
What Is a System Administrator? Roles, Skills, Salary & Career Guide
Oct 22, 2025 6 Min Read 4578 Views
(Last Updated)
Ever wondered who keeps the lights on in the digital world? Whenever you are sending an email, connecting to a file at the workplace, or watching a video on a company server, an unseen force is at work to make sure everything works as expected. This force is commonly a System Administrator.
If you’ve ever asked, “What is a system administrator?” or been curious about the person behind the “our systems are down” email, then you are at the right place. This blog is going to make all that you should know about this key tech position easy to understand. We will see what the system administrator’s definition is, his major duties, the skills required, as well as what type of salary you might get.
Now, we are going to go underground and into the engine room of the web that is the modern internet and we will be introduced to the unsung heroes, the SysAdmins.
Table of contents
- What Is a System Administrator?
- The Role of a System Administrator
- System Administrator Job Examples
- System Administrator Tasks and Duties
- Daily Duties:
- Weekly/Monthly Duties:
- Project-Based Duties:
- The IT System Administrator in Network Management
- Essential System Administrator Skills
- System Administrator Tools
- The System Admin Career Path
- System Administrator Certification
- The Big Question: Salary System Administrator
- System Administrator Examples in the Real World
- Final thoughts…
- FAQs
- Is a system administrator a good career in 2025?
- Do system administrators need coding skills?
- How is a SysAdmin different from a DevOps engineer?
- What is the biggest challenge of sysadmins today?
What Is a System Administrator?
The definition of the system administrator is simple: A System Administrator (which could also be referred to as Sysadmin) is the individual who installs, maintains, and oversees the computer networks of a company.
Imagine them as the computerized building superintendent. A super will not be there to create the apartment complex; they come in later and ensure that the heat, water, electricity, and security are on at all times for the tenants. Likewise, a SysAdmin does not necessarily write the software, but he or she is invaluable in ensuring that the hardware, software, and network that a firm uses and depends on are functioning, safe, and efficient.
Their playground is the IT infrastructure of the company, which is a combination of servers, networks, and all the important software on which the business is operating.
The Role of a System Administrator
Another myth is that a SysAdmin represents a job title of the fancy tech guy who repairs printers and changes passwords. Although those may be included in the job, the role of the system administrator is very much more strategic and complicated.
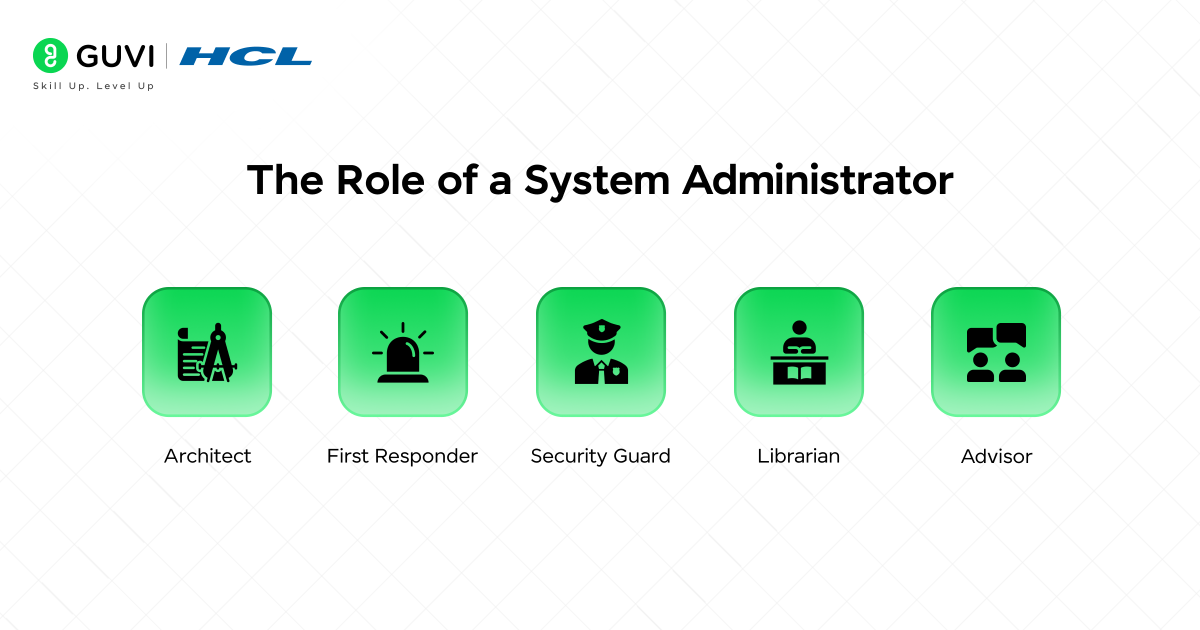
A SysAdmin is a multitasking type of expert, some of the key tasks are:
- Architects: They design and build system infrastructures.
- First Responder: They are problem solvers of emergencies and outages.
- Security Guard: They defend the digital fortress from attacks.
- Librarian: They work with massive data and make sure that it is correct.
- Advisor: They recommend new technologies and strategies to assist the business in growing.
The central objective of their practice is to provide high availability and reliability of IT services. In simple terms, they ensure that the technology of the company is up and running at all times and is functioning properly.
System Administrator Job Examples
System administrators serve a variety of industries and may serve specialized roles. Here are some examples of system administrators:

- Windows System Administrator: Manages and supports Windows servers and applications.
- Linux System Administrator: Works mostly with Linux/Unix-based operating systems.
- Database Administrator: Manages the overall health and security of databases.
- Network Administrator: Manages network hardware and connectivity.
- Cloud Administrator: Manages cloud platforms such as AWS, Azure, and GCP.
- The term “SysAdmin Day” exists! It’s celebrated every year on the last Friday of July to honor system administrators worldwide.
- According to surveys, over 70% of system downtime is prevented by proactive monitoring—something sysadmins do daily.
- In many companies, a system administrator manages hundreds or even thousands of devices at once, ensuring seamless performance.
- The first official system administrator role dates back to the 1980s, when businesses started using centralized servers for operations.
System Administrator Tasks and Duties
What exactly does a SysAdmin do all day, then? The system administrator tasks and system admin duties are so diverse. There is no single day that is similar to another, and this is one of the reasons why the job can be so interesting. The following is an overview of some of their weekly, monthly, and daily activities:
Daily Duties:
- Monitoring Systems: Checking the dashboards/alerts and making sure that servers and networks are healthy. This has the effect of verifying the vital signs of the IT infrastructure.
- Maintenance of Backups: Ensuring that automated backups are successful. In the event of a failure, the backup is the company’s safety net.
- Response to Help Desk Tickets: Respond to users, including password reset requests, software installations, etc.
- Application of Updates and Patches: It involves the installation of important software patches to fix bugs and, most importantly, security vulnerabilities.
- Checks of Performance: Making sure that systems are not running slow or operating at overcapacity.
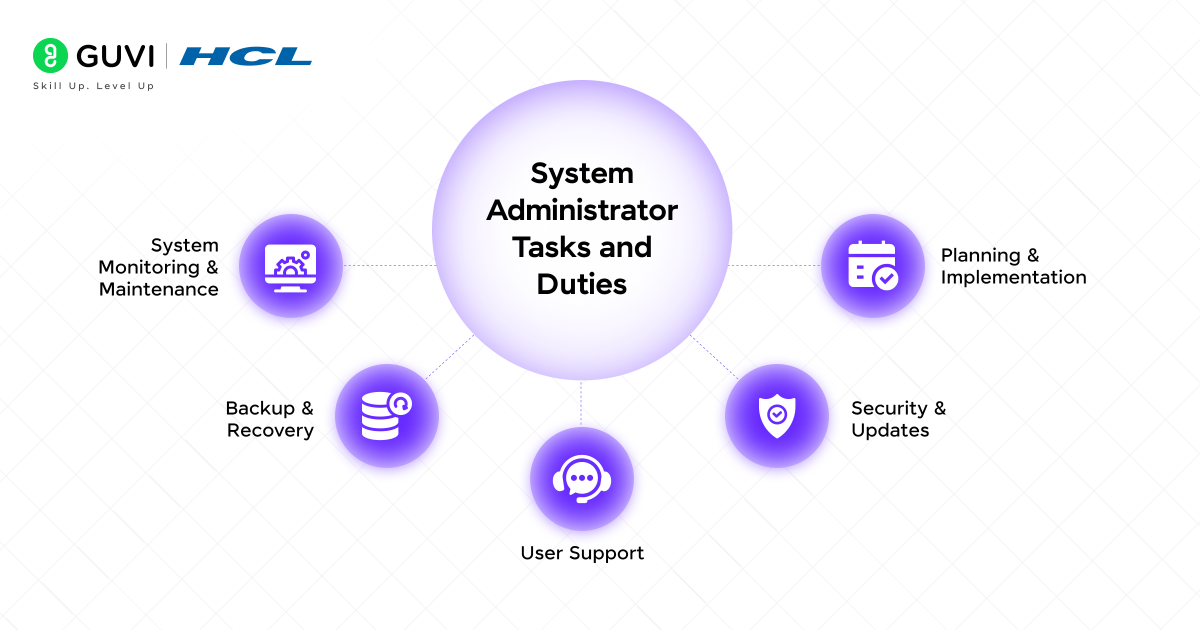
Weekly/Monthly Duties:
- Maintenance of Servers: Rebooting, removal of unnecessary files, and optimizing systems to improve performance.
- Security Audits: Checking logs for any type of suspicious activity and strengthening the defence.
- Reporting: Preparing reports to the management regarding system uptime, performance metrics, and issues fixed.
- Planning: Assessing future requirements, such as the need to have more or higher-quality storage or the need to upgrade.
- Disaster Recovery Drills: Testing the backup restoration process to ensure it actually works in a crisis.
Project-Based Duties:
- Installation of New Systems: Installation of new servers, software or even complete new offices.
- Migrating Data: The process of transferring the data between new systems and former systems.
- Adoption of New Technologies: Study and implementation of new security or efficiency enhancement tools.
The IT System Administrator in Network Management
Although the term SysAdmin is a broad term, a great number of them specialize; one of the most important ones is the system administrator in network management, commonly referred to as Network Administrator. Their focus is narrower but just as critical.
Their system admin responsibilities are centered on the network itself:
- Network Hardware Management: Switches, access points, routers, firewalls, and Wi-Fi.
- Enhancing Network Connectivity: Ensuring that all the devices can communicate with one another and access the internet without difficulties.
- Application of Security: Installing firewalls and Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) to block the entry of external threats to the network.
- Traffic Surveillance: Keeping an eye on the network that might indicate a security violator or a malfunctioning device.
- IP Address Management: Assigning and managing IP addresses to all the devices connected to the network.
Think of the general SysAdmin as the one taking care of the servers (the brains) and the Network Admin as the one taking care of the nervous system that will join the brains to the rest of the body.
Essential System Administrator Skills
This is not a job that can be stumbled into. It needs a certain combination of hard technical skills and essential soft skills. The following is the breakdown of the most essential system administrator skills:
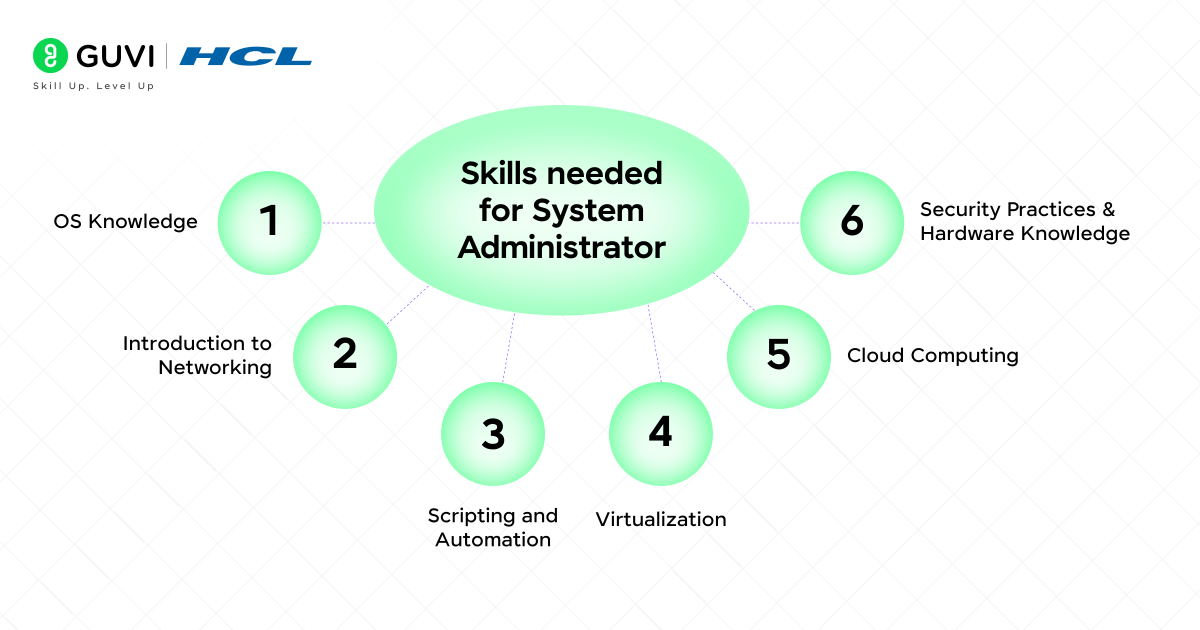
Technical Skills (The Hard Skills):
- OS Knowledge: Extensive experience with Windows Server (and/or Linux) (with particular distributions such as Red Hat and Ubuntu, in particular).
- Introduction to Networking: It is essential to understand key concepts such as TCP/IP, DNS, DHCP, VLANs, and VPNs.
- Scripting and Automation: Understanding how to write scripts in PowerShell (Windows) or Bash/Python (Linux) to automate routine work is an enormous boost to time.
- Virtualization: It is essential to have experience with platforms such as VMware or Hyper-V, as most businesses utilize virtual machines to run their servers.
- Cloud Computing: The understanding of the cloud provider, such as AWS, Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform, has become a mandatory demand.
- Security Practices: Knowledge of security measures such as firewalls, antivirus programs, intrusion detection, and other security measures is obligatory.
- Hardware Knowledge: Understanding how to deal with and troubleshoot server hardware.
Soft Skills (The Human Skills):
- Problem-Solving: This is the first and most important skill. SysAdmins are professionals who are puzzle solvers and are required to solve complex problems under pressure.
- Communication: They should be able to clarify technical issues to the non-technical (such as managers or users) and do it in a patient manner.
- Patience and Calm Under Pressure: When the system crashes, the whole world is panic-stricken. The SysAdmin has to be the composed, zero-distracted storm-centre.
- Continuous Learning: Technology is evolving. An effective SysAdmin is a constant learner and a constantly changing entity.
- Focus on detail: It takes one command typed incorrectly or one overlooked configuration to result in a significant outage. Precision is key.
System Administrator Tools
The tools are all the man can be. Tools that they use to do their work effectively are system administrator tools. Common tools include:
- Monitoring Tools: Nagios, Zabbix, SolarWinds.
- Remote Desktop Tools: RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol), SSH (Secure Shell), TeamViewer.
- Ticketing Systems: Jira Service Desk, Zendesk, Freshservice (to monitor user requests)
- Configuration management: Ansible, Puppet, Chef (to automate the setting up of servers).
- Backup Software: Veeam, Acronis, BackupExec.
The System Admin Career Path
The system administrator career is clear and presents a lot of opportunities in terms of development. It often looks like this:
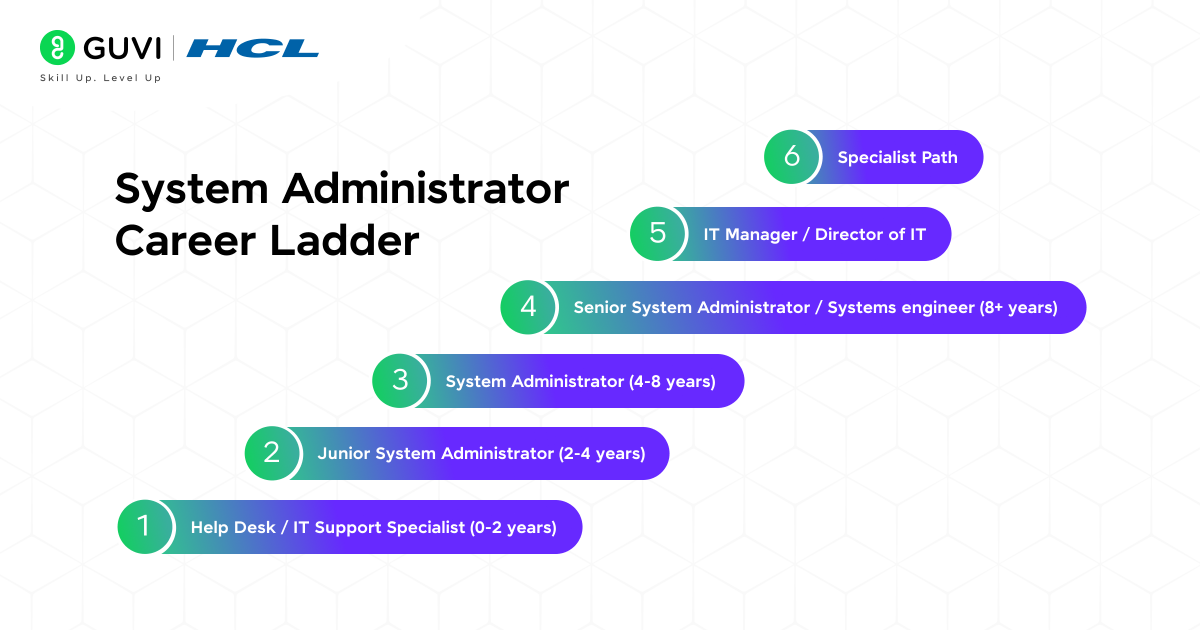
- Help Desk / IT Support Specialist (0-2 years): This is the standard entry-level. You get to know the fundamentals of user support and troubleshooting.
- Junior System Administrator (2-4 years): You begin to have a greater responsibility in servers and networks under the supervision of senior personnel.
- System Administrator (4-8 years): The essence of the position that we have already addressed. You are the owner of critical systems and make critical decisions.
- Senior System Administrator / Systems engineer (8+ years): You design and architect complex systems, project head, and mentor junior admins.
- IT Manager / Director of IT: You start to work in management, where you do not do as much practical tech, but rather more strategy, budget, and team management.
- Specialist Path: You can also be a specialist in a highly demanded field, such as Cloud Architecture, Cybersecurity, or DevOps Engineering, instead of being in a management position.
System Administrator Certification
Although a university education in Computer Science or IT is typical, the tech world values certifications so much. System administrator certification is a certification that confirms your capabilities and may lead to improved employment and increased salary.
Certificates that are the most valuable include:
- CompTIA Server+: An excellent beginning to the basics of server knowledge.
- CompTIA Network+: The way to get basic knowledge of networking.
- Microsoft Certified: Azure Administrator Associate: Essential to Windows-oriented admins shifting to the cloud.
- AWS Certified Sysops Administrator: The counterpart to Amazon Web Services.
- Red Hat Certified System Administrator (RHCSA): The gold plaque certification of Linux system administrators.
- GUVI System Administration & Cloud Courses: Hands-on, project-based learning program designed for beginners and IT professionals to advance their knowledge in Linux, cloud computing, DevOps, and system admin tools, and provide job assistance.
The Big Question: Salary System Administrator
Let’s talk numbers. What types of systems administrator salaries are possible? The salaries are very diverse in accordance with the location, experience, industry, and specific skills.
| Experience Level / Category | Suggested Salary |
| Entry-Level / Junior SysAdmin (0–2 years) | ₹3 LPA – ₹6 LPA |
| Mid-Career System Administrator (3–5 years) | ₹4 LPA – ₹10 LPA |
| Senior System Administrator/ Systems Engineer (5–10 years) | ₹10 LPA – ₹18 LPA+ |
| Experts (Cloud, Security, Virtualization Specialists) | ₹18 LPA – ₹25 LPA+ |
The salary can differ based on the location of the company; for example, salaries are higher in metro cities compared to lower-tier cities. You can check the updated salary using AmbitionBox or Glassdoor.
System Administrator Examples in the Real World
To bring it all into reality, we will consider some system administrators in various industries:
- At a Medium-Sized Marketing Firm: The SysAdmin takes care of the file servers of the company, keeps the design team accessing their large files whenever they want them, monitors the email server, and monitors the web hosting.
- In a Hospital, the IT system administrator is a decisive factor. They keep the servers that contain the patients’ records, make sure the network does not go down, and take extreme security measures to maintain the sensitive health information (as it is mandated by law).
- At a University, SysAdmins have to maintain the gigantic network to serve thousands of students and faculty with internet, the learning management system (such as Canvas or Blackboard), and user accounts of all campus members.
- In an E-commerce Company, The SysAdmin only has one primary task, and that is to make sure the site does not shut down, particularly on black Friday. They deal with the web servers, database servers and collaborate with the cloud to deal with massive traffic spikes.
If you are curious about software development and want to become a software developer, then grab the opportunity to learn with HCL GUVI’s IITM Pravartak and MongoDB Certified Online AI Software Development Course. The NSDC-endorsed course gives you a globally recognized certificate to add to your résumé, which is a significant advantage that will help you stand out in the competitive employment market.
Final thoughts…
So, what is a system administrator? In simple terms, they are the unsung professionals of IT, the individuals who ensure that systems are operating efficiently, data is kept secure, network operations are running smoothly, and employees are being supported.
A system administrator job can be a fulfilling career opportunity if you enjoy solving problems, working with technology and learning continuously. By following the right system administrator skills, certifications, and career path, you can transition into advanced IT roles and earn a lucrative salary.
Whether you are a high school or college student, just starting your IT career or someone seeking to transition careers, becoming a system administrator is a potential first step into the IT field.
FAQs
1. Is a system administrator a good career in 2025?
Yes. The demand is consistent because there will always be businesses that need professionals to manage servers, networks, and cloud systems. If you have skills in both cloud monitoring and security, the role will be future-proof.
2. Do system administrators need coding skills?
Not really substantial coding, but having experience with basic scripting in Bash, Python, or PowerShell is certainly beneficial. This will allow you to automate tasks such as backups, monitoring, and software updates.
3. How is a SysAdmin different from a DevOps engineer?
A sysadmin’s role is to maintain IT systems, whereas the DevOps engineer will work with teams to automate the development and deployment pipeline. Often, sysadmins enter a role as a DevOps engineer with additional skills.
4. What is the biggest challenge of sysadmins today?
The biggest challenge of sysadmins today is all the rapid transformations they are facing, cloud migration, cybersecurity, and automation, while providing 24/7 uptime.



































Did you enjoy this article?