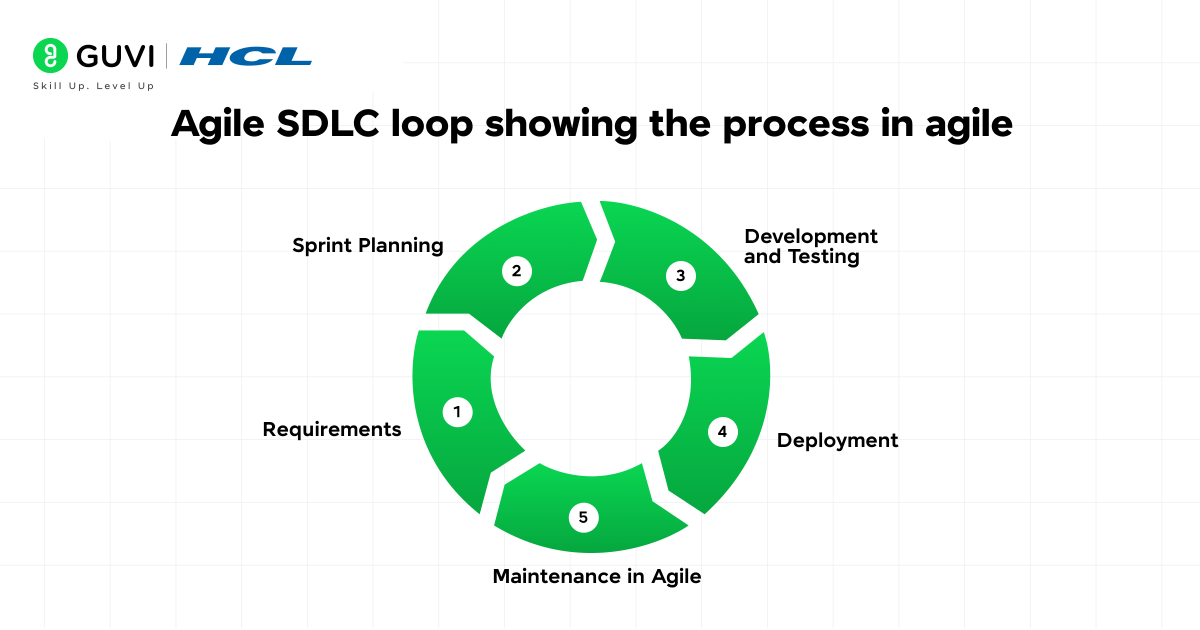
Here’s a detailed look at each Agile methodology step:
1. Requirements Gathering
In agile, unlike traditional models that gather requirements at the start of the project, Agile gathers only enough features that are needed to get started. The rest are collected and prioritized later when the project unfolds.
2. Sprint Planning
A sprint is a time frame in which you complete the tasks. During this time, the team identifies:
- The features or tasks from the backlog (which is basically a list of requirements) that will be completed during the sprint.
- Who will work on what?
- How you (and the client) will measure success.
3. Development and Testing
In contrast to the Waterfall approach, wherein coding and testing are separated, Agile teams do development and testing simultaneously. This allows:
- Bugs to be identified early in the process
- Features to be tested continuously
- Quality to remain high
Agile uses additional practices, including Test Driven Development (TDD) and Continuous Integration (CI), to make the process smooth.
4) Deployment
With traditional approaches, deployment just happens once at the end of the project. Agile deployment happens frequently and incrementally.
- At the end of every sprint, a usable version of the product is delivered.
- Teams may deploy to staging (for testing) or production (for users).
- Continuous Deployment (CD) tools streamline the process, allowing the deployment to happen as quickly as possible (and to be automated).
5) Maintenance in Agile
Agile has maintenance as continuous, rather than the last step of the process.
- Bugs are fixed quickly, not waiting until the end of all sprints.
- Features are updated based on feedback to keep product offerings and capabilities current.
- Performance and security, as well as any other improvements, remain ongoing.
Principles of Agile Methodology
The 12 Agile methodology principles are the foundation of Agile. These principles shape how teams work and ensure software creates real value for users.

In beginner terms, Agile emphasizes:
- Customer Satisfaction – Deliver value early and continuously.
- Welcome Change – Even late changes improve customer advantage.
- Frequent Delivery – Working software delivered in weeks, not months.
- Collaboration – Business people and developers work together daily.
- Motivated Teams – Give teams trust and support; they’ll deliver better.
- Face-to-Face Communication – Direct talks beat lengthy documents.
- Working Software is Key – Progress is measured by software, not paperwork.
- Sustainability – Maintain a steady pace without burning out.
- Technical Excellence – Good coding and design improve agility.
- Simplicity – Focus only on what matters and avoid unnecessary complexity.
- Self-Organizing Teams – Teams should decide how best to work.
- Continuous Improvement – Keep reflecting and adapting to get better.
These principles help teams remain flexible, efficient, and user-focused at all times.
Agile Scrum Methodology
Scrum methodology is the most popular among the variations of Agile.
How Scrum Works:
Specifically, Scrum methodology separates work into sprints (generally 2–4 week intervals of work). During each increment, the team works on the most valuable items in the backlog, then delivers a working product increment.
Scrum also defines roles:
- Product Owner – Defines priorities and acts as the voice of the customer.
- Scrum Master – Facilitates the team and makes sure Agile practices are followed.
- Development Team – The people who design, develop, and test.
There is a reason Scrum is simple, practical, and used commonly in startups and enterprises alike.
Other Agile frameworks include:
Kanban methodology – Visualizing work tasks on a Kanban board.
Extreme Programming (XP) – Emphasizes technical excellence to get working software out frequently.
Benefits of Agile Methodology
- Faster Delivery: Agile methodology breaks projects into smaller timeframes (called sprints), allowing software developers to deliver small, usable pieces of code sooner, providing customers with feedback and results more quickly than traditional methods.
- Flexibility to Change: Agile allows for changes easily, so if requirements are adjusted or shifts in the market occur, updates can be made without being disruptive to the entire development process.
- Higher Customer Satisfaction: Customers are continuously involved and engaged throughout the development process, resulting in regular feedback and ultimately the delivery of software that meets user needs and expectations.
- Lowered Risks: The ability to conduct frequent Sprint Reviews allows customers to provide feedback and expose bugs early in the development process, thereby lowering the risks of failures and assuring the consistent delivery of quality software.
- Increased Team Collaboration: Agile encourages daily meetings and open communication, promoting teamwork, transparency, and accountability across the entire project team.
- Improved Quality: Agile methodologies emphasize repeatable, ongoing best practices, including continuous integration, code reviews, and working retrospectives, encouraging continued learning and improvement within the team, resulting in improved quality of the final software.
- Faster ROI: Businesses can deliver usable software before a final software package is achieved, so that users can start using the software and companies start generating value previously locked away during the entire development process.
Agile Methodology Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages of Agile methodology:
- Responds quickly to market changes.
- Encourages teamwork and communication.
- Produces working software fast.
- Reduces dependency on lengthy documentation.
Disadvantages of Agile methodology:
- It can be less predictable compared to Waterfall.
- Requires experienced team members.
- Constant changes may frustrate clients if not managed carefully.
- Not always ideal for very large projects with fixed contracts.
Difference between Agile vs Waterfall Methodology
One of the most common comparisons in software development is Agile vs Waterfall methodology.
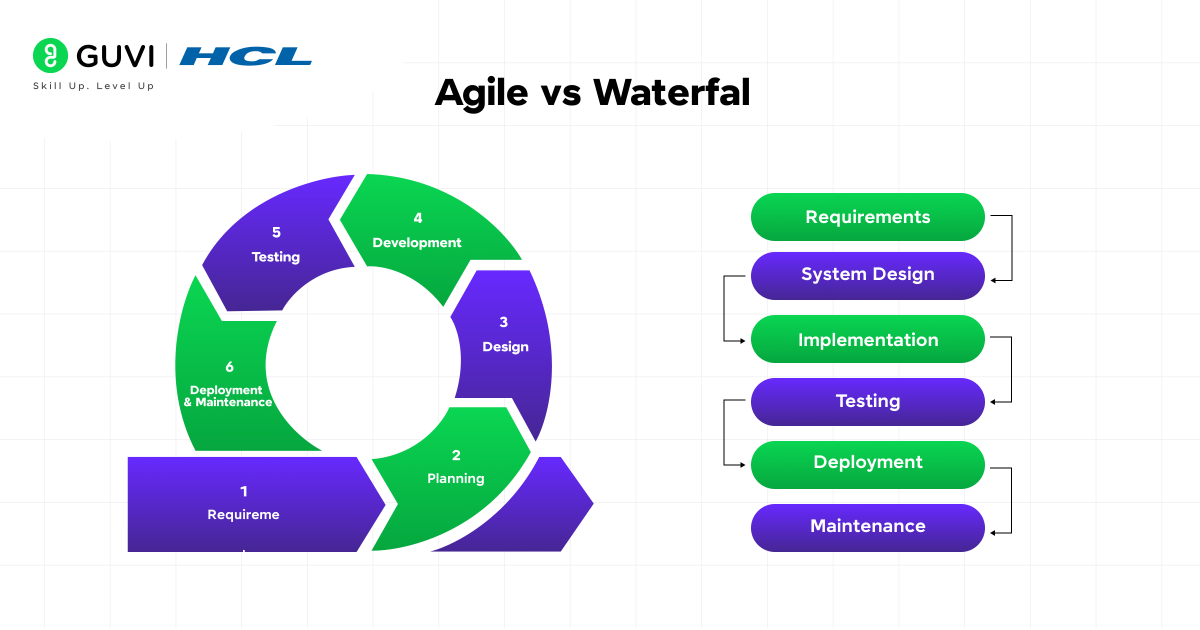
- Waterfall methodology: The Waterfall methodology is a linear, sequential process where you cannot progress to the next phase until you are finished with the previous phase. Waterfall is best suited for projects that have fixed and very well-defined requirements, e.g., government systems or banking. However, it does not allow for any changes once development begins, and usually, the customer does not see the final product until the end of the project.
- Agile methodology: The Agile methodology is flexible and iterative. Work is divided into short sprints, and small usable portions of functionality are delivered repeatedly and frequently. Changes can be accommodated at any point, and the customer is involved throughout the process to ensure that the product solves the problem, fits their needs, and is what they expect. Therefore, Agile is better suited for fast-paced projects with changing or evolving requirements e.g., mobile apps, and customer-driven software.
If this is something that interests you, and you want to become a software developer, then take the chance to get started and learn with GUVI’s IITM Pravartak and MongoDB Certified Online AI Software Development Course. This NSDC-approved course offers a certificate recognized globally, which adds serious bragging rights to your résumé and will help you set yourself apart in a highly competitive employment market.
Final thoughts…
So now you know: What is Agile methodology and how is it related to software development? Agile is a collaborative, adaptive, and customer-centric approach that has transformed the way software is developed. Unlike traditional models that use a rigid approach, such as Waterfall, Agile uses agile models that break down the project into smaller cycles, enabling continuous delivery, continuous feedback, and increased customer satisfaction.
I hope that you found this blog useful to help you understand better about Agile methodology. If you are just getting started with software development, learning Agile practices is a great way to begin your journey!
FAQs
1. What is Agile methodology in simple words?
Agile is how you create software incrementally and in small parts Ready to use, rather than waiting months until the end of the project to receive your final product. Agile is the ability to deliver working product/increments regularly/as needed.
2. Is Agile better than Waterfall?
Agile is usually more successful in projects where you expect the requirements to change quite a bit and the customer helps form the product throughout the process, such as mobile apps and new startup development. Waterfall is typically better for projects where you know the requirements won’t change, such as building software for banking and government systems. So generally, it depends on your project, not whether Agile is better than Waterfall (or vice versa).
3. What are the main types of Agile?
Scrum and Kanban are probably the most common frameworks used. Scrum organizes a project into sprints with specific roles. Kanban uses boards to visualize what work is outstanding. Extreme Programming (XP) focuses on good coding standards and practices. Lean, focuses on running efficient teams and eliminating waste. Each framework will have its own benefits based on how teams work.
4. How long is an Agile sprint?
An Agile sprint typically lasts anywhere from 1 week to 4 weeks depending upon the size and complexity of the project. The shorter sprints provide faster feedback and allow adjustments to be made more rapidly, while slightly longer sprints give the team more time for complex features. The goal is to deliver something of use at the end of every sprint.
5. Why is Agile important for Software Development?
Agile is important because it allows teams to produce software faster, adapt to change easier, reduce risks, and keeps customers happy. Agile introduces users throughout the entire development process, which creates an end product that clearly encompasses the real-world needs of the user versus assumptions. This is why Agile is one of the most adopted methodologies today.



































Did you enjoy this article?