Ever wondered why Python throws an error just because of a few extra spaces? That small detail is indentation in Python, and it plays a bigger role than most beginners expect.
In this blog, you will learn what indentation in Python really means, why it is mandatory, where it is used, common mistakes beginners make, and simple best practices to follow. By the end, you will be confident in writing clean, properly structured Python code without indentation errors.
Quick Answer
Indentation in Python refers to the spaces at the beginning of a line that define how code blocks are structured. Python uses indentation instead of brackets to understand which lines belong together. Without proper indentation in Python, programs will either fail or behave incorrectly.
Table of contents
- What Indentation Means In Python
- Why Indentation Is Mandatory In Python
- Where Indentation Is Used In Python
- Common Indentation Mistakes Beginners Make
- Best Practices For Indentation In Python
- 💡 Did You Know?
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- What Happens If Indentation Is Incorrect In Python?
- How Many Spaces Should Be Used For Indentation In Python?
- Can Tabs Be Used Instead Of Spaces?
- Why Does Python Use Indentation Instead Of Braces?
- Is Indentation Required In Functions, Loops, And Conditions?
What Indentation Means In Python
Indentation in Python simply means adding spaces at the beginning of a line to show that the line belongs to a specific block of code. Python uses indentation to understand structure, such as which statements are inside a condition, loop, function, or class.
Unlike many other programming languages, Python does not use curly brackets to group code. Instead, indentation in Python visually and logically connects related lines. This makes Python code easier to read, but it also means indentation must be correct for the program to work.
Key Points
- Block Identification: Indentation tells Python which lines belong to the same block.
- Syntax Rule: Indentation is not optional; it is part of Python’s syntax.
- Readable Structure: Code structure becomes clear just by looking at the spacing.
- Beginner-Friendly Design: Helps learners understand program flow visually.
Coding Example
age = 18
if age >= 18:
print("You are eligible to vote")
print("Please carry your ID")
print("Program finished")
In this example, the if condition checks whether the age is 18 or above. The two print statements that are indented below the if condition belong to that condition. This means they will run only when the condition is true. The last print statement is not indented, so it is outside the if block. This line will run no matter whether the condition is true or false.
Python understands all this purely because of indentation. If the indentation is removed or placed incorrectly, Python will either throw an error or change the program’s behavior. This clearly shows how indentation in Python defines which lines are grouped and how the program flows.
Do check out HCL GUVI’s Python Hub for more tutorials, examples, and resources to practice indentation in Python, helping you build strong coding habits and confidence in real-world
Why Indentation Is Mandatory In Python
Indentation in Python is mandatory because the language uses it to understand the structure and flow of a program. Instead of using brackets to group code, Python relies entirely on indentation to decide which statements belong together.
When Python sees a colon at the end of a statement like if, for, while, function, or class, it expects the next line to be indented. This tells Python that a new block has started. If indentation is missing or inconsistent, Python cannot interpret the code correctly and raises an error.
Key Points
- Defines Code Blocks: Indentation tells Python where a block starts and ends.
- Controls Program Flow: Determines which lines run under conditions and loops.
- Strict Syntax Rule: Even small indentation mistakes cause errors.
- Improves Code Clarity: Makes Python programs easy to read and maintain.
Where Indentation Is Used In Python
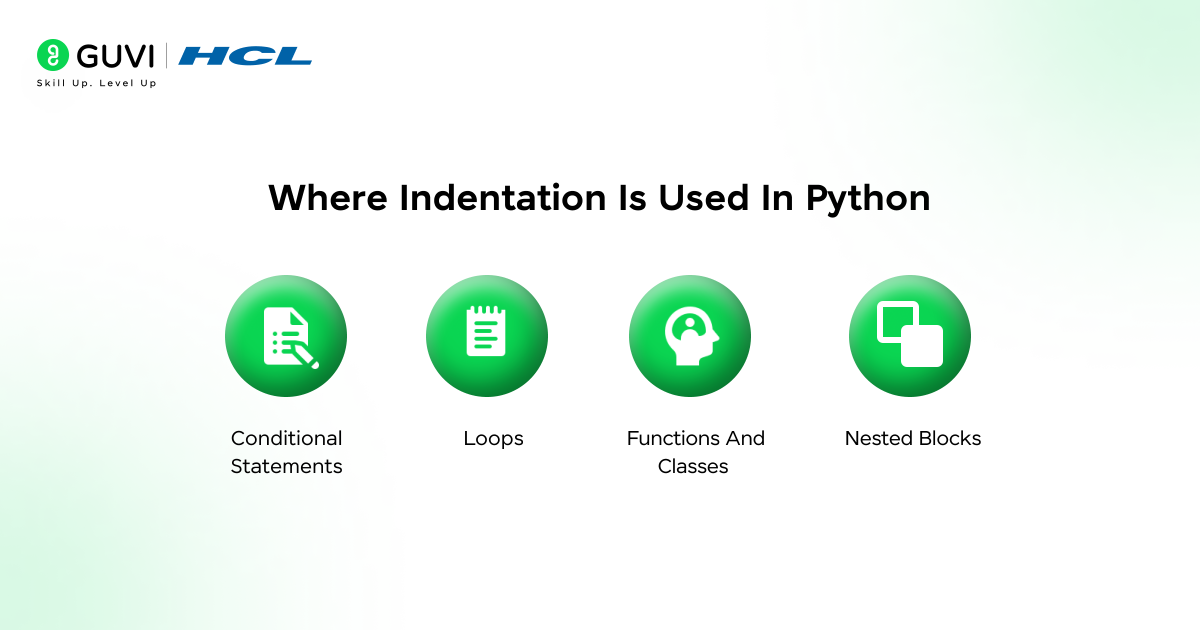
Indentation in Python is used wherever a block of code needs to be grouped. Any statement that ends with a colon expects the following lines to be indented, showing that they belong to that block.
Beginners usually encounter indentation first in conditions and loops, but it is also required in functions and classes. As code becomes more complex, indentation helps show nested logic clearly and keeps the program structured.
1. Conditional Statements: Used in if, elif, and else blocks.
age = 20
if age >= 18:
print("Adult")
else:
print("Minor")
Here, indentation tells Python which print statement runs under the if condition and which one runs under else.
2. Loops: Required in for and while loops.
for i in range(3):
print("Hello")
The indented line runs repeatedly because it belongs to the loop block.
3. Functions And Classes: All internal code must be indented.
def greet():
print("Welcome")
print("Have a nice day")
Both print statements are indented, so they execute when the function is called.
4. Nested Blocks: Each new level requires additional indentation.
number = 5
if number > 0:
if number % 2 == 0:
print("Positive even number")
else:
print("Positive odd number")
Here, a deeper indentation shows one condition placed inside another.
Common Indentation Mistakes Beginners Make
Many beginners find indentation in Python confusing at first because even a small spacing mistake can break the program. Most indentation errors happen due to a lack of consistency or a misunderstanding of how blocks are formed.
Understanding these common mistakes helps beginners avoid errors and write cleaner, more reliable Python code.
1. Mixing Tabs And Spaces: Using tabs in some places and spaces in others causes indentation errors.
if True:
print("Hello")
print("World")
Here, mixing a tab and spaces confuses Python and results in an indentation error.
2. Missing Indentation After Colon: Forgetting to indent a block after statements like if or for leads to syntax errors.
if True:
print("Hello")
Python expects an indented line after the colon, so this code will not run.
3. Over-Indenting Code: Adding extra indentation changes program logic unintentionally.
if True:
print("Start")
print("End")
The extra indentation makes Python treat the second print as invalid, causing an error.
4. Inconsistent Indentation Levels: Uneven spacing across lines breaks block structure.
for i in range(2):
print(i)
print("Done")
The last line is not aligned with the loop block, so Python raises an error.
Do check out HCL GUVI’s online Python IDE that lets you write and test Python code in your browser instantly, helping you practice indentation in Python and see real results as you learn.
Best Practices For Indentation In Python

Using proper indentation in Python is not just about avoiding errors. It also makes your code clean, readable, and easy to maintain. Following simple best practices helps beginners write structured programs and reduces confusion as code gets more complex.
Best Practices
- Use Four Spaces: Standard Python practice is four spaces per indentation level for consistency.
- Do Not Mix Tabs And Spaces: Mixing tabs and spaces can cause hidden errors that are hard to debug.
- Be Consistent Across The File: Ensure all blocks follow the same indentation pattern for readability.
- Use A Code Editor: Editors help manage indentation automatically and prevent mistakes.
- Avoid Overly Deep Nesting: Keep nested blocks simple to maintain code clarity.
- Align Continuation Lines Properly: Indent multi-line statements consistently for readability.
- Indent Inside Functions And Classes: Always indent internal code to clearly define scope.
- Check Nested Blocks Carefully: Each new block level should have additional indentation to avoid errors.
Do check out HCL GUVI’s Python Course if this blog on what is indentation in Python helped you understand how proper spacing controls program flow. While this article explains the concept clearly, a structured course like this helps you practice indentation in Python through hands-on coding, real-world examples, and guided lessons that strengthen your programming fundamentals.
💡 Did You Know?
- Python’s strict indentation rule was inspired by the language ABC, which aimed to make code visually structured and beginner-friendly.
- In Python, even empty blocks require proper indentation using the pass statement to avoid errors.
- Consistent indentation can actually improve performance slightly because Python’s interpreter reads blocks more efficiently when the structure is clear.
Conclusion
Indentation in Python is more than just a style choice. It is a fundamental part of the language that defines how your code runs and ensures programs are structured, readable, and free from syntax errors.
By following simple best practices and understanding where and how indentation is used, beginners can write clean Python code with confidence. Mastering indentation lays a strong foundation for learning advanced Python concepts and building real-world applications.
FAQs
1. What Happens If Indentation Is Incorrect In Python?
Python will raise an indentation error and stop the program from running.
2. How Many Spaces Should Be Used For Indentation In Python?
The standard practice is to use four spaces for each level of indentation.
3. Can Tabs Be Used Instead Of Spaces?
Tabs can be used, but mixing tabs and spaces is strongly discouraged as it causes errors.
4. Why Does Python Use Indentation Instead Of Braces?
Python uses indentation to keep code clean, readable, and structured by default.
5. Is Indentation Required In Functions, Loops, And Conditions?
Yes, all blocks in Python, including functions, loops, and conditional statements, require proper indentation.


























Did you enjoy this article?