
VIBE Computing: The Future of Context-Aware Systems
Sep 26, 2025 2 Min Read 640 Views
(Last Updated)
“Imagine your devices understanding your emotions, location, and habits and acting accordingly. That’s VIBE Computing.”
Technology today is becoming smarter, more human, and hyper-personalized. One of the emerging paradigms pushing this forward is VIBE Computing, an acronym for Vital, Intelligent, Bounded, and Emergent computing.
But what does that really mean? And why should you, as a developer, student, or tech enthusiast, care?
Let’s dive in.
Table of contents
- What is VIBE Computing?
- Simple Real-Life Example
- VIBE Computing vs Traditional Computing
- Key Technologies Behind VIBE Computing
- Use Cases of VIBE Computing
- Healthcare
- Smart Homes
- Education
- Workplaces
- VIBE in Action: Tools & Frameworks
- Challenges in VIBE Computing
- The Future of VIBE Computing
- Who Should Learn About It?
- Want to Explore More?
- Final Words
What is VIBE Computing?
VIBE Computing is about creating systems that understand their context and respond in ways that feel natural, adaptive, and almost empathetic.
VIBE stands for:
- Vital: Aware of human needs (health, emotions, safety).
- Intelligent: Leverages AI/ML to process, adapt, and learn.
- Bounded: Operates within contextual limits (location, time, privacy).
- Emergent: Behaves in dynamic, often unpredictable ways, adapting as new data appears.

Think of VIBE systems as context-aware smart environments that:
- Sense real-time inputs (biometric, sensor, location).
- Use AI to make decisions.
- Adapt actions accordingly.
Simple Real-Life Example
Picture this: you’ve had a stressful day and walk into your home.
A VIBE-powered system might:
- Detect elevated stress from your smartwatch.
- Dim the lights, play soothing music.
- Set the AC to your comfort level.
- Delay non-urgent notifications.
- Prepare a relaxing coffee via a smart machine.
All without you saying a word. This is ambient intelligence driven by VIBE principles.
VIBE Computing vs Traditional Computing
| Feature | Traditional Computing | VIBE Computing |
| Input | Manual (keyboard/mouse) | Sensors, speech, biometrics,and emotion |
| Behavior | Fixed logic | Adaptive, real-time decisions |
| Intelligence | Rule-based | AI/ML-based |
| Awareness | None | Context-aware (location, health, activity) |
| Response | Uniform | Personalized and evolving |
Key Technologies Behind VIBE Computing
Several emerging technologies enable the VIBE ecosystem:
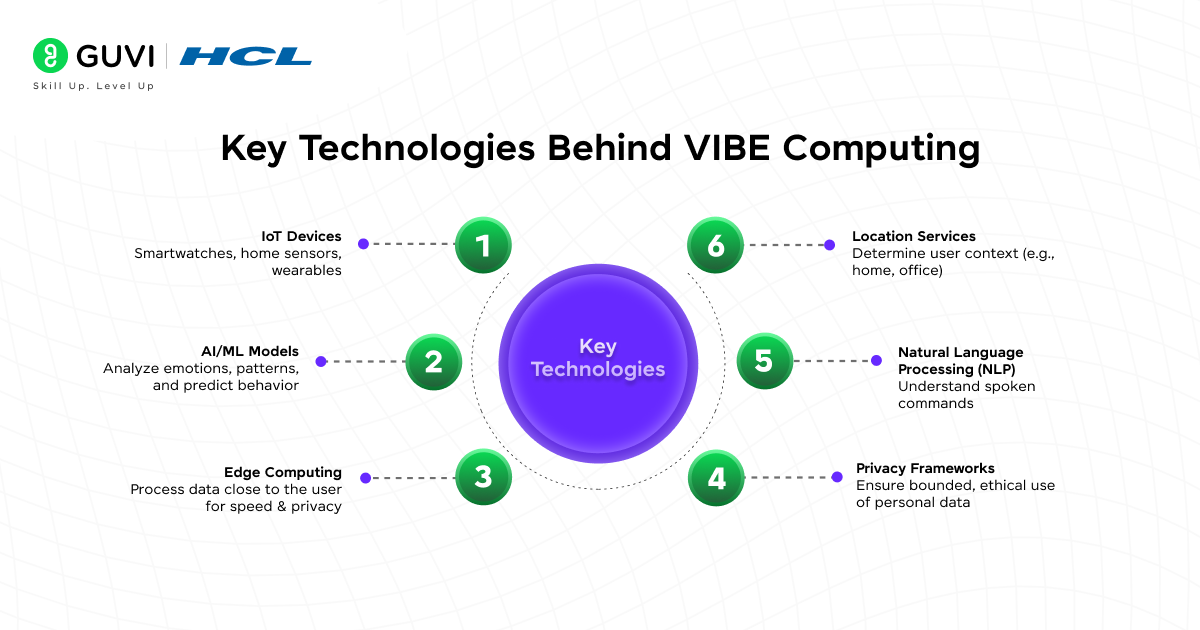
- IoT Devices – Smartwatches, home sensors, wearables
- AI/ML Models – Analyze emotions, patterns, and predict behavior
- Edge Computing – Process data close to the user for speed & privacy
- Location Services – Determine user context (e.g., home, office)
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) – Understand spoken commands
- Privacy Frameworks – Ensure bounded, ethical use of personal data
Use Cases of VIBE Computing
1. Healthcare
- Smart monitoring for elderly care
- Mental health support systems
- Real-time alerts for abnormal vitals
2. Smart Homes
- Mood-based lighting and music
- Energy-saving based on movement and need
- Intelligent reminders and habit tracking
3. Education
- Adaptive learning platforms
- Emotion-aware tutoring systems
4. Workplaces
- Focus enhancement based on cognitive load
- Emotion tracking for remote teams
- Auto-adjusting meeting environments
VIBE in Action: Tools & Frameworks
While still emerging, these tools help prototype VIBE-like experiences:
- Raspberry Pi / Arduino + Sensors (for bounded environments)
- TensorFlow, OpenCV (for emotion recognition)
- OpenAI APIs / Google Dialogflow (for intelligent interaction)
- SmartThings, Home Assistant (for automation)
- Wear OS, Apple HealthKit (vital data collection)

Challenges in VIBE Computing
| Challenge | Why it Matters |
| Privacy | Sensitive data (emotion, vitals) needs protection |
| Ethical AI | Avoiding manipulation and ensuring transparency |
| Real-time Adaptability | Requires low-latency, high-speed inference |
| Hardware Integration | Requires seamless IoT + AI + software stack |
The Future of VIBE Computing
VIBE systems are leading us toward the next generation of computing:
- Ubiquitous, invisible systems
- Tech that feels us, not just listens to us
- Smarter environments that blend with our daily lives
Researchers see VIBE as a stepping stone to empathetic AI technology that can support human emotion, decision-making, and well-being at scale.
Who Should Learn About It?
- Freshers / Students – For future-ready projects (smart home, AI healthcare).
- Professionals – To innovate in IoT, health tech, or human-computer interaction.
- Researchers – To push the boundaries of intelligent context-aware systems.
Want to Explore More?
- Ambient Intelligence on Springer
- Emotion AI with OpenCV & Python
- MIT Media Lab – Affective Computing
- OpenAI API for natural interaction
Want to go beyond vibe coding and actually master the AI powering it? Enroll in GUVI’s Certified AI & ML Course co-designed by Intel & IITM Pravartak and build real-world skills in Generative AI, Agentic AI, and more.
Final Words
“In a world filled with noise, VIBE computing enables your devices to feel the signal.”
Whether you’re building apps, devices, or AI models, understanding VIBE computing puts you at the cutting edge of empathetic, personalized, and adaptive technology.
Let’s move beyond smart and into systems that understand you.




























Did you enjoy this article?