
What is Data Archiving? Definitions, Examples and Benefits
Nov 21, 2025 6 Min Read 819 Views
(Last Updated)
In today’s digital world, businesses generate massive amounts of data every day—from customer transactions and emails to reports, logs, and multimedia files. Managing this data efficiently is essential for reducing storage costs, improving system performance, and ensuring compliance with regulations.
In this blog, we’ll explore key topics such as the types of data archiving, real-life applications across industries, benefits for businesses, best practices, tools and technologies, common challenges, and future trends. By understanding these concepts, you’ll learn how to handle data more effectively, make smarter business decisions, and optimize long-term storage strategies.
Table of contents
- What Is Data Archiving
- Key Concepts of Data Archiving
- Types of Data Archiving
- On-Premises Archiving
- Cloud Archiving
- Hybrid Archiving
- Real-Life Applications of Data Archiving
- Benefits of Data Archiving
- Data Archiving Best Practices
- Tools and Technologies for Data Archiving
- Challenges in Data Archiving
- Future of Data Archiving
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- What is the difference between data archiving and data backup?
- How long should data be archived?
- Can archived data be accessed quickly?
- Is cloud archiving secure?
- What types of data should be archived?
What Is Data Archiving
Data archiving is the process of securely storing older or less frequently used data in a way that keeps it organized and easily accessible when needed. Unlike backups, which are mainly for recovering data after a system failure, archived data is kept for long-term use, compliance, and reference.
Example: A bank might move transaction records older than five years to archived storage. These records are not needed for everyday operations but must be available for audits or regulatory checks.
Want to improve your data management skills step by step? Our 5-Day Free Data Science Email Series delivers bite-sized lessons on archiving strategies, best practices, and real-world applications directly to your inbox, helping you apply these concepts effectively in your work.
Key Concepts of Data Archiving
Successfully managing archived data isn’t just about storing it but also about organizing, protecting, and using it effectively. To get the most value from archived information, businesses need to understand the core principles that govern data archiving. These concepts ensure data is secure, compliant with regulations, and easy to access when needed, supporting smarter business decisions and cost-efficient storage strategies.
- Retention Policies: Guidelines that define how long different types of data should be stored before deletion. Clear retention rules help businesses manage storage costs and comply with regulations.
- Data Lifecycle Management: The process of tracking data from its creation to final archival. This ensures that data moves efficiently through its lifecycle without being lost or forgotten.
- Access Control: Mechanisms to ensure archived data is secure and only accessible to authorized users. Proper access control protects sensitive information from breaches.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to legal and industry-specific standards for storing and protecting data. Compliance prevents legal penalties and ensures accountability.
Deepen your knowledge of data archiving with HCL GUVI’s Data Science eBook, covering key topics like Python, R, data cleaning, exploratory data analysis, machine learning, data visualization, big data tools, NLP, and data privacy to improve your skills and knowledge.
Types of Data Archiving
Data archiving comes in different forms depending on an organization’s storage needs, accessibility requirements, and security priorities. Choosing the right type helps businesses manage inactive or historical data efficiently while reducing costs and ensuring compliance. The main types of data archiving are:
- On-Premises Archiving
- Cloud Archiving
- Hybrid Archiving
1. On-Premises Archiving
If control and security are the most important factors, on-premises archiving is ideal. In this method, data is stored internally on servers, storage arrays, or tape libraries, giving organizations full control over access and storage.
Key Features:
- Complete control over security and access
- Customizable storage setup
- Easier internal compliance management
Example: A law firm archives sensitive client contracts on internal servers to maintain confidentiality and secure access.
2. Cloud Archiving
For businesses that need flexibility and scalability, cloud archiving provides a modern solution. Data is stored on remote servers managed by cloud providers, allowing organizations to scale storage as needed while reducing the costs and maintenance associated with on-premises storage.
Key Features:
- Scalable and cost-efficient storage
- Remote access from anywhere
- Automated backup and redundancy
Example: A media company stores archived video content on AWS Glacier to save costs while ensuring long-term accessibility.
3. Hybrid Archiving
Hybrid archiving combines the benefits of both on-premises and cloud storage, providing a balance of security, accessibility, and cost-efficiency. Frequently used data remains on local servers, while older or less critical data is moved to the cloud for long-term storage.
Key Features:
- Optimized storage costs
- Secure local storage for sensitive data
- Cloud scalability for older or large datasets
Example: An e-commerce company keeps active sales records on local servers for daily operations but archives older transactions in Google Cloud Archive to save storage costs.
Real-Life Applications of Data Archiving

Data archiving plays a vital role across industries by helping organizations manage historical information, meet compliance standards, and optimize storage. From finance to healthcare and education, archiving ensures that critical data remains secure and accessible when needed. Let’s explore some real-world applications across various sectors.
1. Financial Services
In the financial sector, every transaction and report needs to be stored securely for auditing and compliance purposes. Data archiving helps institutions maintain years of transaction records without overwhelming their primary systems.
Key Features:
- Ensures compliance with financial regulations
- Improves audit readiness
- Reduces storage costs for inactive records
Example: A bank archives transaction data older than seven years in a secure, compliant storage system to meet regulatory requirements and simplify audits.
2. Healthcare
Healthcare organizations handle massive amounts of patient data, including medical records, lab results, and treatment histories. Data archiving ensures these records are preserved for legal, research, and reference purposes.
Key Features:
- Long-term preservation of patient data
- Compliance with healthcare regulations (e.g., HIPAA)
- Easy retrieval of old medical records
Example: A hospital archives patient records after treatment completion to comply with data retention laws while keeping them accessible for future medical references.
3. Education and Research
Universities and research institutions generate large volumes of academic papers, student data, and research results. Archiving helps manage this information efficiently and ensures knowledge is preserved for future use.
Key Features:
- Secure long-term storage of academic and research data
- Efficient retrieval for future studies
- Reduced load on active databases
Example: A university archives completed research projects and student thesis papers on a cloud-based system to free up server space while keeping them accessible for academic review.
4. Government and Public Sector
Government agencies deal with huge volumes of records, including citizen data, administrative files, and legal documents. Archiving helps ensure transparency, compliance, and long-term access to public records.
Key Features:
- Compliance with data retention policies
- Enhanced data security and traceability
- Streamlined access to historical records
Example: A municipal office archives citizen records and old case files to comply with record retention laws while making them easily retrievable for audits.
5. Media and Entertainment
With digital content growing exponentially, media companies rely on archiving to store old video footage, photos, and creative assets. This enables easy retrieval for repurposing or reuse in future projects.
Key Features:
- Cost-effective storage for large media files
- Quick retrieval for future productions
- Enhanced data organization and cataloging
Example: A television studio archives past shows and promotional videos on cloud platforms like Google Cloud Archive to manage storage costs while maintaining accessibility.
Benefits of Data Archiving
Data archiving offers several advantages that go beyond simple storage management. It helps organizations save costs, meet compliance requirements, and improve data governance. Whether in finance, healthcare, or IT, these benefits make archiving an essential part of modern data strategies.
1. Cost Efficiency
By moving inactive data to low-cost storage systems, organizations reduce the burden on expensive primary storage. This approach optimizes IT budgets and allows faster access to active data.
Key Features:
- Frees up primary storage space
- Lowers hardware and maintenance expenses
- Reduces overall data management costs
Example: A retail company archives past sales data to cloud storage, cutting storage costs by 40% while keeping critical records safe and accessible.
2. Regulatory Compliance
Many industries are governed by strict data retention laws. Data archiving ensures that information is stored securely for the legally required duration and can be easily retrieved during audits.
Key Features:
- Meets industry-specific retention policies
- Simplifies data retrieval during audits
- Reduces compliance-related risks
Example: A healthcare provider archives patient data as per HIPAA guidelines, ensuring it remains accessible and protected against unauthorized access.
3. Enhanced Data Security
Archived data is often encrypted and stored with controlled access, reducing the risk of breaches or accidental loss. This ensures that even old or unused data remains protected.
Key Features:
- Encrypted storage and restricted access
- Protection against unauthorized usage or tampering
- Regular integrity checks for stored data
Example: A legal firm uses encrypted on-premises servers for archiving confidential case files, safeguarding them from cyber threats.
4. Improved System Performance
Removing inactive data from operational systems improves processing speeds and overall system performance. Teams can work more efficiently without being slowed down by excess data.
Key Features:
- Faster query performance
- Reduced database load
- Streamlined backups and recovery
Example: A logistics company archives completed shipment data to maintain optimal performance of its live tracking system.
5. Long-Term Data Preservation
Archiving ensures that valuable historical data remains accessible for analytics, research, or future decision-making. It preserves data integrity over years without risk of loss or degradation.
Key Features:
- Reliable long-term storage
- Maintains data consistency and integrity
- Supports future reference and analysis
Example: A university archives alumni records and academic results to preserve institutional history and support long-term reporting.
Data Archiving Best Practices

To get the most value from data archiving, organizations should follow these best practices:
- Define Retention Policies: Set clear storage timelines for each type of data to meet business and legal requirements.
- Choose the Right Storage: Use on-premises, cloud, or hybrid solutions based on your data volume, security, and cost needs.
- Balance Security and Accessibility: Protect archived data with encryption and access controls while keeping it easy to retrieve.
- Audit Regularly: Review archived data periodically to ensure compliance and accuracy.
- Use Automation: Automate archiving and deletion tasks to reduce errors and maintain consistency.
Tools and Technologies for Data Archiving
To manage archived data efficiently, modern organizations rely on a range of specialized tools and technologies. These solutions help ensure data is secure, organized, and easily accessible when needed.
Cloud Storage Providers
Platforms like AWS Glacier, Google Cloud Archive, and Azure Blob Storage offer scalable, cost-effective, and secure storage for long-term data retention.
Enterprise Archiving Software
Solutions such as Veritas Enterprise Vault, Commvault, and IBM Spectrum Archive provide advanced management, indexing, and compliance features for large-scale organizational data.
Database Archiving Solutions
Tools like Oracle Advanced Compression and SQL Server Data Archiving help archive database records efficiently, ensuring data integrity and optimized storage performance.
Challenges in Data Archiving
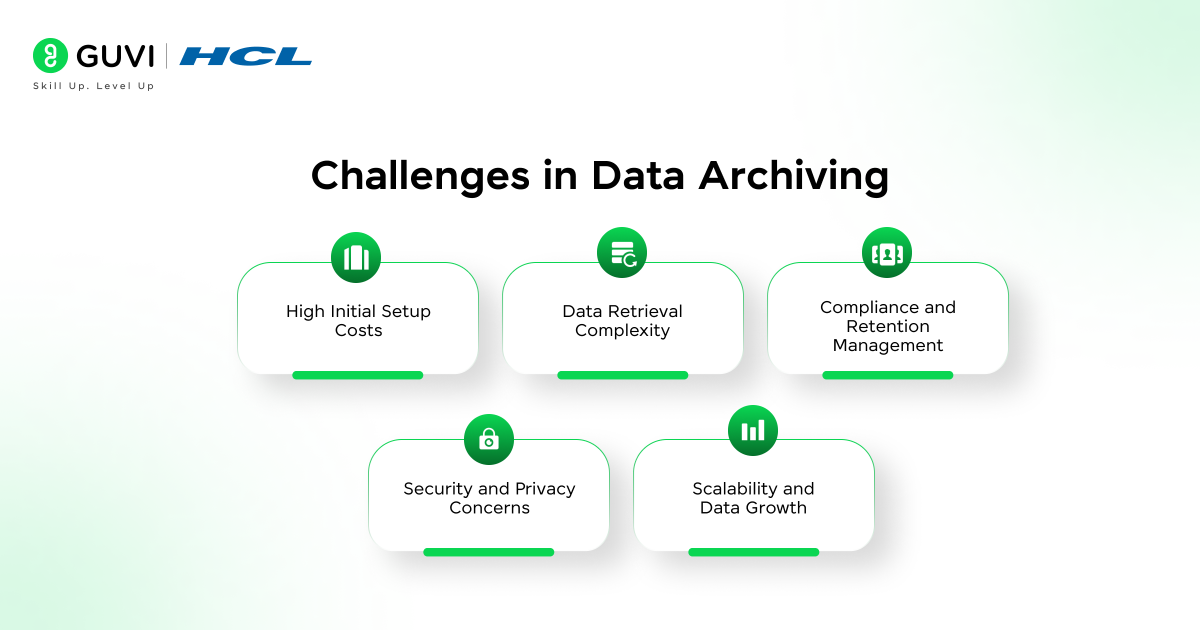
Despite its many advantages, data archiving also presents several challenges that organizations must address to ensure long-term success. These challenges often revolve around cost, security, accessibility, and compliance management. Understanding them helps businesses plan better and choose the right archiving solutions.
High Initial Setup Costs
Implementing a reliable archiving system can involve significant upfront expenses, especially for on-premises setups. The cost of storage infrastructure, data migration, and maintenance can add up before the long-term savings begin to show.
Data Retrieval Complexity
Retrieving archived data efficiently can be difficult, particularly when it’s stored across multiple platforms or formats. Slow retrieval times and compatibility issues with outdated systems can hinder quick access when data is needed urgently.
Compliance and Retention Management
Every industry follows specific data retention rules. Managing these varied policies and ensuring timely deletion of outdated data can be challenging. Failure to comply with regulations may lead to penalties or data management risks.
Security and Privacy Concerns
Even archived data requires strong protection. Without proper encryption and access control, organizations risk exposing sensitive or confidential information to cyber threats or unauthorized users.
Scalability and Data Growth
As data continues to grow exponentially, archiving systems must be able to scale without affecting performance or cost efficiency. Older systems may struggle to handle large datasets, resulting in slower processes and storage inefficiencies.
Future of Data Archiving
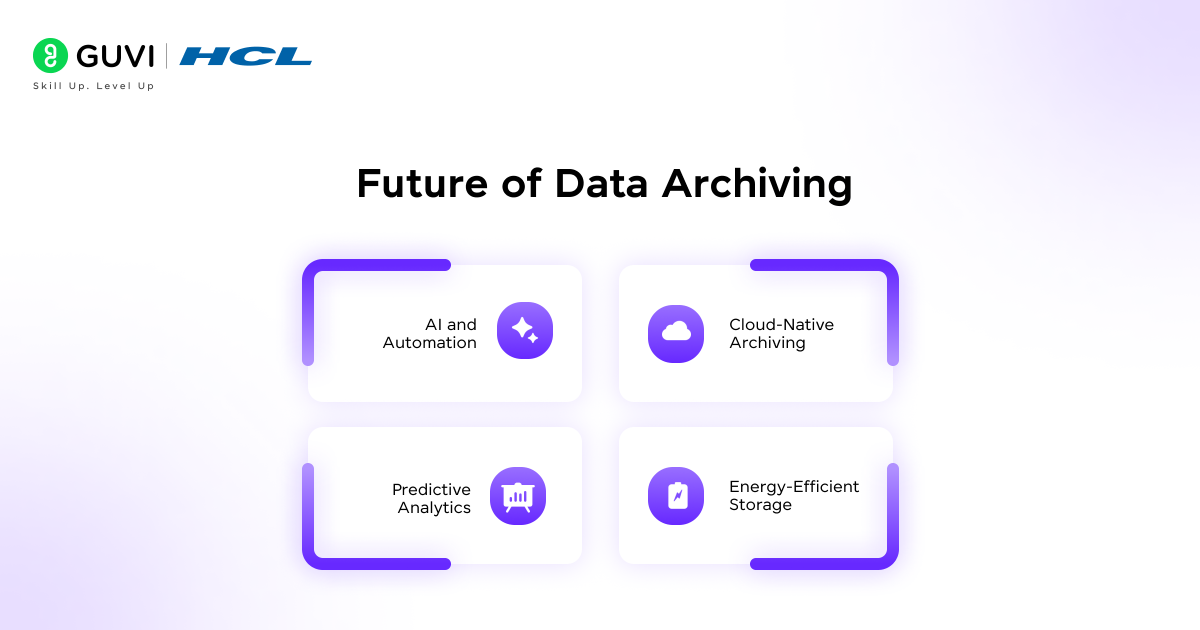
Data archiving is evolving with technology to become smarter and more efficient.
- AI and Automation: Automatically identify inactive data and apply retention policies.
- Cloud-Native Archiving: Scalable, secure, and cost-effective long-term storage.
- Advanced Compliance Tools: Simplify governance and ensure regulatory compliance.
- Predictive Analytics: Determine which data to archive or retrieve for efficiency.
- Energy-Efficient Storage: Reduce operational costs and environmental impact.
Conclusion
Data archiving is a crucial strategy for businesses to save on storage costs, enhance system performance, and maintain regulatory compliance. By leveraging the right types of archiving, following best practices, and keeping up with emerging trends, organizations can manage historical data effectively and make smarter, data-driven decisions.
If you want to gain hands-on skills in data management and data archiving, HCL GUVI’s Zen Class Data Science Course is the perfect place to start. This course offers practical, project-based learning in Python, data visualization, databases, and analytics, helping you build real-world expertise that can be immediately applied in professional settings.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between data archiving and data backup?
Data backup is for disaster recovery, keeping copies of current data. Data archiving stores inactive or historical data long-term for retention and compliance.
2. How long should data be archived?
It depends on legal and business requirements. For example, financial records may be kept for 5–7 years, while healthcare records may require 7–10 years.
3. Can archived data be accessed quickly?
Access speed depends on the storage type. On-premises and hybrid archives are faster than cold cloud storage, though AI-powered systems can improve retrieval efficiency.
4. Is cloud archiving secure?
Yes, if encryption, access controls, and compliance standards are implemented. Providers like AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure follow strict security protocols.
5.What types of data should be archived?
Inactive or historical data such as financial records, transaction logs, legal documents, medical files, and past analytics data should be archived.



































Did you enjoy this article?