Top 20 Graph Algorithms You Must Know: From Dijkstra to Graph Neural Networks
Dec 09, 2025 6 Min Read 1821 Views
(Last Updated)
Have you ever wondered how Google maps your fastest route, or how LinkedIn identifies people you may know? Behind these intelligent systems lie graph algorithms, the invisible engines that decode relationships between connected entities. They transform raw and unstructured connections into meaningful patterns that guide decisions across industries.
Read the full blog to discover the most powerful graph algorithms, their features, and how they drive real-world innovation.
Table of contents
- What are Graph Algorithms?
- Top 20 Graph Algorithms: Features and Applications
- Dijkstra’s Algorithm
- PageRank Algorithm
- Depth-First Search (DFS)
- Breadth-First Search (BFS)
- Bellman-Ford Algorithm
- Floyd-Warshall Algorithm
- Kruskal’s Algorithm
- Prim’s Algorithm
- A (A-Star) Algorithm*
- Tarjan’s Algorithm
- Johnson’s Algorithm
- Kosaraju’s Algorithm
- Edmonds-Karp Algorithm
- Girvan-Newman Algorithm
- Topological Sorting Algorithm
- Louvain Algorithm
- HITS (Hyperlink-Induced Topic Search) Algorithm
- Label Propagation Algorithm (LPA)
- Betweenness Centrality Algorithm
- Graph Neural Networks (GNNs)
- Best Benefits of Graph Algorithms
- Reveal Hidden Relationships Data
- Improve Decision-Making Accuracy
- Optimize Network Efficiency
- Strengthen Real-Time Intelligence
- Enable Scalable Machine Learning
- Real Applications of Graph Algorithms
- Social Network Analysis
- Recommendation Systems
- Fraud Detection and Financial Security
- Supply Chain and Logistics Optimization
- Healthcare and Bioinformatics
- Test Your Knowledge: Graph Algorithms Quiz
- What do nodes and edges represent in a graph algorithm?
- Which algorithm is used by navigation systems to find the shortest path between two points?
- What makes the PageRank algorithm significant in web search?
- Which graph algorithm can handle negative edge weights in pathfinding?
- In fraud detection, why are graph algorithms effective?
- The Bottom Line
- FAQs
- Why are graph algorithms important in modern technology?
- How do graph algorithms differ from traditional algorithms?
- What skills are needed to learn graph algorithms?
What are Graph Algorithms?
Graph algorithms are computational methods designed to analyze and interpret relationships between connected entities. They work on graph structures made of nodes and edges. Here, nodes represent objects and edges define the links between them. Graph algorithms are widely used in social network analysis and supply chain optimization. They allow machines to reason through connections and transform raw relational data into meaningful insights that support decision-making and prediction across industries.
Top 20 Graph Algorithms: Features and Applications
1. Dijkstra’s Algorithm
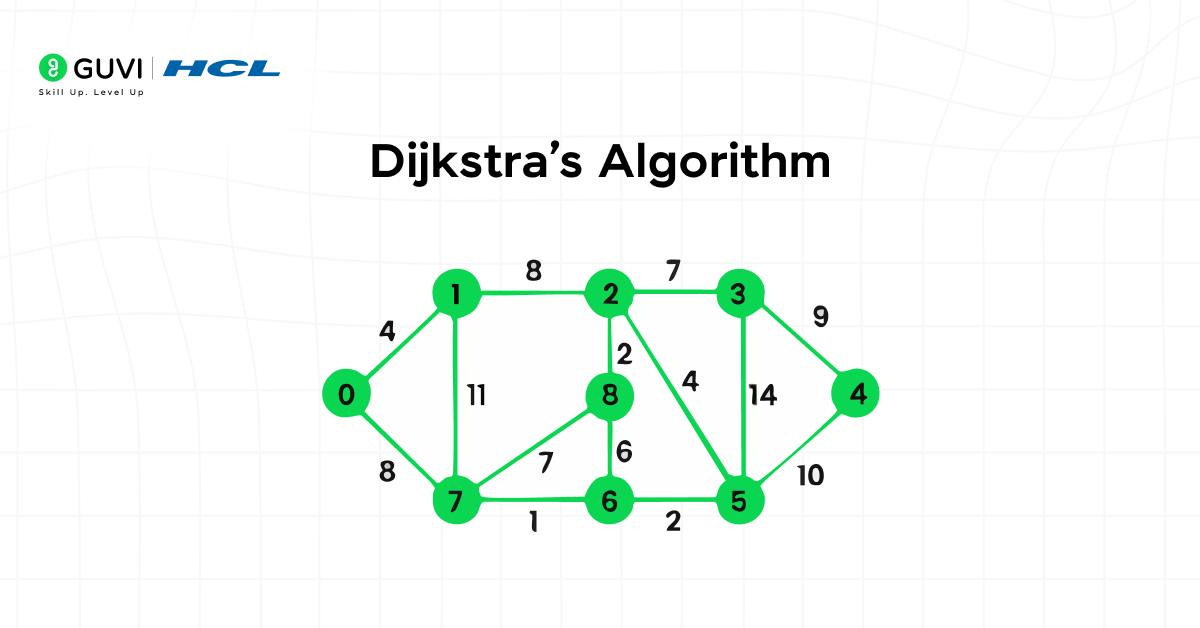
Dijkstra’s Algorithm finds the shortest path between nodes in a weighted graph. It is used extensively in navigation, logistics, and network routing, where efficiency and precision are essential.
Features:
- Calculates optimal routes with minimal computational waste
- Handles weighted edges to represent real-world distances or costs
- Supports both single-source and multi-target pathfinding
Applications:
- GPS and map-based navigation systems
- Internet packet routing and data exploration
- Logistics optimization and delivery route planning
2. PageRank Algorithm
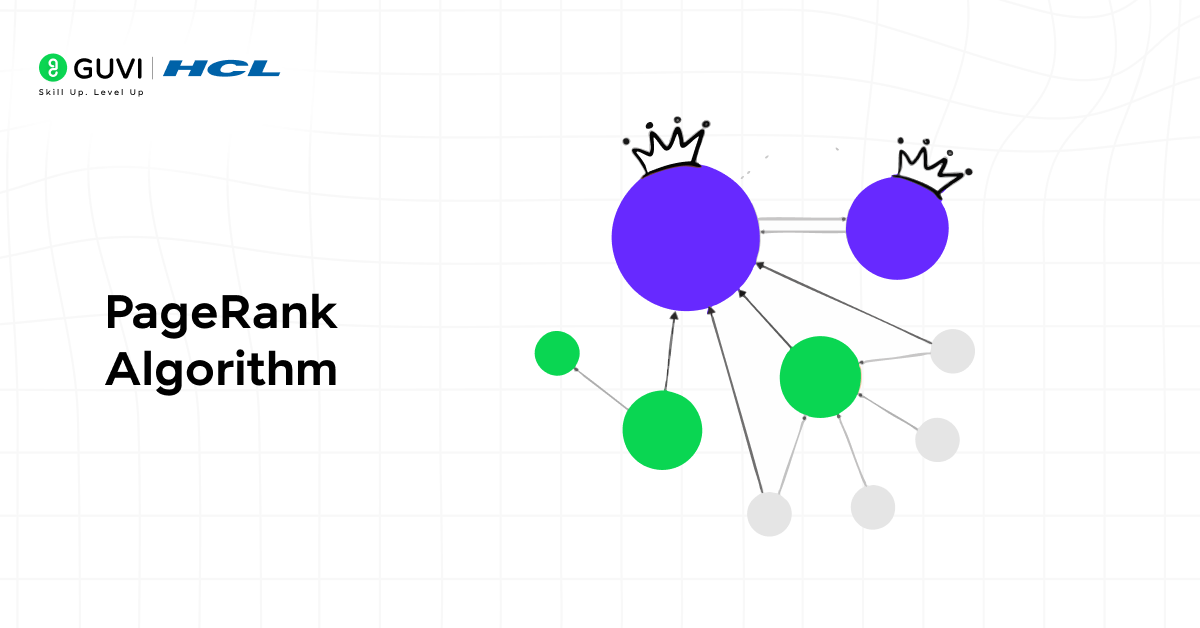
Originally developed by Google, PageRank measures the importance of nodes based on their connections. It evaluates influence and credibility in networks where relationships define value.
Features:
- Scores nodes according to incoming and outgoing links
- Adapts to dynamic networks through iterative updates
- Works effectively on large-scale web or social graphs
Applications:
- Search engine ranking and web indexing
- Social media influence measurement
- Citation and content relevance analysis
Also, Read: How Long Does it Take to Learn Machine Learning? A Know-it-All Guide
3. Depth-First Search (DFS)
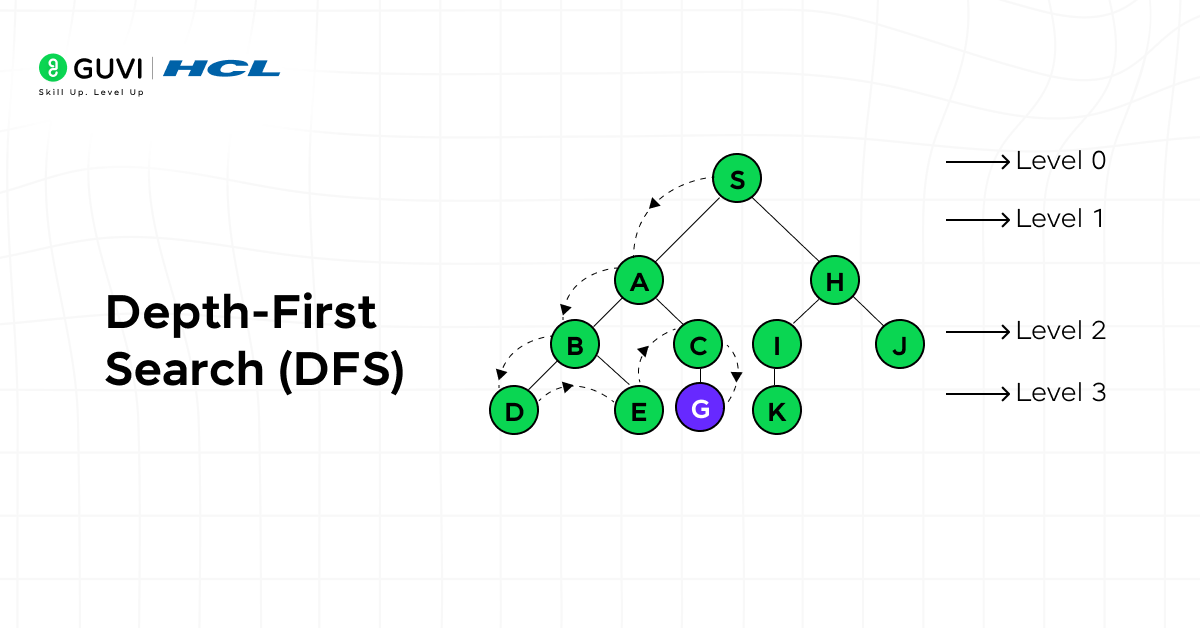
Depth-First Search explores a graph by moving as deep as possible before backtracking. It provides a systematic way to traverse or search through connected components.
Features:
- Uses a stack-based structure for efficient exploration
- Identifies connected components and cycles
- Simplifies the foundation for other complex graph algorithms
Applications:
- Pathfinding in maze and game environments
- Analyzing dependencies in software and project networks
- Detecting connectivity in social or biological systems
4. Breadth-First Search (BFS)
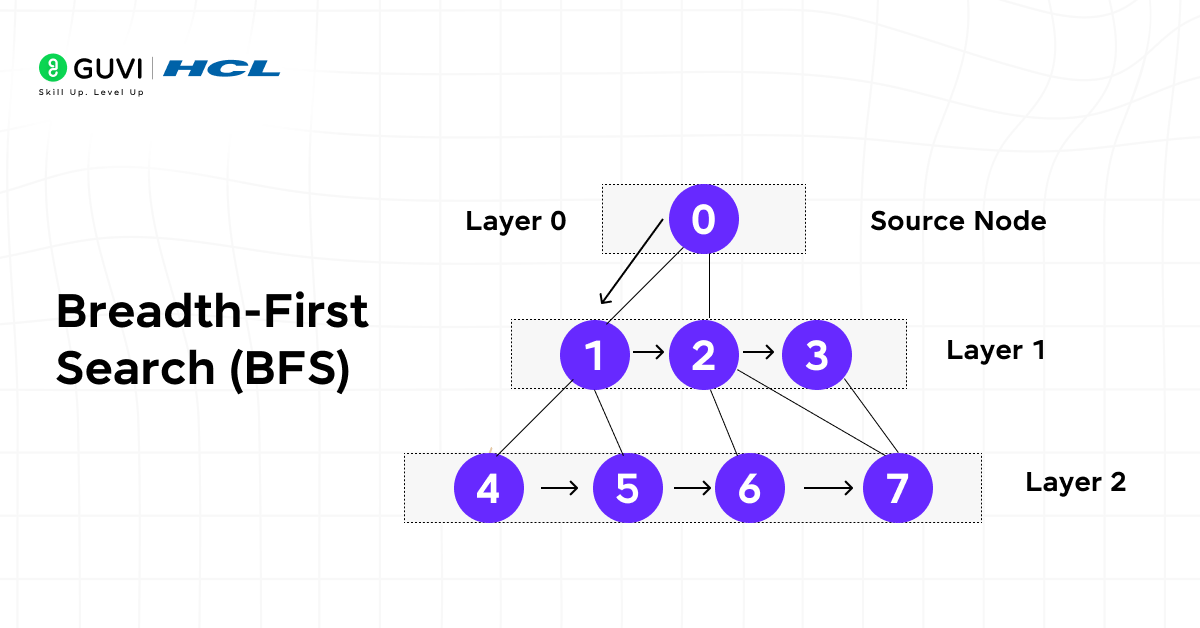
Breadth-First Search explores all neighboring nodes before moving deeper, making it ideal for finding the shortest path in unweighted graphs.
Features:
- Uses a queue-based approach for systematic traversal
- Guarantees shortest path discovery in equal-weight graphs
- Serves as a basis for graph layer analysis and level mapping
Applications:
- Network broadcasting and peer discovery
- Friend recommendation in social media platforms
- Workflow scheduling and resource mapping
5. Bellman-Ford Algorithm
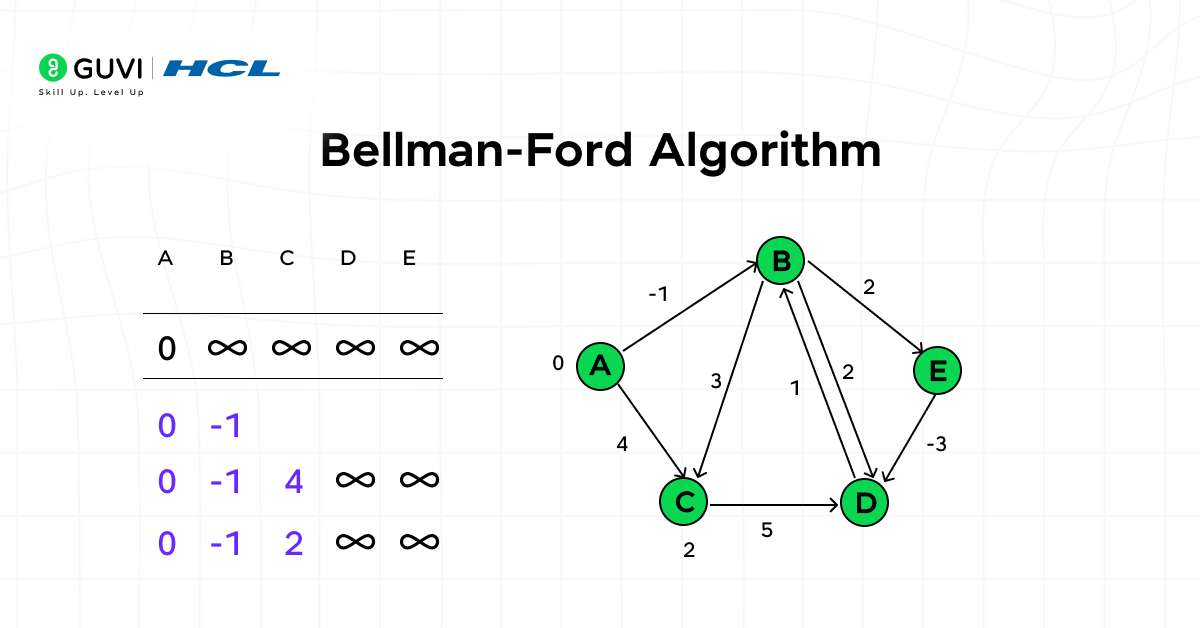
Bellman-Ford extends pathfinding to handle negative weights, which makes it suitable for systems with fluctuating or penalized costs.
Features:
- Supports graphs with negative edge weights
- Detects negative cycles that affect optimization
- Offers flexibility in cost-sensitive route calculations
Applications:
- Currency exchange and financial risk modeling
- Transportation cost prediction and dynamic routing
- Detecting anomalies in weighted big data networks
6. Floyd-Warshall Algorithm
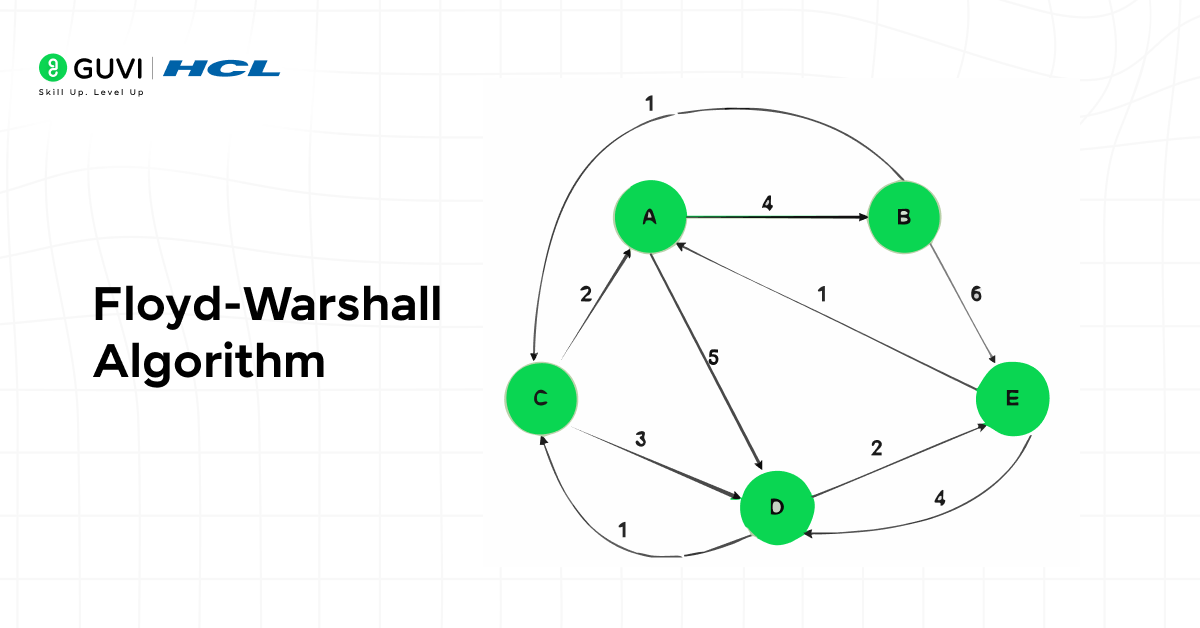
Floyd-Warshall computes the shortest paths between all pairs of nodes within a graph. It is known for its clarity and versatility when applied to dense networks.
Features:
- Solves all-pairs shortest path problems efficiently
- Works on both directed and weighted graphs
- Detects negative cycles within complex datasets
Applications:
- Network analysis in telecommunications
- Cost optimization in logistics and transportation
- Simulation of connectivity in computer and road networks
Read: Neural Networks in Machine Learning: The Artificial Brain
7. Kruskal’s Algorithm
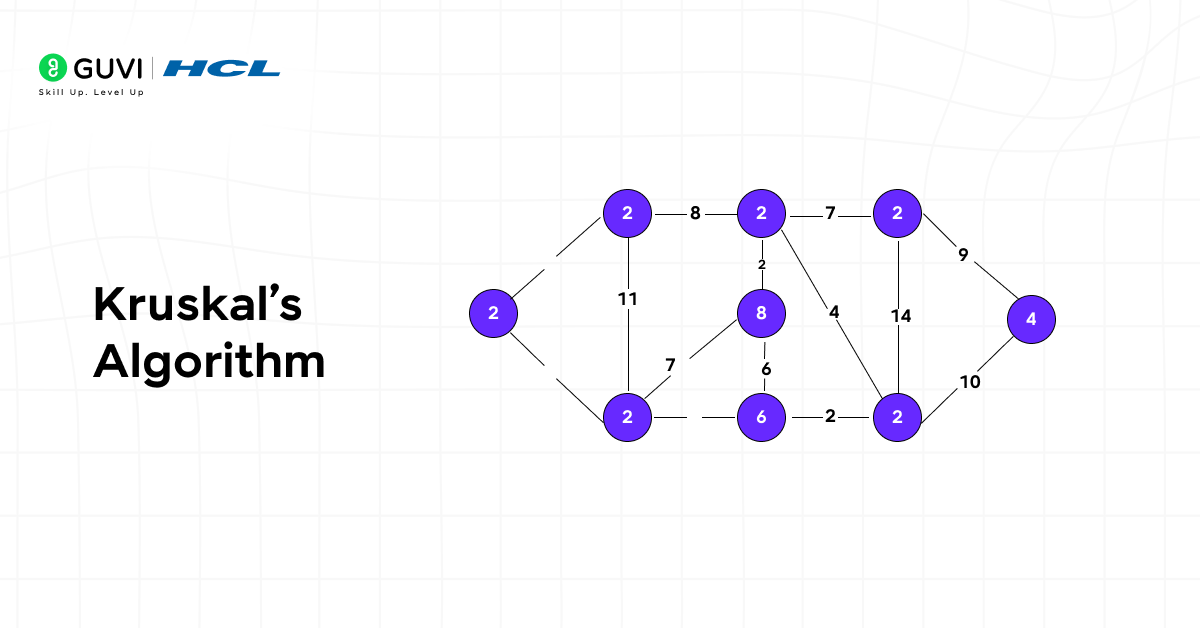
Kruskal’s Algorithm builds a minimum spanning tree that connects all nodes with the lowest total edge weight. It helps identify efficient structures without redundant connections.
Features:
- Selects edges based on increasing weight order
- Prevents cycles to maintain network simplicity
- Produces globally optimal results for spanning structures
Applications:
- Designing efficient communication and power grids
- Network layout and cable routing optimization
- Reducing infrastructure costs in connected systems
8. Prim’s Algorithm
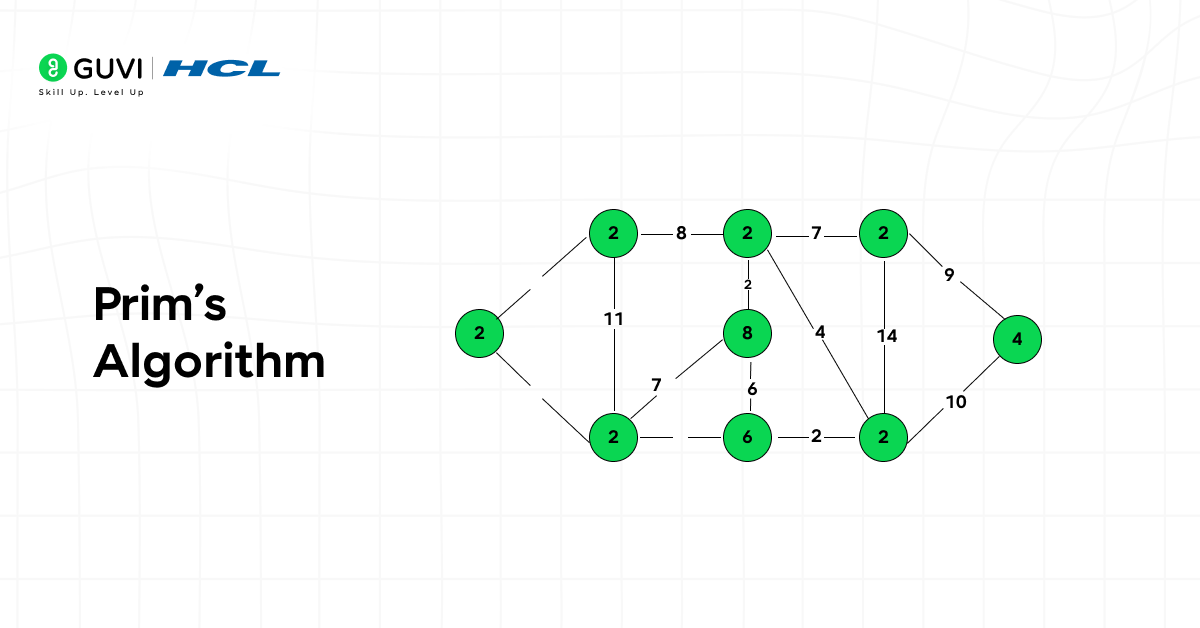
Prim’s Algorithm is another technique for finding a minimum spanning tree but grows the tree one edge at a time from a starting node. It performs well in dense graphs and structured networks.
Features:
- Builds minimal connection paths iteratively
- Maintains a single expanding tree throughout computation
- Offers high performance in graphs with numerous edges
Applications:
- Network design and cluster analysis
- Efficient data linkage in distributed systems
- Spatial modeling and optimization problems
9. A (A-Star) Algorithm*
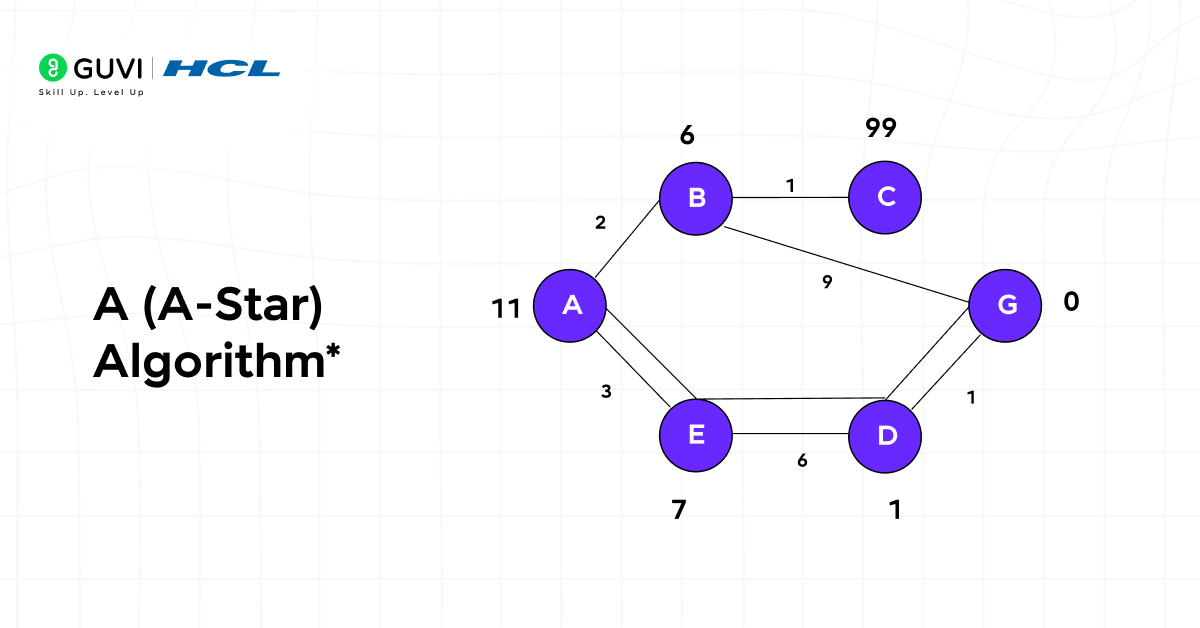
A* combines heuristic analysis with pathfinding to find the most efficient route. It estimates cost to the target while exploring paths intelligently, balancing speed and accuracy.
Features:
- Uses both actual and estimated costs for decision-making
- Optimizes searches using heuristic evaluation
- Adapts dynamically to changing environments
Applications:
- Game development and virtual navigation
- Robotics and autonomous vehicle route planning
- Real-time logistics and warehouse movement systems
10. Tarjan’s Algorithm
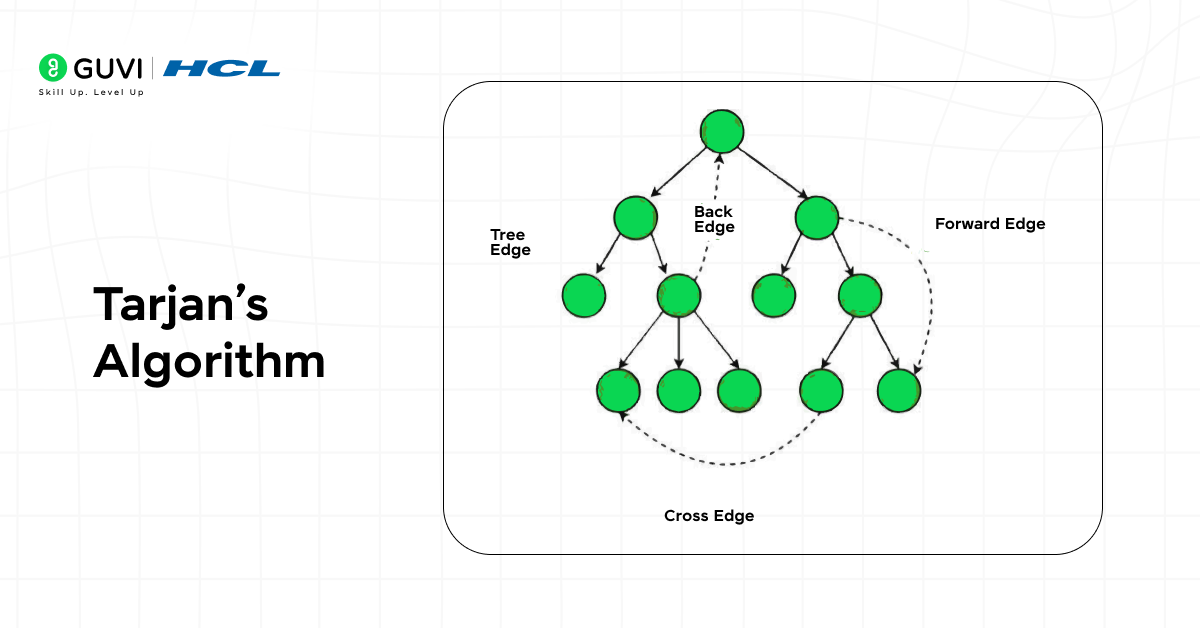
Tarjan’s Algorithm detects strongly connected components in directed graphs. It helps identify clusters or loops where information or influence continuously flows.
Features:
- Uses depth-first traversal to identify connected subgraphs
- Works efficiently with minimal recursion overhead
- Supports hierarchical decomposition of large networks
Applications:
- Analyzing social or citation networks
- Detecting feedback loops in financial systems
- Organizing modular structures in large codebases
11. Johnson’s Algorithm
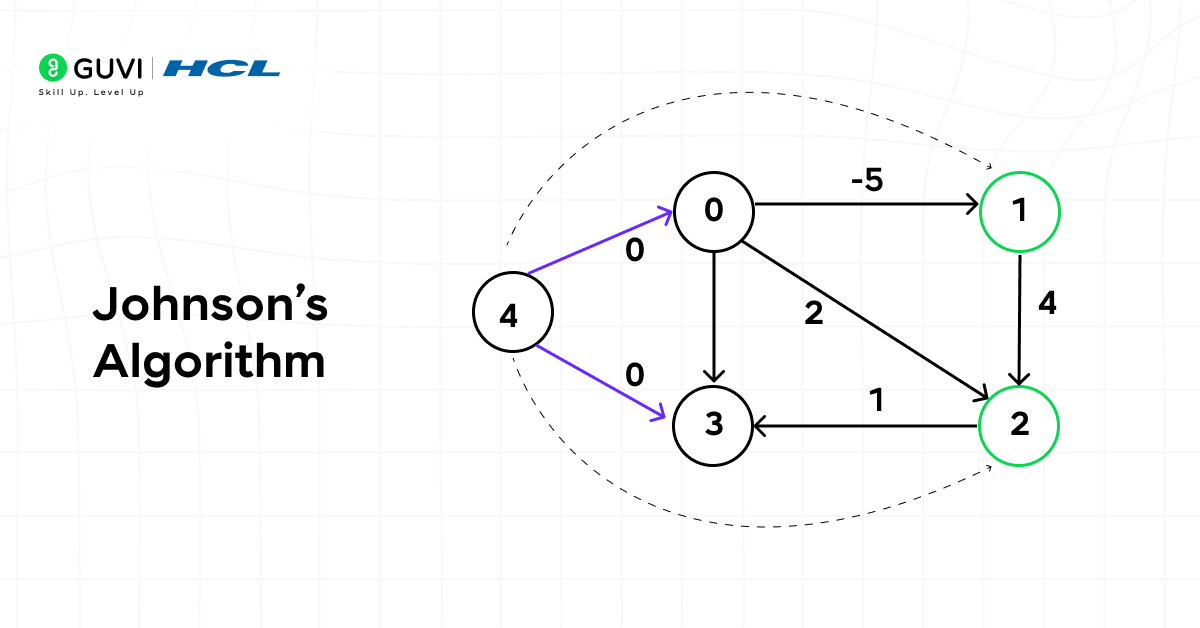
Johnson’s Algorithm finds the shortest paths between all pairs of vertices in a sparse, weighted graph. It combines the Bellman-Ford and Dijkstra approaches to achieve speed and flexibility.
Features:
- Efficiently handles both positive and negative edge weights
- Works well on sparse graphs with fewer connections
- Reuses optimized paths to reduce overall computation time
Applications:
- Transportation and network optimization
- Resource allocation in distributed systems
- Predictive routing in large-scale logistics platforms
12. Kosaraju’s Algorithm
Kosaraju’s Algorithm identifies strongly connected components within a directed graph. It helps reveal hidden substructures where nodes maintain mutual reachability.
Features:
- Performs two depth-first searches for complete accuracy
- Works efficiently on large directed graphs
- Builds a foundation for hierarchical network analysis
Applications:
- Understanding communities in social networks
- Detecting influence circles in communication systems
- Organizing feedback loops in control networks
13. Edmonds-Karp Algorithm
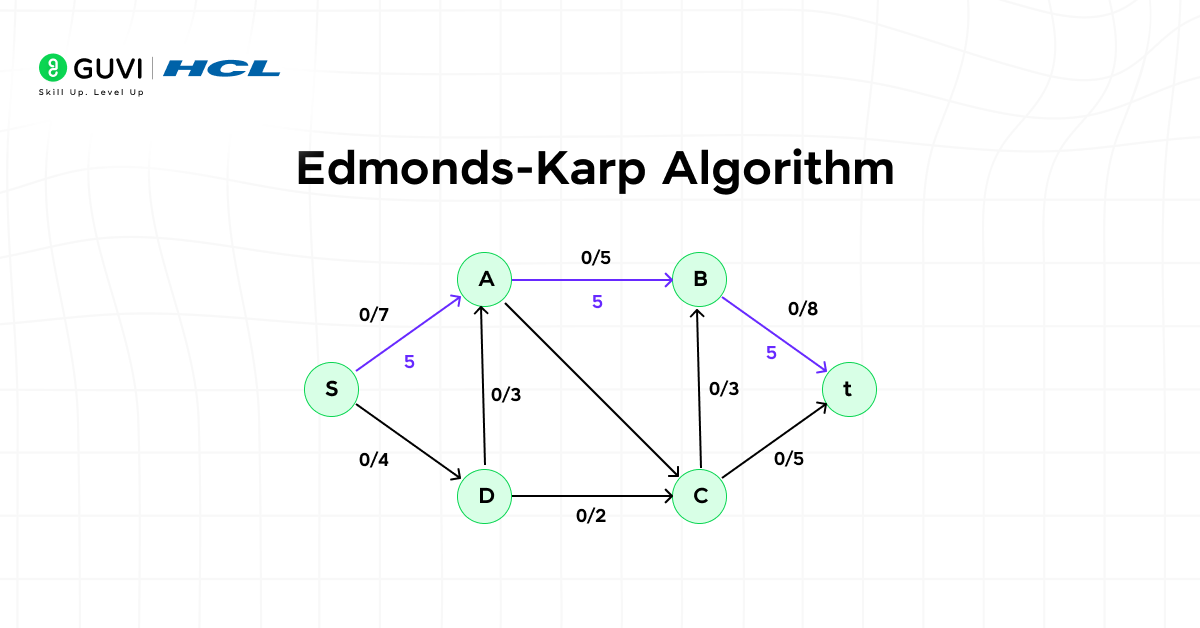
This algorithm calculates the maximum flow in a network using breadth-first search principles. It ensures reliable capacity management where flow or transfer constraints exist.
Features:
- Uses BFS to find the shortest augmenting paths
- Provides polynomial-time performance for flow problems
- Ensures stable and repeatable results across large datasets
Applications:
- Traffic flow optimization and congestion analysis
- Data packet transfer in computer networks
- Resource distribution in supply chain management
14. Girvan-Newman Algorithm
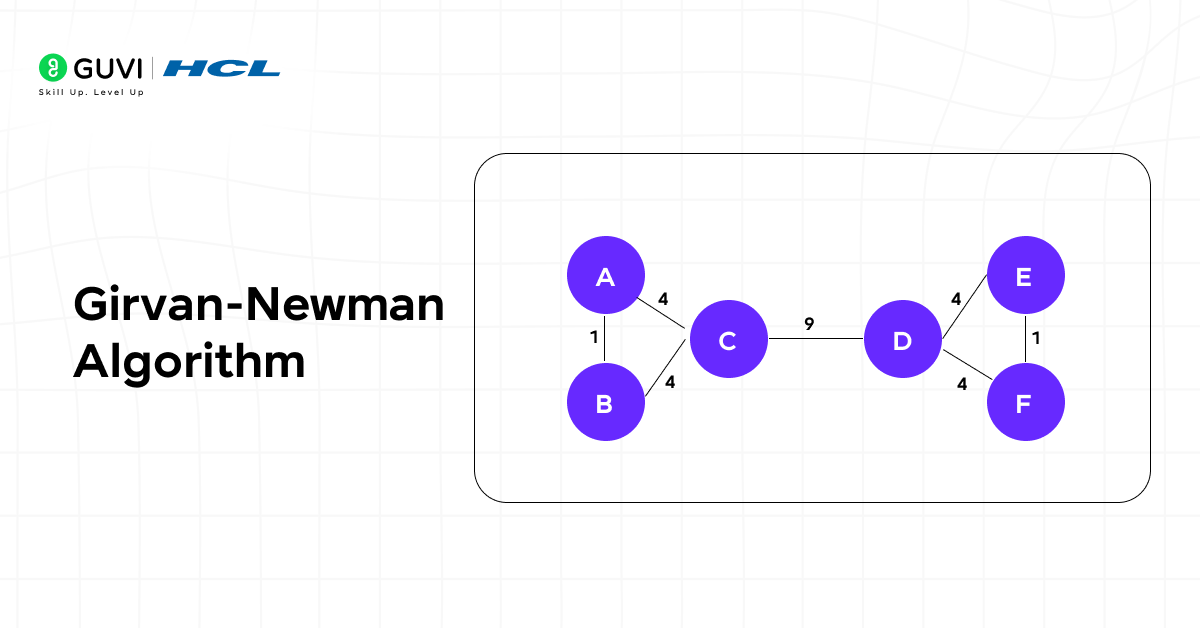
Girvan-Newman is designed for community detection within graphs. It identifies groups by progressively removing edges with the highest betweenness, exposing natural divisions.
Features:
- Detects modular structures through edge analysis
- Measures betweenness to identify critical connections
- Adapts to both weighted and unweighted graphs
Applications:
- Social network community detection
- Market segmentation and behavioral clustering
- Identifying key influencers and bridge nodes in networks
15. Topological Sorting Algorithm
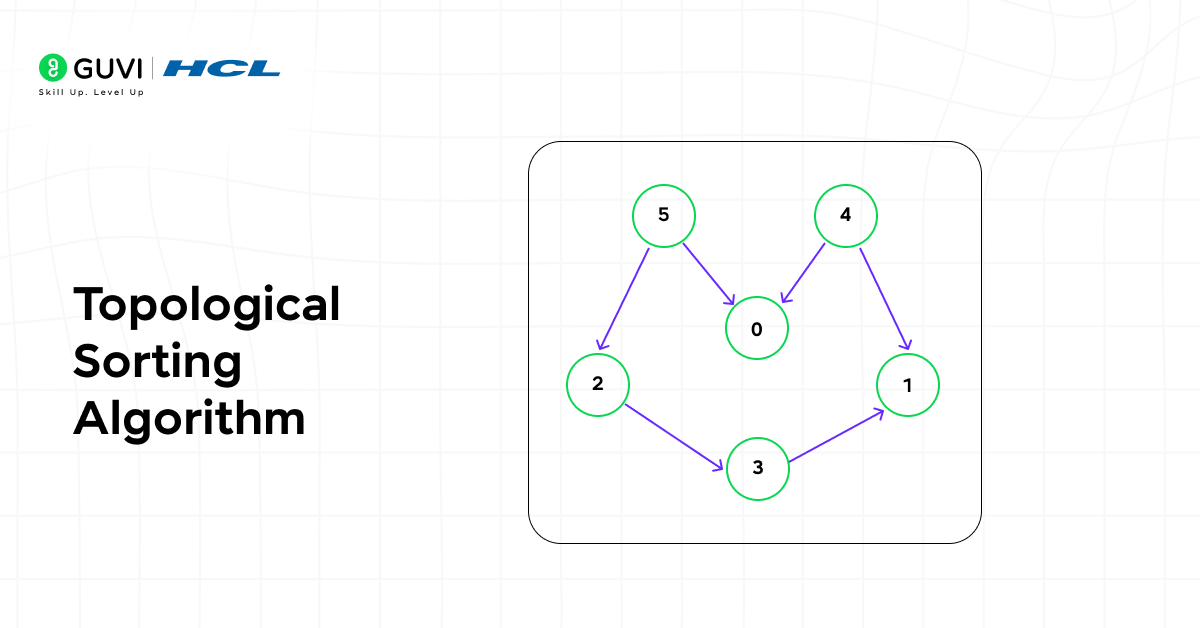
Topological Sorting orders the nodes of a directed acyclic graph based on dependencies. It ensures that prerequisites appear before dependent tasks, maintaining logical sequencing.
Features:
- Establishes dependency order without cycles
- Supports scheduling and task management in complex systems
- Forms the basis for compiler and workflow design
Applications:
- Job scheduling and project dependency management
- Compilation and software build systems
- Data pipeline and workflow optimization
16. Louvain Algorithm
The Louvain Algorithm is one of the most efficient methods for detecting communities in large networks. It works by optimizing modularity, grouping nodes that share dense internal connections.
Features:
- Automatically detects communities through modularity maximization
- Scales efficiently to handle millions of nodes
- Works dynamically with weighted and unweighted graphs
Applications:
- Social and business network clustering
- Market segmentation and customer behavior analysis
- Community mapping in biological and research data
17. HITS (Hyperlink-Induced Topic Search) Algorithm

The HITS Algorithm identifies authority and hub nodes within a network. It assigns two scores, one for credibility and one for influence, based on interlinked connections.
Features:
- Distinguishes between authoritative and hub nodes
- Updates scores iteratively for improved precision
- Works effectively for web, citation, and social graphs
Applications:
- Web ranking and search engine optimization
- Identifying influencers in online communities
- Academic citation and research impact analysis
18. Label Propagation Algorithm (LPA)
Label Propagation detects communities by spreading labels across a network until a stable structure emerges. It is fast and suitable for large, evolving datasets.
Features:
- Requires no prior knowledge of community count
- Converges rapidly through local label updates
- Handles massive graphs with minimal computational cost
Applications:
- Dynamic community detection in social media
- Fraud network identification in financial systems
- Discovering natural clusters in biological and sensor data
19. Betweenness Centrality Algorithm
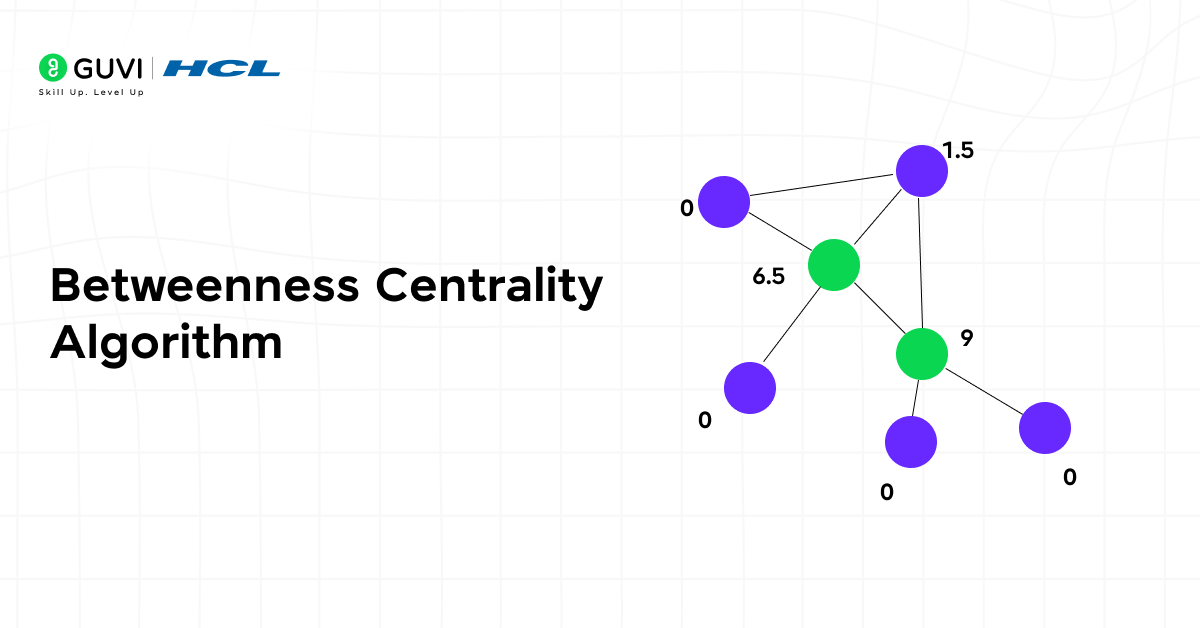
This algorithm measures how often a node acts as a bridge along the shortest path between other nodes. It helps determine influence and control points within a network.
Features:
- Calculates node importance based on path mediation
- Reveals bottlenecks and high-impact connectors
- Supports both directed and undirected graphs
Applications:
- Identifying key connectors in communication systems
- Traffic flow optimization and bottleneck detection
- Influence mapping in organizational and social networks
20. Graph Neural Networks (GNNs)
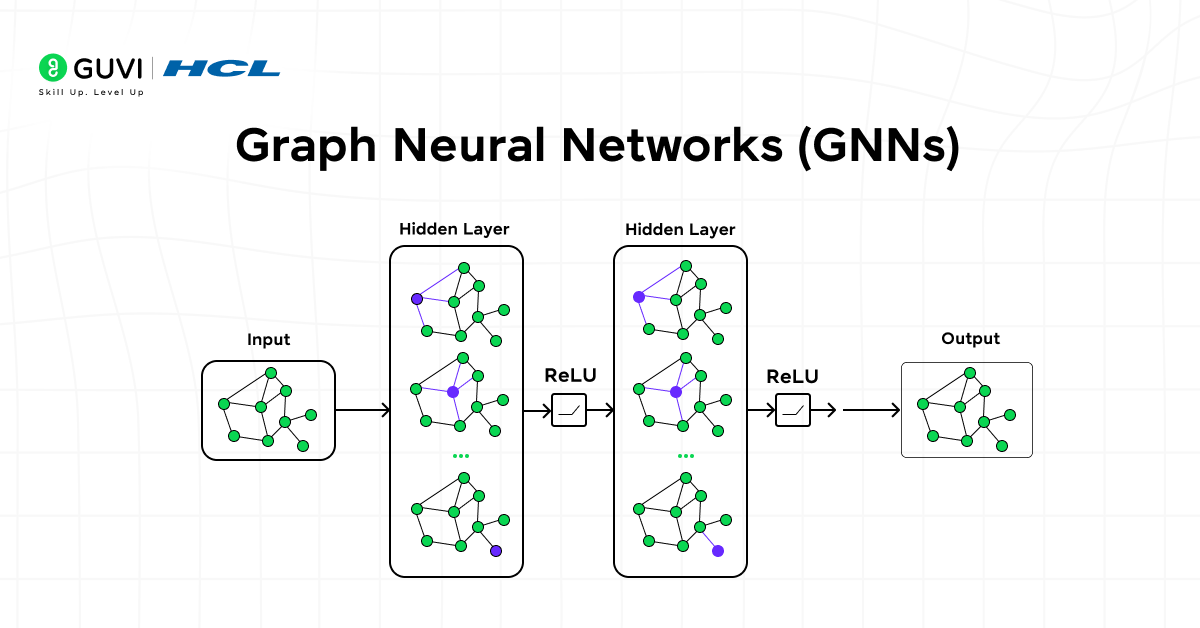
Graph Neural Networks represent the latest evolution of graph algorithms, combining deep learning with relational reasoning. They learn from both node features and graph structure, enabling predictive insights at scale.
Features:
- Learns representations directly from graph data
- Supports inductive reasoning for unseen nodes and edges
- Integrates seamlessly with machine learning pipelines
Applications:
- Fraud detection and financial intelligence
- Drug discovery and molecular interaction prediction
- Recommendation systems and social graph analysis
Impressed by how graph algorithms power AI, navigation, and recommendation systems? Learn to build and optimize these algorithms yourself with our Data Structures & Algorithms using Java Course. Strengthen your logic, master graph-based problem-solving, and develop efficient real-world solutions, from shortest path calculations to Graph Neural Network foundations. Gain hands-on coding experience, industry-ready skills, and the confidence to crack top tech interviews.
Best Benefits of Graph Algorithms
1. Reveal Hidden Relationships Data
Graph algorithms excel at finding links that traditional methods overlook. They map how entities connect, exposing underlying structures such as communities or influence networks. This relational insight helps organizations understand not just what exists, but how and why it interacts.
2. Improve Decision-Making Accuracy
Graph algorithms bring deeper context to predictions by analyzing connections rather than isolated metrics. They identify dependencies and patterns that guide smarter recommendations and resource allocation. They also enable generative AI models to predict outcomes or generate content that reflects real-world connections by mapping dependencies and causality.
3. Optimize Network Efficiency
Graph-based optimization enhances the performance of communication, transport, and data systems. Algorithms like Dijkstra, Prim, and Edmonds-Karp minimize costs and reduce latency by calculating the most efficient paths and connections. This efficiency becomes a measurable competitive advantage as networks scale.
4. Strengthen Real-Time Intelligence
Modern AI applications depend on instant analysis, and graph algorithms make that possible. They power adaptive routing, personalized suggestions, and real-time monitoring by processing dynamic relationships continuously. This responsiveness keeps systems relevant even as data changes moment by moment.
5. Enable Scalable Machine Learning
Graph algorithms provide the structural backbone for Graph Neural Networks and relational learning models. They allow AI systems to generalize across unseen nodes and new data, extending intelligence without retraining from scratch. This scalability supports long-term innovation in recommendation and predictive modeling.
Real Applications of Graph Algorithms
1. Social Network Analysis
Social media platforms like Facebook, LinkedIn, and X (Twitter) use graph algorithms to identify connections, suggest new relationships, and detect communities. They track how information spreads through networks, which allows companies to understand influence and behavioral clusters.
2. Recommendation Systems
Streaming platforms and e-commerce giants rely on graph-based recommendation engines to personalize user experiences. By mapping relationships between users, items, and preferences, algorithms like PageRank and Label Propagation deliver accurate, context-aware suggestions.
3. Fraud Detection and Financial Security
Banks and fintech companies use graph analytics to detect suspicious patterns in transactional networks. Algorithms such as Betweenness Centrality and GNNs uncover hidden relationships that signal potential fraud or money laundering activities across accounts and entities.
4. Supply Chain and Logistics Optimization
In logistics and transportation, algorithms like Dijkstra and Bellman-Ford optimize routing and predict disruptions. Organizations can visualize dependencies and build resilience against real-world constraints by modeling supply chains as graphs
5. Healthcare and Bioinformatics
Graph algorithms map molecular interactions, disease pathways, and genetic relationships. From predicting drug efficacy to identifying biological clusters, tools like Graph Neural Networks help researchers make faster and more accurate medical discoveries.
Test Your Knowledge: Graph Algorithms Quiz
1. What do nodes and edges represent in a graph algorithm?
A) Numbers and equations
B) Entities and their relationships
C) Layers and weights
D) Inputs and outputs
Answer: B) Entities and their relationships
2. Which algorithm is used by navigation systems to find the shortest path between two points?
A) Prim’s Algorithm
B) PageRank Algorithm
C) Dijkstra’s Algorithm
D) Floyd-Warshall Algorithm
Answer: C) Dijkstra’s Algorithm
3. What makes the PageRank algorithm significant in web search?
A) It measures the visual layout of websites
B) It scores pages based on the number and quality of links
C) It tracks user login data
D) It predicts site load times
Answer: B) It scores pages based on the number and quality of links
4. Which graph algorithm can handle negative edge weights in pathfinding?
A) A* Algorithm
B) Bellman-Ford Algorithm
C) Kruskal’s Algorithm
D) Tarjan’s Algorithm
Answer: B) Bellman-Ford Algorithm
5. In fraud detection, why are graph algorithms effective?
A) They visualize connections between entities to uncover suspicious patterns
B) They replace manual auditing entirely
C) They monitor only transaction frequency
D) They work without access to network data
Answer: A) They visualize connections between entities to uncover suspicious patterns
The Bottom Line
Graph algorithms reveal the hidden logic behind modern connectivity. They power systems that think relationally, optimizing routes and driving recommendations with precision. As AI evolves, these algorithms form its structural core, transforming data into intelligent insight. Understanding them means understanding how machines reason through relationships.
FAQs
1. Why are graph algorithms important in modern technology?
Graph algorithms form the foundation of connected intelligence. They help systems like Google Maps, LinkedIn, and Netflix understand relationships between locations, people, and preferences.
2. How do graph algorithms differ from traditional algorithms?
Traditional algorithms process data in isolation, while graph algorithms focus on relationships. They analyze how data points connect rather than treating them as separate entities. This relational approach makes them ideal for applications such as social networks and recommendation systems that depend on understanding complex linkages.
3. What skills are needed to learn graph algorithms?
To master graph algorithms, a strong grasp of data structures, especially graphs and trees, is essential. Familiarity with Python or Java helps in practical implementation. Knowledge of mathematics, network theory, and problem-solving frameworks also enhances understanding. It supports learners to apply these algorithms effectively in AI and data science projects.
























Did you enjoy this article?