
Get Ready with 52 Zoho Interview Questions for Success!
Dec 23, 2025 12 Min Read 2093 Views
(Last Updated)
Ever wondered what actually helps candidates stand out in a Zoho software developer interview? Here’s the thing: Zoho hires people who understand the fundamentals, think logically, and communicate clearly.
If you’re aiming to join their engineering team, you’ll want to walk in with more than surface-level prep. This article brings you 52 carefully chosen Zoho interview questions and answers, including technical and HR as well, so you can sharpen your problem-solving approach, revisit key concepts, and understand how Zoho evaluates you.
So, without further ado, let us get started!
Quick Answer:
To prepare for a Zoho software developer interview, focus on core programming fundamentals, practice common data structures and coding questions, and review key HR topics so you can explain your thinking clearly and solve problems with confidence.
Table of contents
- Technical Zoho Interview Questions and Answers
- Behavior and HR Zoho Interview Questions
- General HR Questions
- Zoho-Specific and Culture Questions
- Conclusion
Technical Zoho Interview Questions and Answers
Preparing for a Zoho interview can feel daunting, but you can boost your confidence by knowing what to expect. Its hiring process typically involves multiple rounds: written and coding tests to check your programming fundamentals (C/C++, OOPS, DBMS, algorithms), followed by technical interviews and finally HR rounds to assess fit and communication. Let’s dive in!
1. What is a data structure?
A data structure is a way of organising a collection of data to allow efficient access and operations. In other words, it defines how data is stored, accessed, and manipulated.
2. What is the difference between static and dynamic memory allocation?
Static memory allocation is done at compile-time: the size and storage are fixed (usually on the stack) and cannot change during program execution. Dynamic memory allocation happens at runtime: memory is requested from the heap and can be resized or freed when not needed.
3. ArrayList vs LinkedList: What are the key differences?
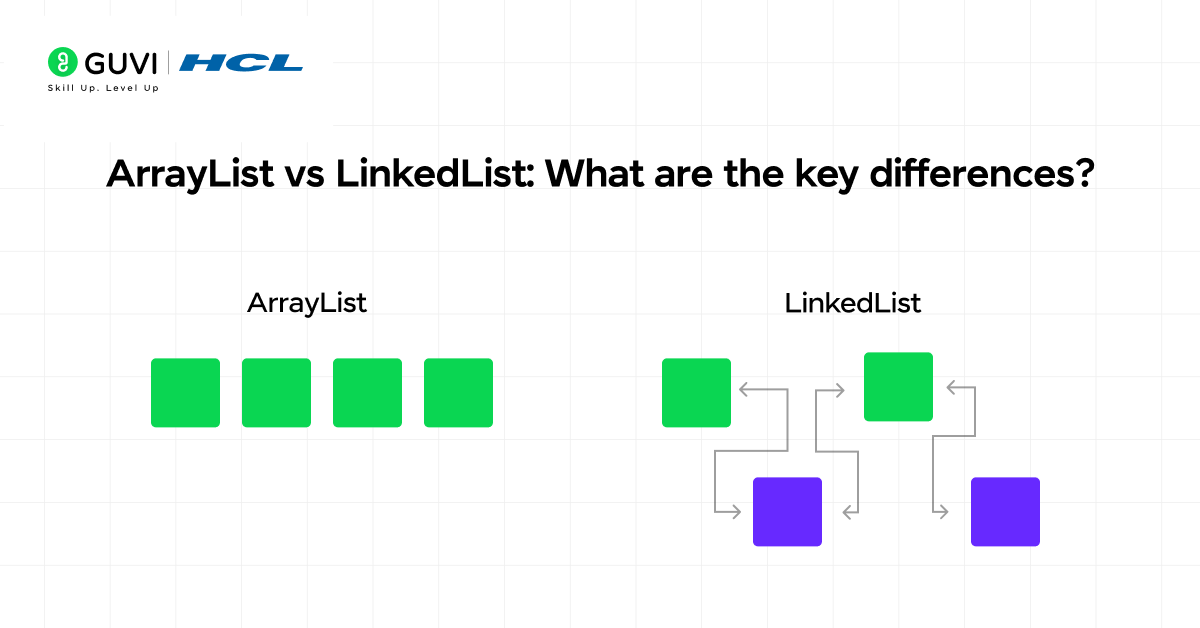
- ArrayList: Uses a contiguous dynamic array for storage. Good for fast random access by index (O(1) access time) and uses less memory overhead for pointers.
- LinkedList: Uses nodes that are linked by pointers. No contiguous memory is needed, and inserting or deleting a node (given a pointer to it) is fast (O(1)). But accessing by index is slower (O(n)) because you may have to traverse the list.
4. What is Bubble Sort?
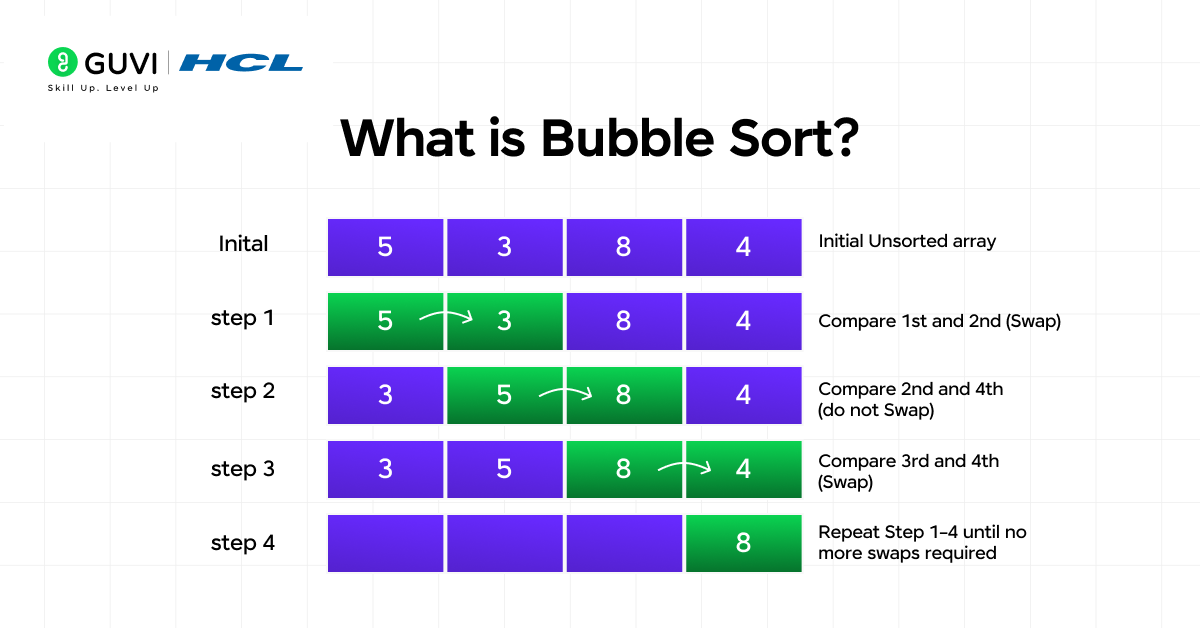
Bubble Sort is a simple comparison-based sorting algorithm. It repeatedly steps through the list, compares each pair of adjacent elements, and swaps them if they are in the wrong order. Each pass “bubbles” the largest unsorted element toward its correct position at the end.
5. What are the basic principles of Object-Oriented Programming (OOP)?
OOP is based on the idea of objects (data plus methods). The four core principles are:
- Encapsulation: Grouping data (attributes) and methods (functions) into a single class; internal details are hidden from outside.
- Abstraction: Hiding complex implementation details and exposing only relevant features. This lets users interact with an object through a simple interface.
- Inheritance: A mechanism where a new class (child) inherits attributes and behaviors (methods) from an existing class (parent), promoting code reuse.
- Polymorphism: The ability of different classes to be treated as instances of the same parent class, often by overriding methods. In simple terms, one interface (like a method name) can have multiple implementations (e.g., method overloading or overriding).
6. How would you reverse a string in C?
One simple way is to use the strrev() function (in C99, you may implement it manually if not available). For example:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main() {
char str[100];
scanf("%s", str);
printf("%s", strrev(str)); // reverses string in place
return 0;
}This program reads a string and prints it reversed. Internally, strrev swaps characters from the ends inward. (If strrev isn’t available, you can swap characters manually by looping from start and end pointers.)
7. In what way is a stack different from a queue?
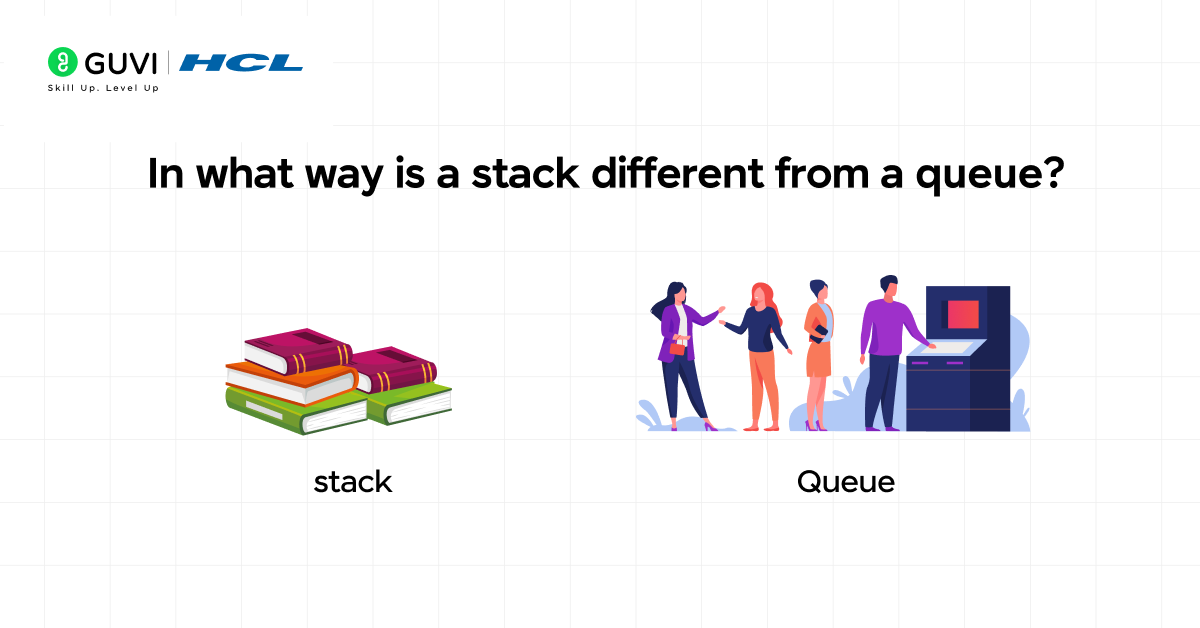
- Stack: Follows Last-In First-Out (LIFO) order. You push elements onto the top and pop from the top. Think of a stack of plates: the last plate placed is the first you remove.
- Queue: Follows First-In First-Out (FIFO) order. You enqueue at the rear and dequeue from the front. Think of a line of people: the first person in line is served first. Queues are used in scheduling and buffers.
8. Define “pass by value” vs “pass by reference”.
- Pass by Value: The function gets a copy of the variable. Changes made to the parameter inside the function do not affect the original variable. Most languages (e.g. Java for primitives, C for basic types) use pass-by-value.
- Pass by Reference: The function gets a reference (or pointer) to the actual variable. Changes to the parameter inside the function affect the original. C++ can use pass-by-reference (using &), and C uses pointers to simulate it.
9. What is inheritance in OOP?
Inheritance lets a class (child) inherit fields and methods from another class (parent), enabling code reuse and logical hierarchy. For example, a Dog class can inherit from an Animal class. In code, Dog extends Animal means Dog automatically has Animal’s properties (like sound() method). The child class can override or extend the parent behavior.
10. When would a linked list be better than an array?
Linked lists are superior when you need frequent insertions or deletions of elements, especially at arbitrary positions. Unlike arrays (which have a fixed size and contiguous memory), a linked list can easily grow or shrink. Inserting/deleting a node only involves updating a couple of pointers (O(1) time) if you have the reference.
Arrays or ArrayLists would require shifting elements (O(n) cost). Linked lists are also more memory-efficient if you don’t know the number of elements up front. However, arrays offer faster random access by index, so use a linked list when dynamic size and fast insert/delete are priorities.
If you want to learn Data Structures and Algorithms and ace the Zoho interview, consider enrolling in HCL GUVI’s Data Structures and Algorithms Course with Python – IIT-M Pravartak Certified which includes four in-depth courses across Python, Java, C, and JavaScript. It also helps you to master algorithmic problem-solving and prepare for technical interviews with industry-grade certification!
11. What is the purpose of the final keyword in Java?
In Java, final can be applied to variables, methods, or classes:
- Final variable: The value cannot change once assigned (it becomes a constant).
- Final method: The method cannot be overridden by subclasses.
- Final class: The class cannot be subclassed.
For example, final int MAX = 100; means MAX will always be 100. Using final helps you prevent accidental changes and enforce design constraints.
12. What are pointers in C?
A pointer is a variable that holds the memory address of another variable. For example, int *ptr = &x; stores the address of x in ptr. Pointers allow direct memory access and manipulation (important for dynamic memory and data structures like linked lists).
13. What is the difference between == and equals() in Java?
- == operator: Compares object references (i.e. checks if two references point to the same memory location). For objects (like String), == is true only if both variables reference the same object.
- equals() method: Compares the contents or state of objects. For example, str1.equals(str2) checks whether two strings have the same sequence of characters, even if they are different objects. (By default, equals() in Object does reference comparison, but many classes like String override it to compare values.)
14. What’s the difference between String, StringBuffer, and StringBuilder in Java?
- String: Immutable sequence of characters. Once created, its contents cannot change. Any modification to a String (concatenation, etc.) creates a new object.
- StringBuffer: A Mutable sequence of characters. It can be modified (append, insert, etc.) without creating new objects, and it is thread-safe (synchronized), making it slower.
- StringBuilder: Similar to StringBuffer (mutable), but not synchronized (not thread-safe), so it’s faster for single-threaded use. Use String for constant text, StringBuilder for efficient string manipulation in most cases, and StringBuffer when you need thread safety.
15. Why use the super keyword in Java?
The super keyword refers to the parent (super) class of the current object. You use it to:
- Invoke a parent class constructor: super(); must be the first line in a child’s constructor.
- Call a parent class method that the child has overridden (e.g., super.methodName() to use the parent implementation).
- Access parent class fields that are hidden by child fields. For example, if Dog extends Animal and both have a sound() method, inside Dog you can call super.sound() to run the Animal version first. This is useful for reusing or extending parent behavior.
16. What is a deadlock (in operating systems)?
A deadlock is a situation where two or more threads or processes are each waiting for the other to release resources, so none can proceed. For example, Thread A holds lock X and waits for lock Y; Thread B holds lock Y and waits for lock X. Both are stuck indefinitely. Deadlocks can occur with multiple locks or resources. To avoid deadlocks, ensure a consistent order of lock acquisition or use lock-free algorithms.
17. How is throw different from throws in Java?
- throw: Used inside a method to actually throw an exception instance. Example: throw new IOException(“Error”);.
- throws: Used in a method signature to declare that the method might throw certain exceptions, passing responsibility to the caller. Example: void readFile() throws IOException { … }.
In summary, throw launches an exception in code, while throws tells callers to handle the possibility of that exception.
18. What is the purpose of the this keyword in Java?
The this keyword refers to the current object instance. You use this to distinguish between instance variables and local variables when they have the same name. For example:
class MyClass {
int num;
MyClass(int num) {
this.num = num; // 'this.num' is the field, 'num' is the parameter
}
}Here, this.num refers to the field of the class, while num is the constructor’s parameter. You can also use this() to call another constructor in the same class (constructor chaining).
19. Why is the finally block significant in Java?
In a try-catch statement, the finally block (if present) is guaranteed to execute whether or not an exception is thrown. It’s typically used for cleanup: releasing resources like closing files, database connections, or network sockets.
Code in finally runs after the try and any matching catch, even if an exception propagates. This ensures that important cleanup tasks happen. For example, if you open a file in try, you would close it in finally, to avoid resource leaks.
20. What is the difference between a class and an interface in Java?
- Class: A blueprint for creating objects. It can have concrete methods (with code), instance variables, and can be instantiated (unless it’s abstract). Example: class Car { … }.
- Interface: A contract that declares methods without implementations (before Java 8, all methods were abstract). A class implements an interface and must provide the method bodies. Interfaces can have default and static methods (with code) in newer Java versions. Unlike classes, interfaces cannot hold instance fields (only constants). You can inherit from one class but implement multiple interfaces.
21. Why use the static keyword in Java?
The static keyword means the member belongs to the class itself, not to any particular instance.
- Static variable: A single copy is shared by all instances. For example, static int count is the same for every object.
- Static method: Can be called without creating an instance (ClassName.method()), since it doesn’t operate on instance data.
22. What is a constructor in Java?
A constructor is a special method that is called when a new object is created. It has the same name as the class and no return type. The constructor initializes the new object’s fields. Java provides a default (no-argument) constructor if you don’t define one. You can also define parameterized constructors to set fields on creation. Example:
class Student {
String name;
Student(String name) {
this.name = name; // initialize the field
}
}When you do a new Student(“Alice”);, the constructor sets the name to “Alice”.
23. What is multithreading?
Multithreading is the ability of a program (especially in languages like Java, C++, or Python) to execute multiple threads of execution concurrently. A thread is a lightweight process; multithreading allows a CPU to perform multiple tasks at once (concurrently or in parallel on multi-core systems).
24. How does malloc differ from calloc in C?
Both functions allocate memory on the heap, but:
- malloc(size) allocates a block of memory of size bytes. The content of the newly allocated memory is uninitialized (it contains garbage).
- calloc(n, size) allocates memory for an array of n elements, each of size bytes, and initializes all bits to zero (so for primitive types, values are 0).
Example: malloc(10 * sizeof(int)) vs calloc(10, sizeof(int)). Use calloc when you want zero-initialized memory.
25. What is polymorphism in C++?
Polymorphism (literally “many shapes”) in C++ (and OOP) means that a single function or operator can work in different ways depending on context. There are two main types:
- Compile-time polymorphism: Achieved through function overloading (same function name, different parameters) or operator overloading. The compiler decides which function to use based on argument types.
- Run-time polymorphism: Achieved through inheritance and virtual functions. A base class pointer or reference can call a derived class method. The actual method invoked depends on the object’s runtime type (late binding).
26. How can you find the intersection of two integer arrays?
One approach is to use a hash set for fast lookup. For example (in Java-like pseudocode):
put all elements of array1 into a HashSet;
for each element x in array2:
if HashSet contains x, add x to result list.This way, each element of the first array is stored uniquely, and then checking membership from the second array is fast (O(1) average). The result will be the common elements. This approach is O(n) time (assuming hashing) and uses extra space for the set.
27. How do you find duplicates in an array?
A simple way is to use a hash set to track seen elements. For example:
create an empty HashSet seen;
for each element x in array:
if seen contains x, print or store x (duplicate found);
else add x to seen.This identifies duplicates in one pass through the array (O(n) time). Alternatively, you could sort the array first (O(n log n)) and then check adjacent elements for equality, but using a set is more direct if extra space is allowed.
If you want to know more about web development, consider enrolling in a professionally certified online Full Stack Development Course by a recognized institution that can also offer you an industry-grade certificate that boosts your resume.
Behavior and HR Zoho Interview Questions
General HR Questions
28. Tell me about yourself.
Start with a brief introduction of your background, education, and experience relevant to the role. Highlight a couple of strengths or projects (e.g., “I’m Alice, a recent CS graduate who interned at XYZ on a Java project…”). Focus on aspects that relate to the job: your skills, accomplishments, and what motivates you. Keep it concise (1–2 minutes) and end with why you’re excited about this Zoho opportunity.
29. Why do you want to work at Zoho?
Mention specific reasons that show you’ve done your research. For example, you might say: “I admire Zoho’s reputation for building comprehensive, user-friendly software (like Zoho CRM and Zoho Mail). I’m excited by the challenge of solving complex business problems as part of a product-focused team. Zoho’s culture of innovation and global reach (with 55+ apps and millions of users) really interests me. I feel my technical skills and passion for learning would fit well here.”
30. What skills do you bring to this role?
Describe your relevant technical and soft skills. For a software developer role, mention programming languages you know (Java, C/C++, Python, etc.), and key areas like data structures, algorithms, databases, or frameworks you’ve used. Also include problem-solving ability, teamwork, or communication skills. For example: “I’m proficient in Java and C++, and I’ve built projects using OOP and MVC frameworks. I have strong problem-solving skills (as shown by solving coding challenges in my last internship) and I work well in teams. I’m eager to apply these skills at Zoho.”
31. Where do you see yourself in 5 years?
Frame your future goals in a way that aligns with growth at Zoho. For example: “In five years, I hope to have grown into a senior developer role, having learned deeply about our product domain and taken on more responsibilities. I’d like to master new technologies and contribute to key projects, maybe even mentor others. I see myself continuously learning and adding value, and ideally taking part in larger design decisions.”
32. What are your strengths and weaknesses?
For strengths, pick a few that match the job: e.g., “strong coding skills, quick learner, good communicator, or attention to detail.” Give a brief example of a strength in action. For weaknesses, choose something real but not critical (and show how you’re improving). For example: “I tend to be a perfectionist with my code, which used to slow me down; but I’ve learned to set better time limits and trust code reviews. I’m also working on public speaking by giving team presentations.”
33. Describe a challenging problem you faced and how you handled it.
Use the STAR method (Situation, Task, Action, Result). Pick a concrete example (preferably technical or project-related). For instance: “At my internship, I had to integrate two software modules that used incompatible data formats. I met with my team to brainstorm solutions. We decided to write a data adapter class to convert formats. I implemented the adapter, tested it thoroughly, and documented it. In the end, the modules worked together seamlessly, and we saved the project timeline. This taught me the value of communication and iterative testing.”
34. How do you handle stress or tight deadlines?
Show that you stay organized and calm. For example: “I prioritize tasks and break them into manageable pieces. When under a deadline, I plan my time carefully and communicate early if there are risks. I stay focused, and I try to maintain a work-life balance so I don’t burn out. In school, when project deadlines piled up, I used lists and set mini-deadlines for myself. This helped me submit all projects on time without sacrificing quality.”
35. Why should we hire you?
Summarize why your background and skills make you a good fit. For example: “You should hire me because I have a solid foundation in [relevant skills], proven by [projects or experiences], and I’m passionate about learning. I work well in teams and take ownership of my work. Specifically, I bring strong problem-solving abilities and a willingness to adapt, traits I know are valued at Zoho. I’m excited to contribute to your team’s success and grow with the company.”
36. What motivates you to work hard?
Be genuine. You might say: “I’m motivated by solving challenging problems and seeing the impact of my work. Learning new technologies and improving my skills drives me. For example, I enjoy debugging tough issues and the satisfaction of getting them resolved. Also, contributing to a team’s success and achieving shared goals (like completing a big project) really motivates me.”
37. Can you describe a time you worked as part of a team?
Give a brief example of teamwork. For example: “In my final year project, I led a team of four to build a web app. My responsibility was the back-end logic and database. I coordinated closely with the front-end developer. When we ran into integration bugs, I organised a meeting, we debugged together, and I documented the fixes. In the end, we delivered the project on time. This taught me the importance of clear communication and collaboration.”
38. How do you stay up to date with new technology trends?
Show you’re proactive about learning. For example: “I regularly read tech blogs and articles, participate in online coding communities, and take MOOCs on new topics. I follow open-source projects and try out new languages or frameworks in small personal projects. For instance, I recently completed a course on machine learning and implemented a small project to practice.” This demonstrates enthusiasm for continuous learning.
39. Do you have any questions for us?
Always have a couple of questions prepared. Good questions could be about the role (“What does a typical day look like for a developer here?”), team structure (“What technologies is this team currently using?”), or company culture (“How does Zoho support professional growth?”). Asking shows you’re interested and have thought about where you’d fit in.
Zoho-Specific and Culture Questions
40. What do you know about Zoho’s products or culture?
Zoho offers a wide range of cloud-based business software (CRM, office suite, finance, etc.) across 55+ categories. It’s known for being bootstrapped, profitable, and customer-focused. You can mention Zoho’s emphasis on privacy (no ads on products) or that it has a global user base..
41. How do you prioritize your tasks?
Describe your approach to organization. For example: “I typically make a list of tasks and identify their deadlines and importance. I tackle high-priority or time-sensitive items first, and break large tasks into smaller steps with mini-deadlines. I use tools like calendars or to-do lists to track progress. If new tasks arise, I reassess priorities accordingly. This keeps me efficient even under a workload.”
42. What are your salary expectations?
It’s best to be prepared but realistic. If asked, you can say you’re flexible: “My main focus is finding the right role. Based on my research and the market rate for this position, I’d expect something in the range of [provide a range if comfortable]. However, I’m open to discussion, as I value the growth and learning opportunities here.”
43. Are you willing to relocate or travel if needed?
Be honest. If you’re open, say so: “Yes, I am open to relocating. I understand Zoho has offices in [locations], and I’m flexible if relocation is needed.” If you are not willing, you can say, “I would prefer a location close to [your location], but I am willing to discuss possibilities.” Zoho values transparency, so answer based on your situation.
44. Tell me about a time you failed or made a mistake. How did you handle it?
Pick a brief example where you learned something. For instance: “In one project, I underestimated the time needed for a feature and missed a deadline. I owned up to it, analyzed what went wrong, and communicated early with my mentor. I then re-prioritised remaining tasks and worked extra hours to catch up. The feature was delivered, and I learned to plan more buffer time and ask for help sooner. This experience taught me better time management and honesty in communication.”
45. What leadership qualities do you have?
Even as a junior, you can talk about initiative and teamwork. For example: “I show leadership by taking initiative on projects (like volunteering for difficult tasks) and helping teammates. In my project, I organized our workflow and ensured communication. I also listen to others’ ideas and coordinate efforts. For example, when a teammate was stuck, I offered to work on his task so we could meet our deadline. This kind of collaborative leadership is how I’d contribute at Zoho.”
46. Describe a project or accomplishment that you are proud of.
Pick a specific example, preferably technical. For instance: “I’m proud of a web app I built for class where I led a small team. We designed it from scratch (choosing the tech stack, setting up a database). My code optimized a core algorithm, improving performance. The final app was used by my department and received positive feedback. I’m proud because I learned a lot about end-to-end development and teamwork, and it boosted my confidence in taking ownership of a project.”
47. What is your process for learning a new programming language or technology?
Outline how you approach learning. For example: “I usually start with official tutorials or documentation to get fundamentals. Then I build a small project or solve practice problems to apply what I’ve learned. I also read blogs or watch videos for best practices. Finally, I review code examples from experienced developers (on GitHub, for instance). This hands-on approach helps me learn deeply. I also reflect on what patterns or concepts are similar to languages I know.”
48. Why are you leaving (or did you leave) your current job/studies?
Keep this positive and forward-looking. If you’re a fresher, focus on your future: “I recently graduated (or completed my degree), and I’m looking for a challenging first role where I can grow. I chose to interview at Zoho because I want to work on meaningful products.” If switching jobs: “I’ve learned a lot in my current role, but I’m looking for new challenges and opportunities to develop my skills further, ideally in a product-focused environment like Zoho.” Avoid speaking negatively about past employers or colleagues.
49. How would you handle a conflict with a coworker?
Stress communication and problem-solving. You might say: “I would first try to discuss the issue privately and calmly, listening to their perspective and explaining mine. I believe in finding common ground. If needed, I’d involve a supervisor or use formal conflict resolution channels. For example, in a past group project, two team members disagreed on the design. I helped mediate by asking each to list pros/cons. We eventually combined the best parts. Maintaining professionalism and focusing on the project goals is key.”
50. What is your approach to code reviews?
Show that you welcome feedback and strive for quality. For example: “I see code reviews as an important learning opportunity. When someone reviews my code, I listen and ask questions to understand their suggestions. I appreciate constructive feedback, as it helps improve code quality and learning. When reviewing others’ code, I try to be respectful and clear, focusing on logic, style, and potential issues, not personal comments. In this way, the team’s codebase gets better and we all grow as developers.”
51. Tell us about a time you had to learn something quickly.
Choose a brief example. For instance: “During an internship, I was given a task to work with a new web framework I had never used. I dedicated a weekend to studying the documentation and tutorials. Then I built a small demo app to practice. By Monday, I was able to confidently make the requested changes in the real project. This showed that I’m resourceful and can quickly ramp up on new technologies when needed.”
52. Do you have any questions about Zoho or the role?
This is a chance to ask about things you genuinely want to know: team projects, growth paths, or specifics of the job duties. For example: “I’d love to know what challenges this team is currently facing and how a new hire could help solve them.” This shows your interest and engagement.
If you are still clueless on how to prepare for an interview, read the blog – How to Prepare for an Interview
Zoho is one of the world’s largest bootstrapped tech companies, meaning it scaled to millions of users without taking a single rupee of external funding. Their interview process reflects this mindset too, they focus heavily on strong fundamentals rather than flashy résumés. Many of their engineers were hired straight from campus because they showed clear thinking, solid problem-solving skills, and the ability to learn fast.
Conclusion
In conclusion, you’ve now walked through the types of questions Zoho asks, why they ask them, and how you can frame your answers with clarity and confidence. What this really means is that you’re no longer preparing blindly; you know the core areas that matter and the thinking style Zoho looks for.
Keep practicing these questions, revisit your fundamentals, and try explaining each answer in your own words. When you show both competence and curiosity in the interview, you make it easier for the panel to see you as someone who’ll thrive at Zoho. Step in prepared, stay calm, and let your work speak for you. You’ve got this.




































Did you enjoy this article?