
Explainable AI (XAI): Top Techniques, Models, Benefits, Use Cases, Challenges & More
Jan 19, 2026 6 Min Read 1726 Views
(Last Updated)
Can you trust a decision if you do not know how it was made? That question sits at the center of artificial intelligence today. Powerful models predict disease and guide autonomous vehicles, yet their inner workings are often hidden from human understanding. This opacity creates doubt and raises ethical concerns. Explainable AI (XAI) deals with this problem by offering methods that reveal why a model produced a certain output.
Keep reading this blog to explore top techniques, models, benefits, use cases, challenges, and more around Explainable AI.
- Global spending on XAI reached over USD 7.3 billion in 2024. Forecasts from IMARC Group expect it to grow to USD 27.6 billion by 2033. It will rise at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.85%.
- A report by FCA demonstrated that 75% of firms are now using AI, but only 34% know how it works.
- According to one study, 90% of consumers show higher confidence in a company when its AI outputs come with explanations.
Table of contents
- What is Explainable AI?
- Best Benefits of Explainable AI
- • Greater Transparency in Decision-Making
- • Stronger Accountability and Governance
- • Improved Reliability and Model Quality
- • Better Human Understanding and Collaboration
- Top Explainable AI Techniques You Need to Know
- Local Interpretable Model-Agnostic Explanations (LIME)
- SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP)
- Counterfactual Explanations
- Partial Dependence Plots (PDP)
- Individual Conditional Expectation (ICE)
- Feature Importance Analysis
- Attention Visualization
- Rule-Based Surrogates
- Models in Explainable AI
- How XAI Works?
- Step 1: Data Input and Feature Analysis
- Step 2: Model Behavior Evaluation
- Step 3: Generation of Explanations
- Step 4: Delivery to Stakeholders
- Step 5: Feedback and Continuous Improvement
- Top Explainable AI Tools
- Responsible AI vs Explainable AI
- Top Use Cases of Explainable AI
- Challenges and Mitigation in Explainable AI
- Top Companies Using Explainable AI
- The Bottom Line
- FAQs
- Why is explainability important for AI adoption?
- How does explainable AI improve model debugging?
- Is explainable AI only relevant for regulated industries?
What is Explainable AI?
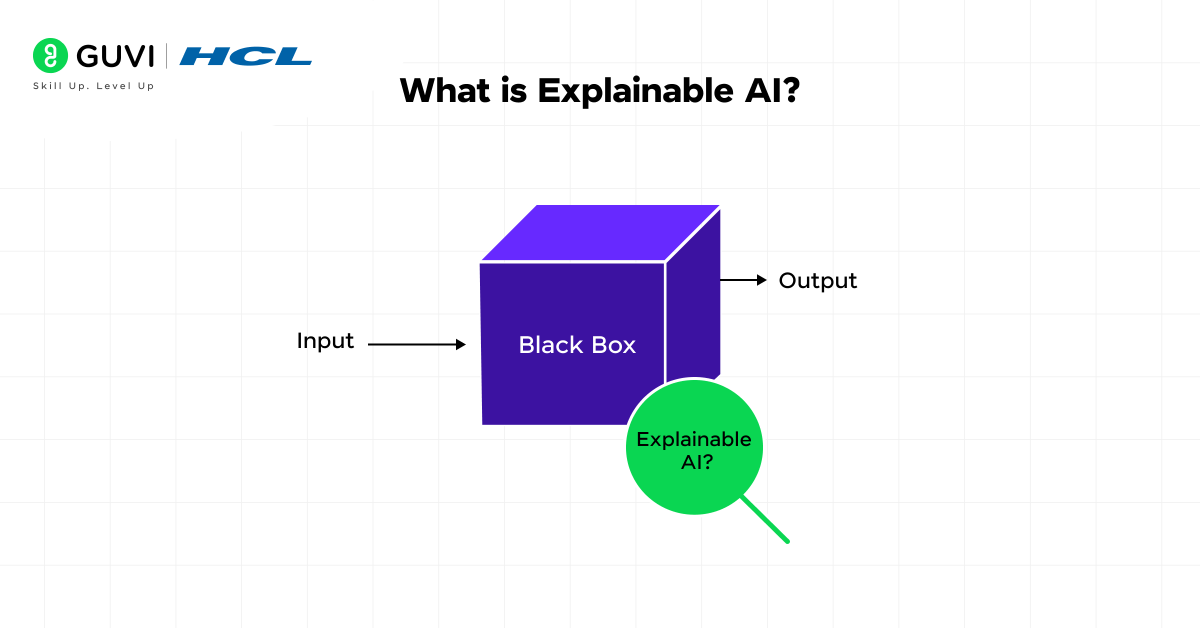
Explainable AI (XAI) refers to a set of methods and design principles that make the decision-making processes of complex artificial intelligence systems transparent and interpretable. Traditional black-box models such as deep neural networks or ensemble methods often achieve high predictive accuracy at the cost of interpretability. XAI deals with this gap by showing why a model produces a specific output.
Best Benefits of Explainable AI
• Greater Transparency in Decision-Making
Black-box models often generate outputs without context. It leaves users uncertain about reliability. XAI improves transparency by showing how inputs connect to outcomes.
In machine learning, explainable AI (XAI) provides transparency by showing how models reach their predictions, which helps users validate outcomes and build trust. Transparency also supports continuous oversight because organizations can monitor how model logic evolves.
• Stronger Accountability and Governance
Generative AI and AI decisions affect individuals and entire organizations. Accountability requires a traceable link between inputs, model operations, and outputs. XAI establishes that link by providing explanations that can be documented and audited.
Governance frameworks rely on these explanations to verify compliance with internal policies and external regulations. Strong accountability reduces the risk of misuse and helps organizations respond when outcomes are questioned.
• Improved Reliability and Model Quality
Complex models often produce unexpected or unstable predictions. Explanations expose weaknesses such as overreliance on irrelevant features or sensitivity to noisy data. Engineers can refine models by analyzing these explanations and correcting sources of error.
Reliability increases when models behave consistently across varied scenarios. XAI also supports validation by showing whether model’s reasoning aligns with domain knowledge. It further reinforces confidence in the system’s accuracy.
• Better Human Understanding and Collaboration
Humans often hesitate to rely on AI systems because the logic behind predictions is unclear. XAI closes this gap by presenting explanations in formats that align with human intelligence, such as feature importance values or visual highlights.
The shared understanding allows experts to combine their judgment with AI insights. Collaboration improves decision-making quality and builds user confidence.
Top Explainable AI Techniques You Need to Know
1. Local Interpretable Model-Agnostic Explanations (LIME)
LIME builds a simplified model around a single prediction to show how input features influenced that output. It perturbs the data by creating synthetic samples with small variations. Predictions from the original black-box model are then compared with results from the simplified model. The coefficients of this surrogate model indicate feature importance for that one prediction.
2. SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP)
SHAP assigns an importance score to each feature using principles from cooperative game theory. The method calculates how much each variable contributes to the difference between the actual prediction and the average prediction. SHAP ensures consistency because the same feature always receives equal or greater importance when it contributes more.
3. Counterfactual Explanations
Counterfactuals highlight minimal changes to input variables that would lead to a different outcome. A rejected credit application may show that a slightly higher annual income or a lower debt ratio could have changed the decision. This approach is intuitive because it translates complex statistical reasoning into practical guidance.
4. Partial Dependence Plots (PDP)
PDPs measure the marginal effect of a feature on the predicted outcome while averaging the influence of all other features. This creates a curve or surface that reflects the model’s general response to changes in one variable.
5. Individual Conditional Expectation (ICE)
ICE plots extend PDPs by showing feature effects for each record instead of relying on averages. A model may assign a positive relationship between income and loan approval for one group of applicants but a negative relationship for another. ICE plots reveal such patterns and make it easier to identify heterogeneous responses.
6. Feature Importance Analysis
Feature importance ranks input variables based on their contribution to predictions. Importance is measured by the reduction in impurity created by each split in tree-based models such as random forests.
Another approach is permutation importance, which randomly shuffles the values of one variable to measure the resulting loss in accuracy. This technique is straightforward and provides an overview of variable influence.
7. Attention Visualization
Attention mechanisms assign weights to input tokens in sequence models. Visualizing these weights reveals how the model distributes focus across different parts of the input. In natural language processing, attention heatmaps show which words in a sentence are linked together to form meaning. This has made transformer-based architectures such as BERT and GPT more interpretable than earlier recurrent models.
8. Rule-Based Surrogates
A surrogate model approximates the behavior of a complex model with a simpler interpretable structure. Decision trees are commonly used for this purpose because they output human-readable rules. For example, a tree can summarize a deep learning model’s decision-making process for loan approvals. Rule-based surrogates are useful in auditing since they create a transparent approximation of opaque systems.
Build your expertise in Explainable AI with our Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Course, certified by Intel. This program empowers you to master AI fundamentals, model building, and deployment while gaining hands-on experience with projects that mirror real-world challenges. With Intel Certification validating your skills, you’ll be equipped to design AI systems that are not just powerful but also transparent, fair, and trustworthy, skills that are highly sought after in industries like healthcare and autonomous systems. Enroll today and lead the way in building AI systems people can trust.
Models in Explainable AI
- Interpretable or glass-box models
Certain models are transparent by their nature. Linear regression and logistic regression present coefficients that directly show how variables influence outcomes.
Generalized additive models extend these principles by allowing non-linear relationships while still keeping results interpretable. These models often work well in structured business environments where clarity is more important than marginal gains in accuracy.
- Tree-based ensemble models
Random forests and gradient boosting machines provide strong predictive performance but are harder to interpret than simple trees. Their decision paths involve many branches, which makes direct inspection difficult.
XAI techniques such as TreeSHAP have become essential for these models because they quantify feature importance at both local and global levels. This balance of power and interpretability explains why they are widely used in finance and risk modeling.
- Probabilistic models
Bayesian networks and probabilistic graphical models encode dependencies among variables in a structured way. Their strength lies in representing uncertainty and causal reasoning.
Explanations from these models are often easier to understand because probabilities are tied to explicit conditional relationships. The challenge is scalability, as complex probabilistic structures can become computationally heavy.
How XAI Works?
Step 1: Data Input and Feature Analysis
The process begins with input data. XAI examines how each feature influences predictions. It highlights patterns, dependencies, and signals that drive outcomes. This step helps reveal whether the model depends on meaningful variables or relies on irrelevant ones.
Step 2: Model Behavior Evaluation
Next, the model’s internal behavior is studied. XAI methods track decision paths, weight distributions, and probability flows. The evaluation identifies strengths and exposes weaknesses such as sensitivity to noise or hidden bias.
Step 3: Generation of Explanations
The system then creates explanations that convert technical behavior into understandable formats. These may be feature importance values, simple decision rules, or visual indicators that show how the model arrived at a conclusion.
Step 4: Delivery to Stakeholders
Finally, the explanations are presented to users in a form that supports decision-making. Engineers may receive detailed technical reports, auditors may see compliance evidence, and end-users may get simplified reasoning. This structured delivery makes AI outputs actionable and trustworthy.
Step 5: Feedback and Continuous Improvement
Feedback from stakeholders is integrated into the process. Models are refined and explanations are adjusted. This way the system becomes more accurate and transparent over time.
Top Explainable AI Tools
- AI Explainability 360 (AIX360):
Developed by IBM, AIX360 collects multiple interpretability algorithms into one framework. It supports explanations for structured and unstructured data. It also emphasizes fairness testing, which makes it useful for teams that must present transparent reports to regulators. - InterpretML: This library by Microsoft provides interpretable models such as Explainable Boosting Machines, along with black-box explainers like SHAP. Teams can use it to compare clarity-focused models with performance-driven ones inside a single workflow. The dual support makes it attractive for enterprise adoption.
- Captum: Captum is designed for PyTorch models. It supports integrated gradients and DeepLIFT. It also supports feature attribution visualization. Captum helps teams understand neural networks by exposing which parts of an input most affected the output.
- What-If Tool: This tool, integrated with TensorFlow, provides a visual interface to explore model behavior. Users can interactively test fairness metrics, generate partial dependence plots, and create counterfactuals. It is valuable for collaborative settings where stakeholders want to explore models without coding.
- ELI5: ELI5 is a Python library that supports multiple algorithms such as linear models and tree-based ensembles. It allows users to inspect weights and prediction breakdowns. Its strength is in providing accessible visualizations during model development and testing.
Read: The Rise (RAISE) Of Artificial Intelligence
Responsible AI vs Explainable AI
| Factor | Responsible AI | Explainable AI |
| Definition | A framework for building and using AI systems that align with ethical, legal, and societal expectations | A set of methods that make model predictions transparent and interpretable |
| Scope | Covers fairness, accountability, privacy, sustainability, and governance | Focuses on interpretability, transparency, and clarity of model behavior |
| Primary Goal | Promote trustworthy AI that respects human rights and societal norms | Provide clear reasoning behind predictions so stakeholders can understand and challenge outcomes |
| Key Activities | Relies on multiple pillars, including explainability, fairness, and accountability | Feature attribution, visualization of decision paths, counterfactual reasoning |
| Stakeholders | Policy makers, compliance officers, organizational leaders, and technical teams | Data scientists, machine learning engineers, auditors, and end-users |
| Dependency | Relies on multiple pillars including explainability, fairness, and accountability | Acts as one of the central pillars within the broader Responsible AI framework |
Top Use Cases of Explainable AI
Below are some of the most significant use cases where XAI is making an impact:
- Healthcare Diagnostics and Decision Support
Medical AI systems classify images and predict disease progression. XAI helps clinicians understand why a model predicts cancer in a scan or flags a patient as high-risk. Saliency maps highlight tumor regions. SHAP values reveal the importance of lab results or vital signs. These explanations give doctors confidence in using AI as a decision-support tool.
Read: The Ultimate Guide to Applications of Artificial Intelligence in 2026
- Financial Credit Scoring and Risk Assessment
Banks and lenders rely on machine learning models to approve loans and evaluate creditworthiness. XAI makes these decisions transparent. Counterfactuals show an applicant what financial changes could alter a decision. SHAP scores clarify how variables such as income or debt ratio influence risk. This transparency is critical for regulatory compliance and customer trust.
- Fraud Detection and Security
Fraud detection systems use anomaly detection and classification models to flag suspicious transactions. XAI methods explain why a specific activity was labeled fraudulent. LIME highlights which features in the transaction profile raised concerns. This context allows investigators to validate alerts quickly. It also reduces false positives, which improves efficiency.
Read: AI and Machine Learning Careers Are Booming: Here’s How to Stay Ahead
Challenges and Mitigation in Explainable AI
- Trade-off between accuracy and interpretability
Complex models such as deep neural networks achieve high accuracy but remain difficult to explain. Simpler models offer clarity but often underperform on complex data. Mitigation includes adopting hybrid approaches where interpretable models handle critical tasks and black-box models are used with advanced explanation methods.
- Computational cost of explanations
Techniques such as SHAP require evaluating many feature combinations. Processing large datasets under these conditions can lead to long delays. Costs increase further when explanations must run in real time. Mitigation requires sampling strategies that reduce the number of combinations without compromising fidelity.
- Risk of oversimplification
Some explanation techniques reduce complex reasoning into a few highlighted features. The result is easier to read but may hide important dependencies. Oversimplification creates a false sense of clarity that misleads decision makers. Mitigating this risk is all about combining multiple explanation methods so that both global and local perspectives are visible.
Top Companies Using Explainable AI
- Microsoft: Uses XAI in Azure Machine Learning with tools like InterpretML.
- Apple: Applies XAI in privacy-focused features such as Siri and health monitoring.
- Google: Provides XAI solutions through Google Cloud and the What-If Tool.
- IBM: Offers AI Explainability 360, a toolkit for transparency and fairness.
- Amazon: Uses XAI in AWS services to improve trust in AI-driven applications.
The Bottom Line
Explainable AI has moved from theory into practical necessity. Organizations no longer ask whether predictions are accurate alone; they also demand to know why those predictions are made. Transparency builds trust, and accountability strengthens governance. Also, clarity enables collaboration between humans and machines. The future of AI depends on systems that are powerful and understandable at the same time.
To make informed decisions and improve adoption, it is the right moment to integrate explainability into every stage of your AI journey.
FAQs
1. Why is explainability important for AI adoption?
Explainability builds trust by showing how inputs influence predictions. Users gain confidence when they see transparent reasoning instead of opaque results. Organizations also benefit because explainability supports compliance and reduces resistance to AI adoption.
2. How does explainable AI improve model debugging?
Explanations highlight which features drive specific outputs, which helps engineers detect errors. When a model depends too heavily on irrelevant variables, the explanation exposes this weakness. Teams can then refine data pipelines or retrain the system to correct the issue.
3. Is explainable AI only relevant for regulated industries?
Regulated sectors such as healthcare and finance rely on explainability for compliance, but its value extends further. Any business using AI can reduce risks and improve decision-making through explanations. Transparency strengthens collaboration between technical and non-technical teams, regardless of the industry.





























Did you enjoy this article?