Quantum Machine Learning Explained: The Ultimate Guide
Feb 11, 2026 6 Min Read 2272 Views
(Last Updated)
Let’s be honest. The terms “quantum computing” and “machine learning” sound like they’ve been pulled straight from a sci-fi movie. One involves mind-bending physics where things can be in two states at once. The other powers the recommendations on your Netflix account and the voice assistant in your living room.
And now, imagine smashing these two giants of technology together. That is Quantum Machine Learning (QML). Rather than simply being an upgrade, QML fundamentally alters possibilities for computation and artificial intelligence.
If your brain is already beginning to feel a bit “stressed out,” do not worry! We will work through it together, in simple terms. We will discuss QML’s potential possibilities and what it means for the future.
Table of contents
- What is Quantum Machine Learning?
- Quantum Algorithms for Machine Learning
- Quantum Neural Networks (QNNs)
- The Role of Quantum Computing in Machine Learning
- Applications of Quantum Machine Learning
- Advantages of Quantum Machine Learning
- Challenges in Quantum Machine Learning
- Quantum Machine Learning Tools and Platforms
- The Future of Quantum Machine Learning
- Final thoughts..
- FAQs
- Is quantum machine learning a reality today?
- Will quantum machine learning replace classical machine learning?
- How can I start learning about QML?
- Do I need a quantum computer to learn QML?
What is Quantum Machine Learning?
Before we take a look at quantum machine learning, let’s get a quick recap:
Machine Learning (ML): ML is fundamentally based on mathematical discovery and empirical validation of patterns in huge piles of data. For example, if you want your computer to recognize a cat, you need to feed a million pictures of cats, and the computer builds a model, which is a complex mathematical recipe for identifying the cats.
Quantum Computing: A traditional computer uses bits (0s and 1s), while a quantum computer uses qubits (quantum bits). Given the strange laws of quantum mechanics (specifically superposition and entanglement), qubits can represent a 0, 1, or both at the same time. This allows the quantum computer to evaluate millions of possibilities simultaneously.
So now, what is Quantum Machine Learning?
In simple terms, quantum machine learning is the use of quantum computers to perform or improve machine learning algorithms faster and more accurately. It is about using the strange behavior of qubits to find patterns in data faster, solve problems that classical computers cannot solve currently, and develop new, more powerful classes of AI models.
A classical computer going through a maze follows one route at a time. A quantum computer can, in a practical sense, take all paths simultaneously. Machine learning is all about determining the optimal path (or the optimal pattern) throughout the data, and this changes the game.
Quantum Algorithms for Machine Learning
Quantum algorithms in machine learning (ML) are the building blocks to quantum machine learning (QML). These algorithms utilize the principles of quantum mechanics to conduct many machine learning tasks. Some of the significant methods include:
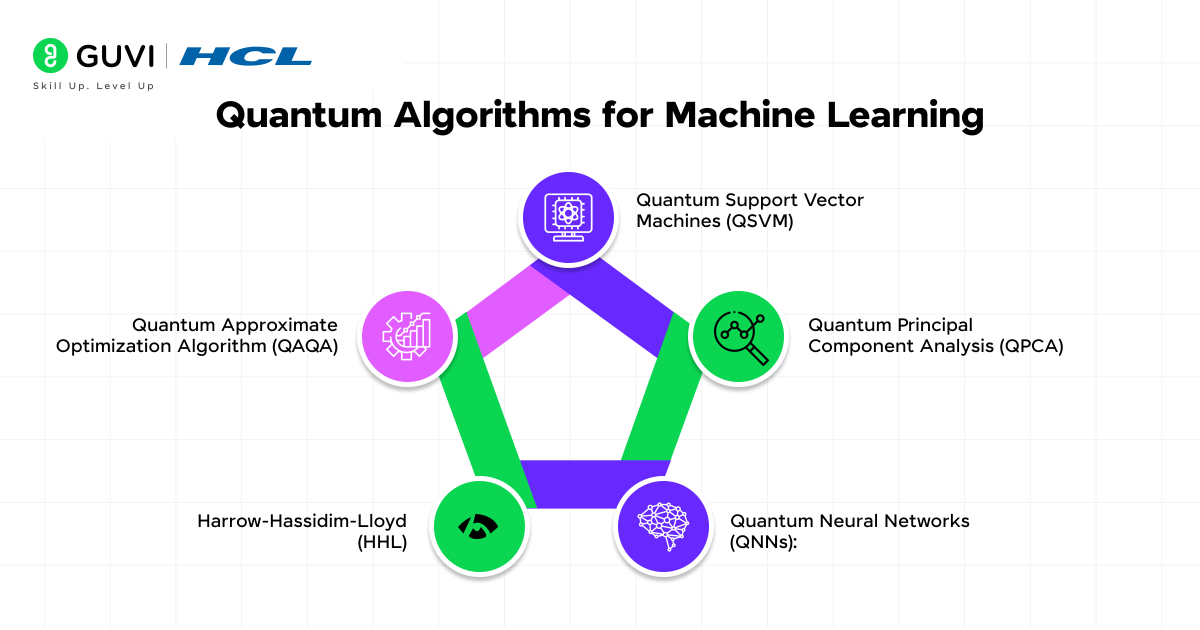
- Quantum Support Vector Machines (QSVM): A quantum version of the classical Support Vector Machine, which is used to optimize classifying hyperplanes. Quantum feature mapping may allow projection of data to higher dimensions more efficiently, improving classification.
- Quantum K-Means: A quantum algorithm for clustering data into ‘k’ number of clusters, where the quantum version may improve significantly on larger datasets than classical machines.
- Quantum Principal Component Analysis (QPCA): A quantum analog for dimensionality reduction of data, which is important for large datasets in ML.
- Quantum Neural Networks (QNNs): Possibly one of the more exciting areas of innovation, where the neural networks integrate quantum circuits into the architecture of the neural networks.
Quantum Neural Networks (QNNs)
Quantum Neural Networks are similar to classical neural networks but use quantum mechanics as their primary computational resource. In classical neural networks, the basic components, such as neurons and weights, are treated using classical bit representations. In QNNs, however, these classical components are replaced by quantum representations: qubits and quantum gates.
There are several approaches to QNNs:
- Variational Quantum Eigensolver (VQE) based QNNs: QNNs of this type use parameterized quantum circuits; those parameters are eventually optimized using classical methods, quantum computer sources, and compute the cost function, a classical optimizer then updates the parameters.
- Quantum Perceptrons: QNNs such as these are the simplest form of a QNN and are analogous to a classical perceptron. Simple classification is modelled via the quantum gates using unitary operations and measurements.
- Quantum Reservoir Computing: Quantum reservoir computing, when representing neural networks and quantum neural networks, uses a fixed complex quantum system, or the reservoir, where a computation is performed, driven by the inner dynamics of the reservoir, and only the readout layer is used to train (learn the representation).
In simple words, the real strength of QNNs is that they can truly compute quantum data, and can ultimately find an even more intricate pattern due to quantumness, specifically due to quantum dynamics which may involve both superposition and entanglement. These dynamics will ultimately provide the underpinnings of Quantum AI.
The Role of Quantum Computing in Machine Learning
QML’s significance is not merely in advancing the speed of machine learning but rather in achieving what others considered impossible.
- Speeding up Computations: Training deep neural networks and complex models can take weeks. In theory, QML has the potential to significantly reduce these training times.
- Working with High-Dimensional Data: Quantum systems can model and process large amounts of multidimensional data practically.
- Solving Optimization Problems: Sufficiently many machine learning tasks, such as clustering and recommendation problems, include optimization that quantum algorithms are advantageous in the optimization category.
- Building AI Applications: Integrating quantum AI will allow us to build intelligent, adaptive systems in healthcare, finance, cybersecurity, etc.
- A single quantum computer could one day outperform the most powerful supercomputer on Earth in solving certain problems.
- Quantum bits (qubits) can exist in multiple states at once, thanks to superpositionlike flipping a coin that lands on both heads and tails simultaneously.
- Tech giants like IBM, Google, and Microsoft already offer cloud-based quantum platforms you can experiment with even without owning a quantum computer.
Applications of Quantum Machine Learning
While large-scale QML is still evolving, serious efforts are being made to develop quantum machine learning applications:
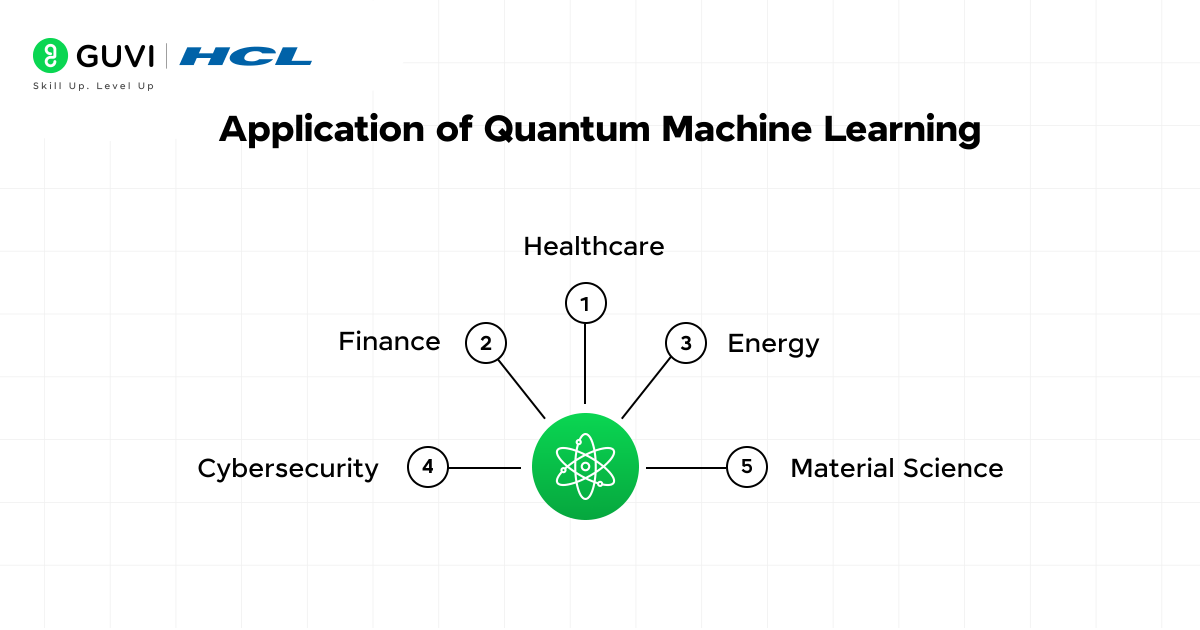
- Drug discovery & material science: Simulating molecules to create new medications or battery materials is very complex for classical computers. Quantum computers are natural simulators of quantum systems. Classical computing will struggle with analyzing these simulations, whereas QML could analyze them years sooner to help discover new drugs and materials.
- Financial modeling: Banks have started to experiment with QML in an effort to use market data for portfolio optimization, fraud detection, and risk modeling in ways that current capabilities would make impossible.
- Logistics & supply chain: QML can tackle nightmarishly complex optimization problems for global shipping by finding optimal routing, delivering vastly different products to complex destinations, or scheduling airlines, which can save billions of dollars and reduce carbon footprints.
- Climate change & weather forecasting: Better climate models can be built today from lots of complex data. QML can help us establish a better understanding of climate patterns and potentially give us more warning of extreme weather events.
- Unbreakable cryptography & cybersecurity: Quantum computers can threaten current encryption; however, even though they can be part of the threat, QML can also help develop new quantum-resistant cryptographic protocols and help identify vulnerabilities in complex or deeply segmented network attacks.
Advantages of Quantum Machine Learning
The theoretical advantages of QML are what lead to massive investment and research in the arena. The main advantages of quantum machine learning include:
- Exponential Speedup: for some specific, well-defined problems, QML algorithms can lead to a huge cut in computation time with respect to classical algorithms, and can effectively convert thousand-year problems into minute problems.
- High-Dimensional Data: quantum computers naturally operate in very high-dimensional spaces, making them ideal for analyzing complexity such as molecular structures, financial markets, or cosmological data.
- Generalization Improvement: QML may help avoid “overfitting” (memorizing the training data) by considering a wider solution space, as QML models may have much wider and more forgiving solutions than classical machine learning models in some cases.
- Reduction in Energy Consumption: While current quantum computers require substantial cooling, a single operation in a ripened quantum processor could substitute billions of classical operations, which potentially offers very considerable energy savings in the arena of resource-intensive large-scale computation.
Challenges in Quantum Machine Learning
There are still many significant hurdles that quantum machine learning (QML) will need to overcome before it enters routine use:
- Hardware Issues: Current quantum computers (NISQ devices) are noisy and imprecise, and the available qubits, as well as connectivity, is limited. Creating a fault-tolerant quantum computer would be an engineering feat.
- Error Correction: Before reliable computation is possible, error correction is a necessity for quantum computing; however, error correction can require a massive overhead in the number of physical qubits for each logical qubit.
- Data Encoding: Encoding classical data into quantum states is not trivial. Additionally, “quantum data loading” can also present a computational bottleneck.
- Scalability: Adapting current QML algorithms to real-world datasets is an essential hurdle that must be surmounted.
- Algorithm Displacement: One of the ongoing research questions is, “Which quantum algorithms have a quantum advantage over an appropriate classical alternative machine learning system?” to understand that not all quantum algorithms will improve performance as a quantum advantage.
- Quantum Software and Tools: The tool and framework ecosystem for quantum machine learning development is in its infancy compared to classical ML.
- Training and Expertise: There is still a very small pool of experts in both quantum mechanics and machine learning so there is a significant disparity in available talent.
Quantum Machine Learning Tools and Platforms
The field is expanding rapidly, and for that reason, there are several quantum ML tools to enable researchers and developers to trial QML:
- Qiskit (IBM): Open source SDK providing a complete set of features to work with quantum computers at the circuit, pulse and algorithm levels. It includes a set of machine learning features (Qiskit Machine Learning) and documentation with examples is available.
- TensorFlow Quantum (Google): Open source library for the evaluation of quantum machine learning models. Its aim is rapid prototyping of the quantum neural networks. The library provides an open-source backend for algorithms and builds on TensorFlow to allow machine learning researchers to build quantum-classical hybrid ML models.
- PennyLane (Xanadu): Python library for quantum machine learning, quantum chemistry, and quantum computing. PennyLane provides a cross-platform framework for building differentiable quantum circuits.
- Cirq (Google): Python framework for creating, editing and invoking quantum circuits – this focuses specifically on NISQ computers.
- PyTorch Quantum (Facebook AI Research/MIT): Open source framework for building quantum neural networks that is built using PyTorch as a backend.
Tools such as these are useful for helping reduce barriers to entry and reduce the timelines of quantum machine learning research.
The Future of Quantum Machine Learning
The future of quantum machine learning is very promising, but there will still be a hybrid ecosystem. Classical computers are not going away anytime soon. Here’s what we expect to see:
- The Near Future (Now – 5 years): Quantum-classical hybrid models will predominate. A classical computer will complete the bulk of the workflow but will delegate the most computationally expensive subtasks to a quantum co-processor. Quantum machine learning research will attempt to substantiate more of these tasks where “quantum advantage” can be applied.
- The Mid-Term Future (5 – 15 years): We will achieve quantum advantage in specific cases in the real world pertaining to real business and scientific challenges, probably in chemistry, finance, and optimization. NISQ (Noisy Intermediate-Scale Quantum) devices will also have significantly higher quality.
- The Long-Term Future (15+ years): The aim will be fault-tolerant, large-scale quantum computing. This will potentially expose the full extent of QML possibilities, unlocking discoveries in quantum AI we may not even comprehend today, possibly even in the area of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI).
Ready to dive into the quantum future?, if you want to become an AI/ML Engineer, then take the chance to get started and learn with HCL GUVI’s IITM Pravartak and Intel Certified Online Advanced AI & Machine Learning Course,. This NSDC-approved course offers a certificate recognized globally, which adds serious bragging rights to your résumé and will help you set yourself apart in a highly competitive employment market.
Final thoughts..
Quantum machine learning is the next great leap in AI. We are still very much in the beginning, but the advancement in recent years has been startling. Quantum machine learning has the potential to change our current systems because it can deal with enormous amounts of data, use the fast processing capabilities of a quantum-environment, develop faster training, and solve problems that cannot be solved today. So this development can be a change for the century.
As researchers improve quantum algorithms, develop error-free hardware, and build new approaches for quantum ML, we are edging closer to a world where quantum and AI are more hand in hand. Hope this blog helped you understand Quantum machine learning basics, why it matters and a starting point for you to explore this interesting topic. Happy learning!
FAQs
1. Is quantum machine learning a reality today?
Yes, quantum machine learning exists in reality, but only in a limited way. Its in active research and still in the development stage.
2. Will quantum machine learning replace classical machine learning?
Most certainly no. Classical machine learning is very effective for most of the tasks that we use computers now, whereas QML is best seen as a specialized tool for specific problems that classical computers struggle to solve.
3. How can I start learning about QML?
Start with the basics of linear algebra and Python programming. Then, get familiar with a quantum computing SDK like Qiskit or PennyLane.
4. Do I need a quantum computer to learn QML?
Not necessarily. You can experiment with QML using simulators and cloud-based platforms like IBM Q, Google Cirq, or PennyLane.




























Did you enjoy this article?