
The Complete Linear Algebra for Machine Learning Guide for Beginners in 2025
Sep 23, 2025 5 Min Read 2206 Views
(Last Updated)
Linear algebra for machine learning serves as the essential foundation you need to master if you’re serious about this field. Without it, you cannot develop a deep understanding and application of machine learning. This isn’t just another mathematical concept to learn—it’s essentially the mathematics of data.
When you begin exploring linear algebra for machine learning, you’ll discover how it simplifies complex tasks like data transformation and dimensionality reduction. The importance of linear algebra for machine learning cannot be overstated, as it’s the cornerstone for understanding and implementing various machine learning algorithms.
This guide breaks down the fundamental concepts you need to know in a beginner-friendly way, without the complexity that makes many avoid this crucial subject. After all, linear algebra is not magic and is not trying to be exclusive or opaque. Let’s begin!
Table of contents
- Why Linear Algebra Matters in Machine Learning
- 1) Linear algebra as the language of data
- 2) How is linear algebra used in machine learning?
- 5 Core Concepts Every Beginner Should Learn
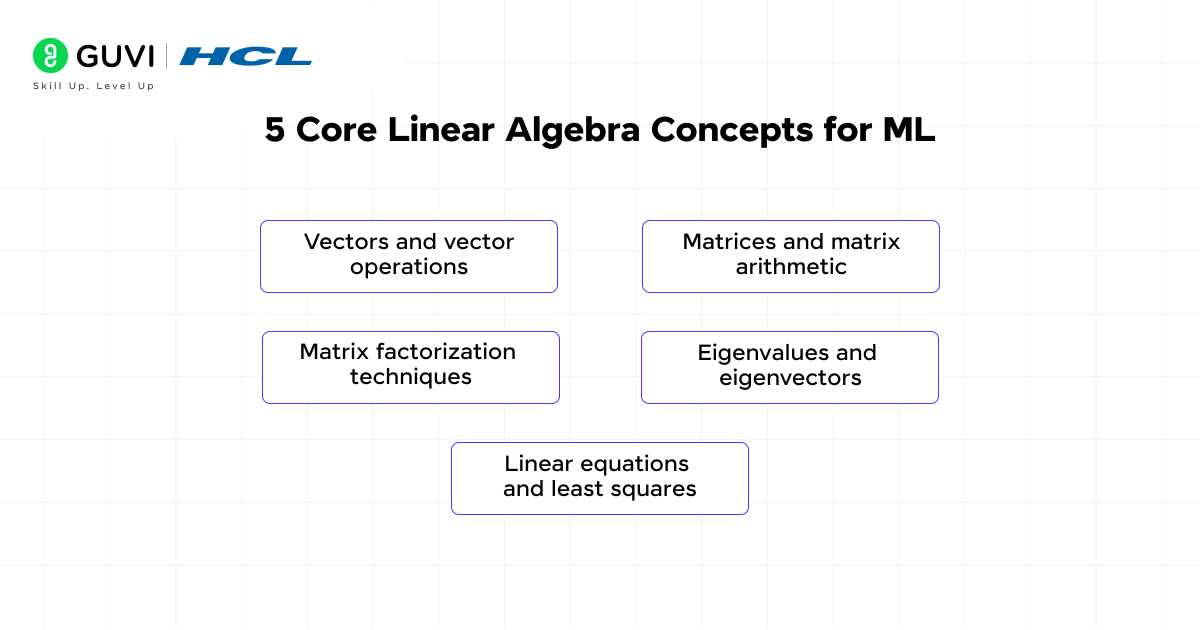
- Vectors and vector operations
- Matrices and matrix arithmetic
- Matrix factorization techniques
- Eigenvalues and eigenvectors
- Linear equations and least squares
- Avoiding Common Mistakes When Learning Linear Algebra for Machine Learning
- 1) Studying too much theory too early
- 2) Learning without practical examples
- 3) Ignoring the connection to machine learning
- Practical Applications of Linear Algebra in Machine Learning
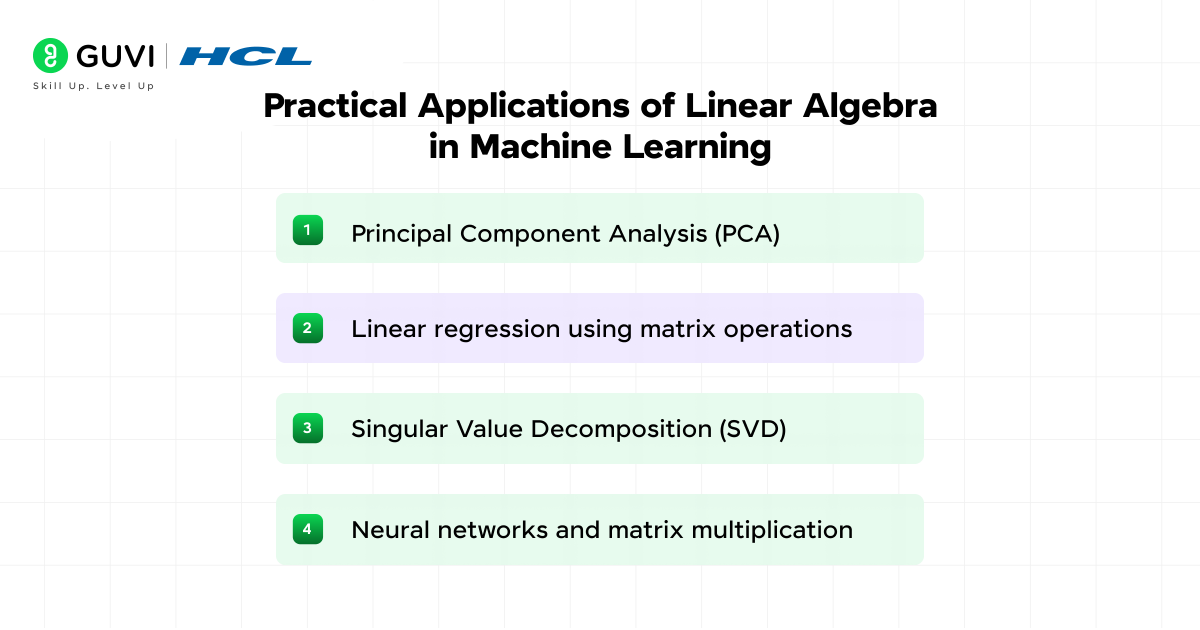
- 1) Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
- 2) Linear regression using matrix operations
- 3) Singular Value Decomposition (SVD)
- 4) Neural networks and matrix multiplication
- Concluding Thoughts…
- FAQs
- Q1. Why is linear algebra important for machine learning?
- Q2. What are the core linear algebra concepts every beginner should learn for machine learning?
- Q3. How can I avoid common mistakes when learning linear algebra for machine learning?
- Q4. What are some practical applications of linear algebra in machine learning?
- Q5. Are there any recommended resources for learning linear algebra for machine learning?
Why Linear Algebra Matters in Machine Learning
Behind every sophisticated machine learning model lies the mathematical foundation of linear algebra. Machines understand only numbers, and linear algebra for machine learning provides the mathematical framework necessary for data representation, manipulation, and modeling.
1) Linear algebra as the language of data
Think of linear algebra as the grammar that structures how machines interpret information. In machine learning, data points are typically represented as vectors, where each number corresponds to a specific feature. These vectors collectively form matrices that serve as data storage units.
For instance:
- Images in computer vision are stored as multi-dimensional arrays
- Word embeddings in natural language processing appear as vectors in high-dimensional space
- Datasets become matrices with rows representing data points and columns representing features
Furthermore, linear algebra for machine learning simplifies tasks like data transformation and dimensionality reduction, making complex computations more manageable.
2) How is linear algebra used in machine learning?
Linear algebra works throughout the entire machine learning pipeline:
- Data Preprocessing: Techniques like normalization and standardization rely on matrix operations to rescale features, ensuring no single feature dominates the learning process.
- Model Training: Many learning algorithms solve systems of linear equations or optimize linear functions. Matrix operations like multiplication (dot product) reveal similarities between vectors and have applications in correlation calculation and numerous algorithms.
- Model Evaluation: Metrics like Mean Squared Error can be calculated using vector operations to find differences between predicted and actual values.
- Optimization: Gradient descent and other optimization methods heavily depend on matrix calculus to update model parameters efficiently.
5 Core Concepts Every Beginner Should Learn
Mastering the foundational concepts of linear algebra for machine learning creates a solid launchpad for your machine learning journey. Let’s explore the five essential building blocks that every beginner should understand.
1. Vectors and vector operations
Vectors form the cornerstone of data representation in machine learning. These ordered lists of numbers (scalars) help machines process information numerically. Each element in a vector typically corresponds to a specific feature of your data point.
Basic vector operations include:
- Addition/subtraction: Performed element-wise between vectors of equal length
- Multiplication/division: Also element-wise, creating a new vector of the same length
- Dot product: Calculating the sum of multiplied elements, essential for determining vector projections and similarities
In machine learning, vectors represent everything from text embeddings to feature sets for house price prediction.
2. Matrices and matrix arithmetic
Matrices expand on vectors by organizing data in two dimensions (rows and columns). They serve as powerful data structures that store datasets with rows representing data points and columns representing features.
Matrix operations include addition, subtraction, scalar multiplication, and matrix multiplication. Two matrices can be added or subtracted only when they have the same dimensions. During matrix multiplication, the number of columns in the first matrix must equal the number of rows in the second.
These operations power tasks like image processing, neural network computations, and data transformations.
3. Matrix factorization techniques
Matrix factorization decomposes a matrix into constituent parts, simplifying complex operations. This technique breaks down large matrices into smaller ones that, when multiplied together, approximate the original matrix.
Applications include recommendation systems (like those used by Netflix and Amazon), dimensionality reduction, and solving systems of linear equations. For instance, in collaborative filtering, matrix factorization helps identify latent factors that explain user preferences.
4. Eigenvalues and eigenvectors
Eigenvectors are special vectors that maintain their direction when transformed by a matrix—they’re merely scaled by a factor called the eigenvalue. This concept might seem abstract initially, but it’s crucial for understanding data structure.
Eigendecomposition helps extract key features from data, reduce dimensionality, and analyze variance patterns. Principal Component Analysis (PCA), which identifies directions of maximum variance in data, relies heavily on these concepts.
5. Linear equations and least squares
When working with real-world data, finding exact solutions to linear equations is often impossible. Least squares provides a mathematical approach to finding the best approximate solution by minimizing the sum of squared differences.
This concept underpins linear regression and finding best-fit lines for scattered data points. The least squares solution minimizes the vertical distances between your data points and the predicted line, making it essential for predictive modeling.
Avoiding Common Mistakes When Learning Linear Algebra for Machine Learning
The path to mastering linear algebra for machine learning is filled with potential pitfalls. Many learners get stuck or discouraged due to common mistakes that can easily be avoided with the right approach.

1) Studying too much theory too early
Diving straight into abstract linear algebra theory is a recipe for frustration. Many beginners make the mistake of trying to learn everything from massive textbooks without context. This traditional approach—focusing on transmitting information to passive learners—is less effective for understanding linear algebra for machine learning.
Better approach:
- Start with basic visualizations from sources like GUVI, Khan Academy or 3Blue1Brown
- Focus on building intuition before tackling complex theorems
- Move from concrete to abstract concepts gradually
2) Learning without practical examples
Linear algebra for machine learning becomes significantly harder to grasp without seeing it in action. Studying solely with pen and paper limits your understanding of how these concepts apply to real-world problems.
Consequently, you might understand the math but struggle to implement it in actual machine learning contexts. Instead, look for resources that combine theory with code examples and practical applications.
3) Ignoring the connection to machine learning
Perhaps the most critical mistake is learning linear algebra concepts in isolation without connecting them to machine learning algorithms. Primarily, your approach should start with understanding a machine learning concept (like linear regression) and then exploring the underlying math.
This “results-first approach” provides a skeleton for progressively deepening your knowledge of algorithms and their mathematical foundations. Ultimately, this connection helps you understand why eigenvectors matter for PCA or how matrix operations enable neural networks.
Linear algebra isn’t just abstract math—it powers the algorithms that shape modern AI:
The Term “Matrix” Comes from Latin: The word matrix means “womb” or “something from which others spring.” In math, it symbolizes a structure from which multiple results can be generated.
Eigenfaces in Facial Recognition: Early facial recognition systems used eigenvectors of images—called eigenfaces—to capture key patterns in human faces, a direct application of linear algebra.
These facts remind us that the formulas you practice aren’t just theory—they’ve been at the core of breakthroughs in AI and real-world applications.
Practical Applications of Linear Algebra in Machine Learning
Linear algebra empowers practical machine learning implementations through efficient mathematical operations. Let’s examine how these concepts translate into real-world applications.
1) Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
PCA serves as a powerful dimensionality reduction technique that transforms data into principal components that capture maximum variance. This statistical approach creates new uncorrelated variables through linear combinations of original features.
The process involves:
- Standardizing data to ensure equal contribution from variables
- Computing the covariance matrix to identify relationships
- Finding eigenvectors and eigenvalues to determine principal components
PCA helps visualization, pattern recognition, and preprocessing for machine learning algorithms by removing redundancy.
2) Linear regression using matrix operations
Matrix algebra elegantly simplifies linear regression through the equation Y=Xβ+ε. This representation allows you to solve complex systems efficiently.
Using least squares method, you can calculate coefficients with: b=(X’X)^(-1)X’Y
This matrix formulation generalizes easily to multiple explanatory variables, making it extraordinarily flexible.
3) Singular Value Decomposition (SVD)
SVD decomposes a matrix into three components: X = UΣV^T. This technique:
- Calculates pseudoinverses for solving linear equations
- Enables data compression by discarding less significant values
- Powers recommendation systems through collaborative filtering
4) Neural networks and matrix multiplication
Neural networks rely fundamentally on matrix operations. Input data transforms through weight matrices, with each layer performing: Y = XW + b
Matrix multiplication enables batch processing of multiple inputs simultaneously, significantly improving computational efficiency.
Level up your ML journey with GUVI’s industry-aligned Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning Course, developed with IIT-Madras’s Pravartak and Intel. This hands-on, live-course (5–6 months) blends Generative AI, Deep Learning, MLOps, and real-world capstone projects—setting you up for high-impact roles in AI.
Concluding Thoughts…
Linear algebra undoubtedly forms the backbone of machine learning, serving as the mathematical language that allows algorithms to process and understand data effectively. Throughout this guide, you’ve seen how vectors, matrices, and their operations provide the essential toolkit for implementing various machine learning techniques.
Consequently, mastering these concepts opens doors to understanding sophisticated algorithms rather than treating them as mysterious black boxes. When applied correctly, these mathematical concepts help you transform raw data into meaningful insights, reduce dimensionality while preserving information, and build models that can effectively learn from patterns.
The journey to mastering linear algebra for machine learning might seem challenging at first, but the clarity and confidence it brings to your machine learning practice is certainly worth the effort. Good Luck!
FAQs
Q1. Why is linear algebra important for machine learning?
Linear algebra is crucial for machine learning as it provides the mathematical foundation for data representation, manipulation, and modeling. It enables efficient implementation of various algorithms, simplifies complex tasks like data transformation and dimensionality reduction, and is essential for understanding how machine learning models work.
Q2. What are the core linear algebra concepts every beginner should learn for machine learning?
The five essential concepts are: vectors and vector operations, matrices and matrix arithmetic, matrix factorization techniques, eigenvalues and eigenvectors, and linear equations and least squares. These form the building blocks for understanding and implementing machine learning algorithms.
Q3. How can I avoid common mistakes when learning linear algebra for machine learning?
To avoid common pitfalls, start with building intuition through visualizations before diving into abstract theory. Focus on practical examples and always connect mathematical concepts to machine learning applications. Avoid studying too much theory too early or learning without context.
Q4. What are some practical applications of linear algebra in machine learning?
Practical applications include Principal Component Analysis (PCA) for dimensionality reduction, linear regression using matrix operations, Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) for data compression and recommendation systems, and neural networks, which rely on matrix multiplication for efficient computations.
Q5. Are there any recommended resources for learning linear algebra for machine learning?
Many experts recommend starting with visual resources like 3Blue1Brown’s “Essence of Linear Algebra” YouTube series for building intuition. Gilbert Strang’s linear algebra course and textbook are also highly regarded. For a more direct connection to machine learning, some suggest books that specifically focus on linear algebra for machine learning and optimization.





























Did you enjoy this article?