What is a Recommendation Engine and How Does it Work?
Feb 12, 2026 7 Min Read 971 Views
(Last Updated)
Have you ever noticed how 80% of the content you watch on Netflix comes from its suggestions? Or how Amazon’s sales are generated through recommended products? These recommendation engines have become essential tools across industries, powering the personalized experiences you encounter daily online.
What is a recommendation engine exactly? Simply put, it’s a system that analyzes your behavior and preferences to suggest products, content, or services you might like. You might not realize it, but recommendation engines work behind the scenes to enhance your digital experiences. When you feel frustrated by non-personalized interactions (as 76% of customers do), you’re experiencing the absence of effective recommendation systems.
In this article, you’ll learn how recommendation engines work, the different types available, and why they’ve become critical for businesses looking to improve user engagement and satisfaction. Let’s begin!
Table of contents
- Understanding Recommendation Engines
- What is a recommendation engine?
- How it helps users and businesses
- Examples from e-commerce and streaming
- How Does a Recommendation Engine Work?
- Step 1: Collecting user and item data
- Step 2: Storing and organizing data
- Step 3: Training the model
- Step 4: Generating recommendations
- Step 5: Learning from user feedback
- Different Types of Recommendation Engines
- 1) User-based collaborative filtering
- 2) Item-based collaborative filtering
- 3) Content-based filtering
- 4) Hybrid models combining both
- Benefits of Using Recommendation Engines
- 1) Improved user experience
- 2) Higher engagement and retention
- 3) Increased conversions and revenue
- 4) Scalable personalization
- Challenges and Limitations
- 1) Cold start problem
- 2) Data sparsity and bias
- 3) Scalability and speed
- 4) Privacy and compliance concerns
- Concluding Thoughts…
- FAQs
- Q1. How do recommendation engines improve user experience?
- Q2. What are the main types of recommendation engines?
- Q3. How do businesses benefit from using recommendation engines?
- Q4. What challenges do recommendation engines face?
- Q5. How do recommendation engines learn and improve over time?
Understanding Recommendation Engines
In today’s digital era, recommendation engines function as virtual assistants that guide you through vast catalogs of products and content. Unlike traditional shopping experiences, where a store clerk might suggest complementary items, modern recommendation systems use complex algorithms to deliver personalized experiences at scale.
What is a recommendation engine?
A recommendation engine is an artificial intelligence system that suggests relevant items to users based on their behavior and preferences. Wikipedia defines it as “a subclass of information filtering system that seeks to predict the ‘rating’ or ‘preference’ a user would give to an item”.
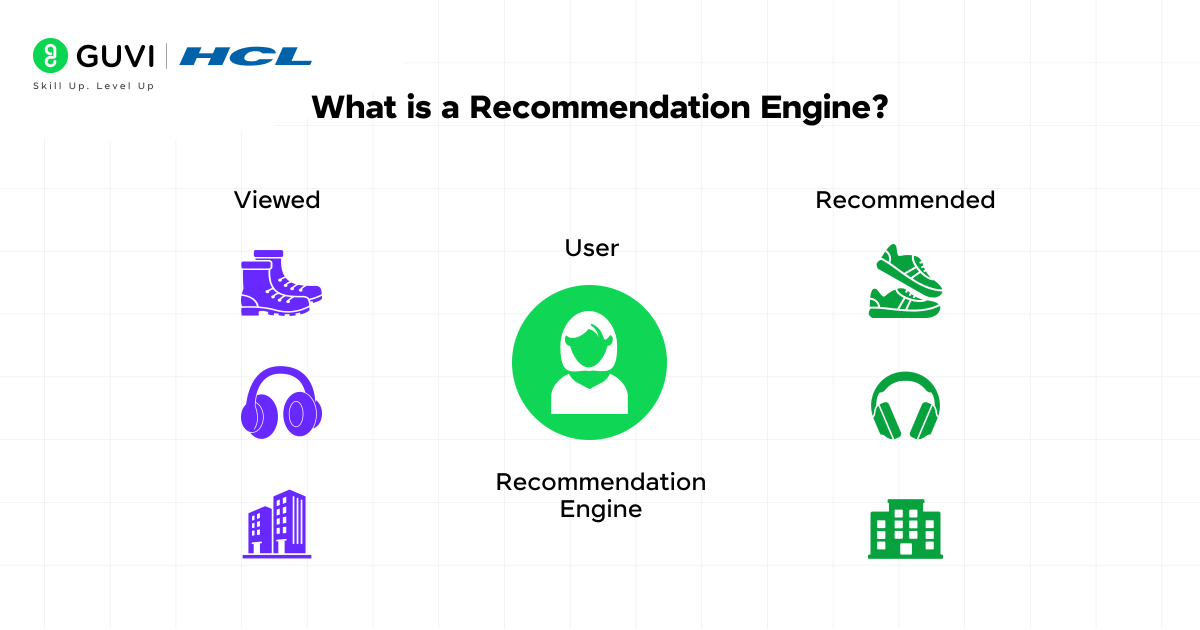
However, these systems are far more sophisticated than this simple definition implies.
At their core, recommendation engines are data filtering tools powered by machine learning algorithms that analyze patterns in user behavior. They process information from multiple sources:
- Past purchases and viewing history
- Browsing behavior and search patterns
- Ratings and reviews provided by users
- Demographic information
The collected data is then analyzed to create personalized recommendations that match individual preferences, making the digital experience feel more human and intuitive.
How it helps users and businesses
For users, recommendation engines offer significant advantages:
- Time-saving: They eliminate endless scrolling through vast product catalogs, helping users find what they need quickly
- Personalized experiences: 71% of consumers expect personalized experiences when interacting with brands
- Product discovery: They introduce users to items they might never have found on their own
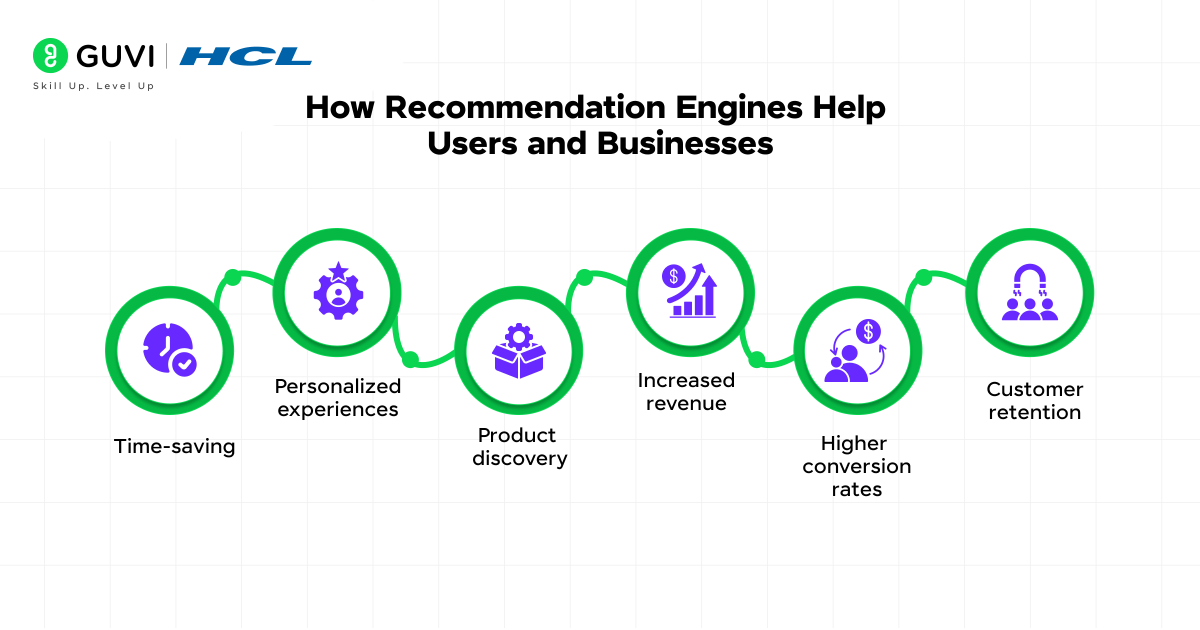
For businesses, the benefits are equally compelling:
- Increased revenue: Companies that excel at personalization generate 40% more revenue from those activities than average competitors
- Higher conversion rates: Personalized product recommendations increase average order value by 10%
- Customer retention: Enhanced customer experiences lead to 20% higher customer satisfaction
Examples from e-commerce and streaming
- Amazon stands as the gold standard for e-commerce recommendation engines. Their system analyzes factors including past purchases, browsing history, ratings, and reviews. A remarkable 35% of purchases made on Amazon result from their recommendations, showcasing the tremendous impact of their algorithm.
- Netflix relies heavily on its recommendation engine to help users navigate its vast library of over 17,000 titles. Their sophisticated system is so effective that 75% of what people watch on Netflix comes from recommendations, saving the company an estimated $1 billion annually.
- Spotify employs recommendation engines innovatively through features like “Discover Weekly” and “Release Radar,” which update personal playlists weekly based on listening patterns. This approach keeps users engaged with fresh content tailored to their tastes.
- YouTube creates personalized recommendations by analyzing users watch history and interactions, helping viewers discover content among millions of videos. Furthermore, platforms like Best Buy revitalized their business after facing fierce competition by implementing recommendation engines that boosted their e-commerce sales significantly.
In essence, recommendation engines have transformed from a luxury feature to a necessity for businesses seeking to provide exceptional user experiences in the digital landscape.
How Does a Recommendation Engine Work?
Behind the sleek interfaces recommending your next favorite movie or product lies a structured process that transforms raw data into personalized suggestions. Recommendation engines follow a five-step workflow that combines data science and machine learning to predict what you’ll likely enjoy next.
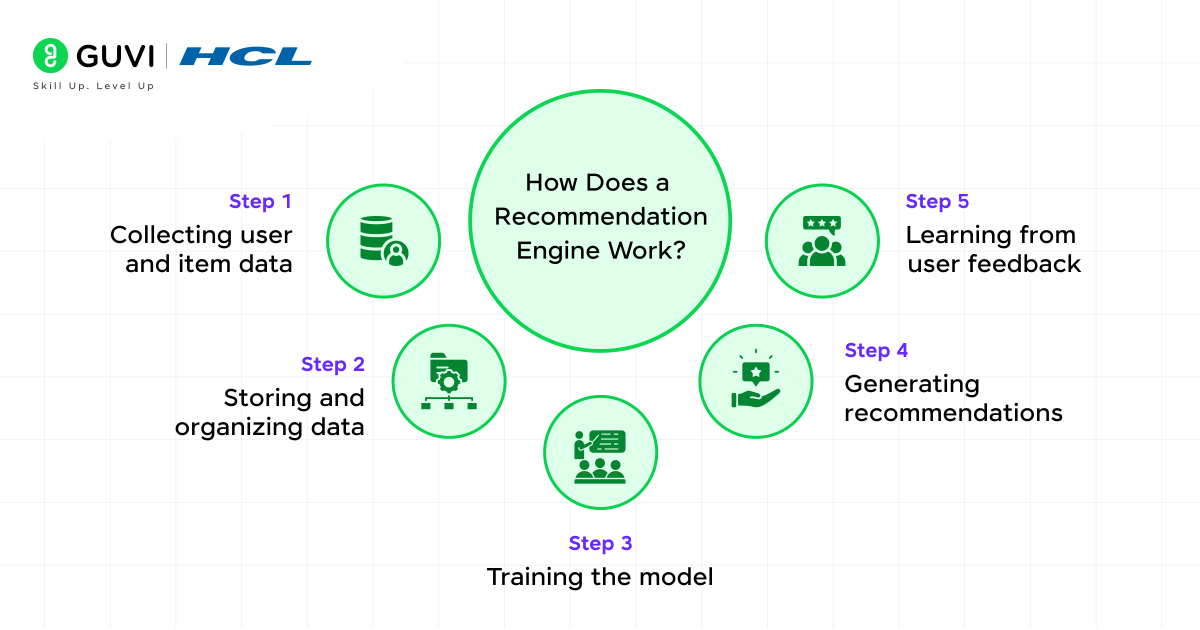
Step 1: Collecting user and item data
The foundation of any recommendation system is data collection. Without quality data, even the most sophisticated algorithms fall flat. Recommendation engines gather two primary types of information:
- Explicit data: Direct user input, including ratings, reviews, likes, and comments that clearly indicate preferences
- Implicit data: Behavioral signals such as browsing history, clicks, search queries, cart events, and purchase history
Beyond these interactions, recommendation engines also collect user attributes (demographics like age and gender) and item features (genre, price range, or category) to better understand similarities between users and products. The more comprehensive this data is, the more accurate your recommendations become.
Step 2: Storing and organizing data
- After collection, the data requires proper storage and organization. The volume of information grows rapidly over time, necessitating scalable storage solutions. Depending on data types, companies implement different storage systems:
- Data warehouses excel at storing structured interaction data, while data lakes handle varied or unstructured data like reviews and images. Modern systems often combine these approaches into a “data lakehouse” architecture for maximum flexibility.
- For real-time recommendation delivery, companies maintain distributed databases or in-memory caches that can be queried quickly when you need suggestions. This ensures recommendations appear within milliseconds of opening an app or website.
Step 3: Training the model
- With organized data in place, recommendation engines apply machine learning algorithms to identify patterns and correlations. This analysis phase can occur in several ways:
- Real-time analysis processes data as it’s created, while batch analysis handles information periodically. The training process involves algorithms detecting patterns, identifying correlations, and weighing the strength of relationships between users and items.
- During training, the system learns to recognize signals like “users who behave like X tend to enjoy Y” or “item A is similar to items B and C”. These learned patterns form the predictive foundation for generating personalized recommendations.
Step 4: Generating recommendations
- The recommendation process typically follows a multi-stage architecture for efficiency. First, candidate generation narrows billions of potential items down to hundreds or thousands that might interest you. This initial screening makes the process computationally manageable.
- Subsequently, a scoring model evaluates and ranks these candidates based on their relevance to your specific preferences. Since this stage deals with far fewer items, it can employ more complex models for greater precision.
- Finally, a re-ranking phase applies additional business rules and adjusts recommendations to account for factors like diversity, freshness, and fairness. This ensures you receive varied and timely suggestions rather than repetitive recommendations.
Step 5: Learning from user feedback
- The recommendation process doesn’t end after suggestions are displayed. Throughout their lifecycle, effective recommendation systems create a feedback loop that continuously improves performance.
- As you interact with recommendations—clicking, purchasing, or ignoring them—this data feeds back into the system. Companies typically implement A/B testing, where new models are compared against conventional approaches with randomly selected user groups.
- Consequently, the system learns from both successes and failures, gradually refining its understanding of your preferences. This iterative improvement process is essential—building a recommendation system requires ongoing optimization based on key metrics like click-through rates, conversion rates, and customer feedback.
By following these five steps, recommendation engines transform vast amounts of data into the personalized experiences that guide your daily digital interactions.
Different Types of Recommendation Engines
The magic behind personalized suggestions stems from different algorithmic approaches that power recommendation engines. Understanding these distinct models helps clarify how your favorite apps and websites deliver tailored recommendations.
1) User-based collaborative filtering
User-based collaborative filtering operates on a simple yet powerful principle: people who shared similar preferences in the past will likely have similar tastes in the future.
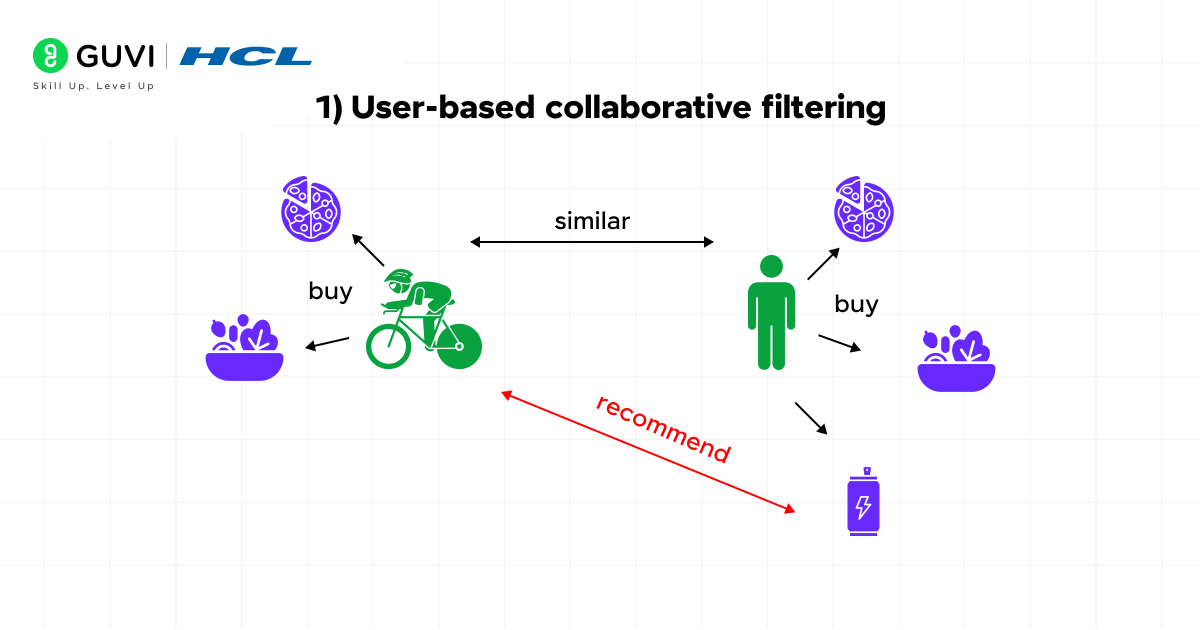
This approach:
- Identifies users with similar rating patterns to yours
- Uses their past behavior to predict what you might enjoy
- Recommends items that similar users have liked but you haven’t yet discovered
Think of it as getting recommendations from friends with matching tastes. When multiple users rate the same items similarly, the algorithm creates “neighborhoods” of like-minded users to generate suggestions. Despite its effectiveness, this method can struggle with new users who have minimal historical data—a challenge known as the “cold start problem”.
2) Item-based collaborative filtering
Item-based collaborative filtering, first pioneered by Amazon in 1998, flips the approach by focusing on relationships between items instead of users.
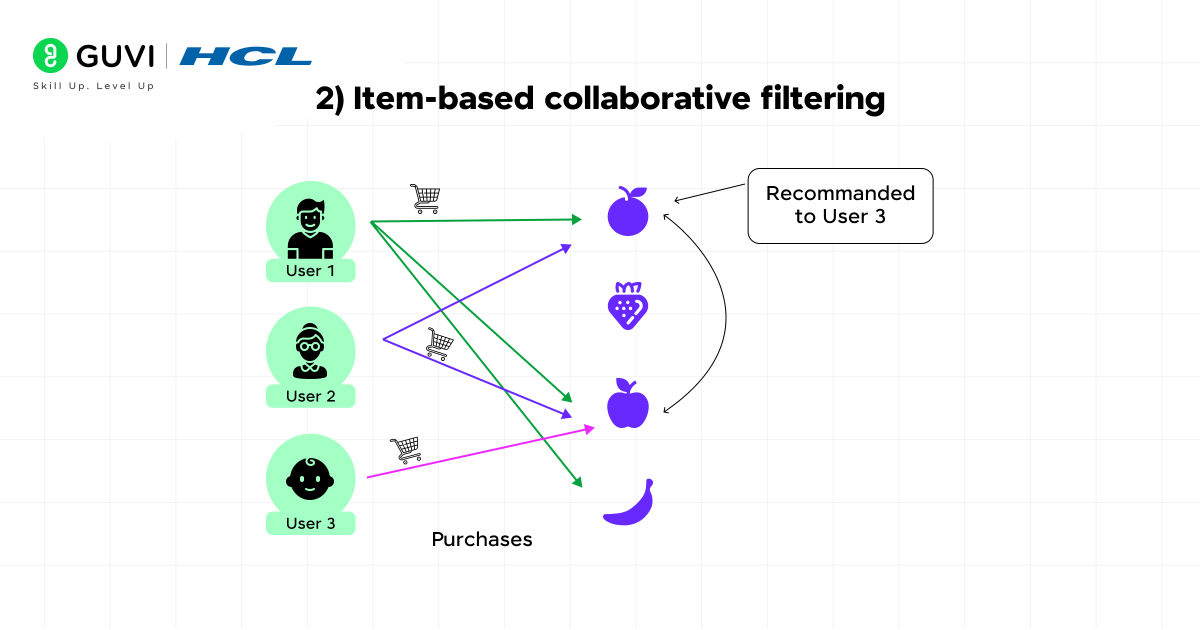
Rather than matching you to similar customers, this method:
- Analyzes items you’ve interacted with
- Identifies other products with similar usage patterns
- Recommends these similar items
The fundamental assumption is that you’ll give similar ratings to similar items. This approach calculates similarity between products using techniques like cosine similarity, which treats items as vectors and measures the angle between them. Item-based filtering performs particularly well when user preferences remain relatively stable over time.
3) Content-based filtering
Unlike collaborative approaches that rely on user interactions, content-based filtering focuses exclusively on item attributes and your personal preferences. This method analyzes the features of items you’ve liked—such as genre, category, or keywords—and recommends products with similar characteristics.
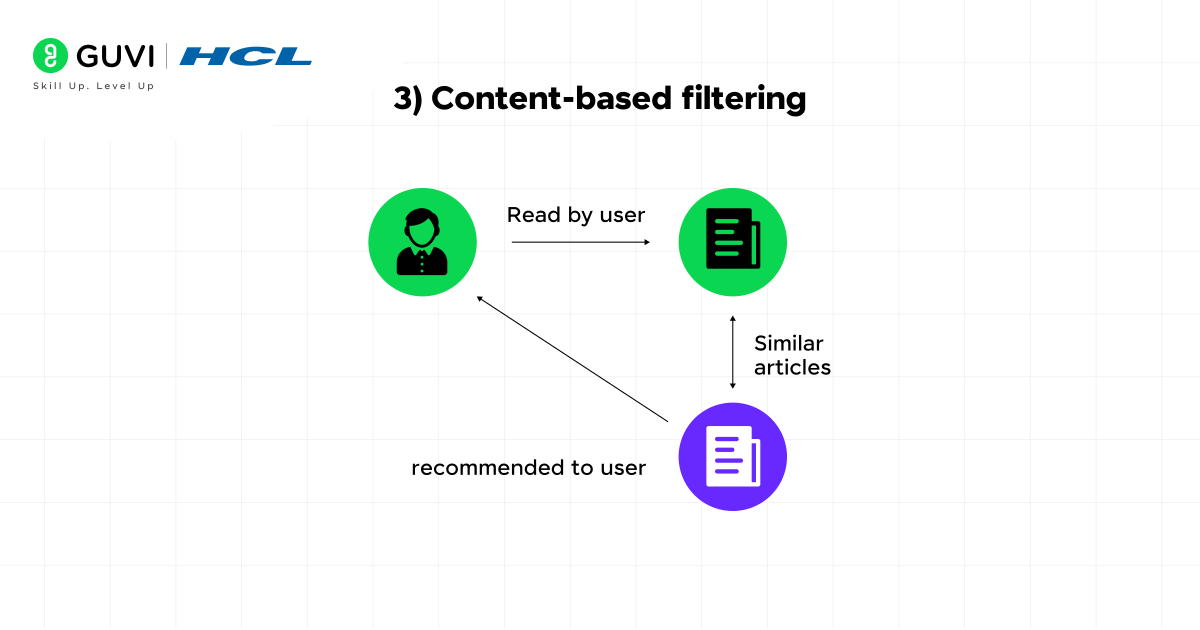
For instance, if you enjoy action movies with specific actors, a content-based system might suggest other films featuring those same actors or similar themes. This approach excels at providing highly relevant recommendations even for new items with limited user interaction data.
4) Hybrid models combining both
Hybrid recommendation systems combine multiple approaches to overcome the limitations of individual methods.
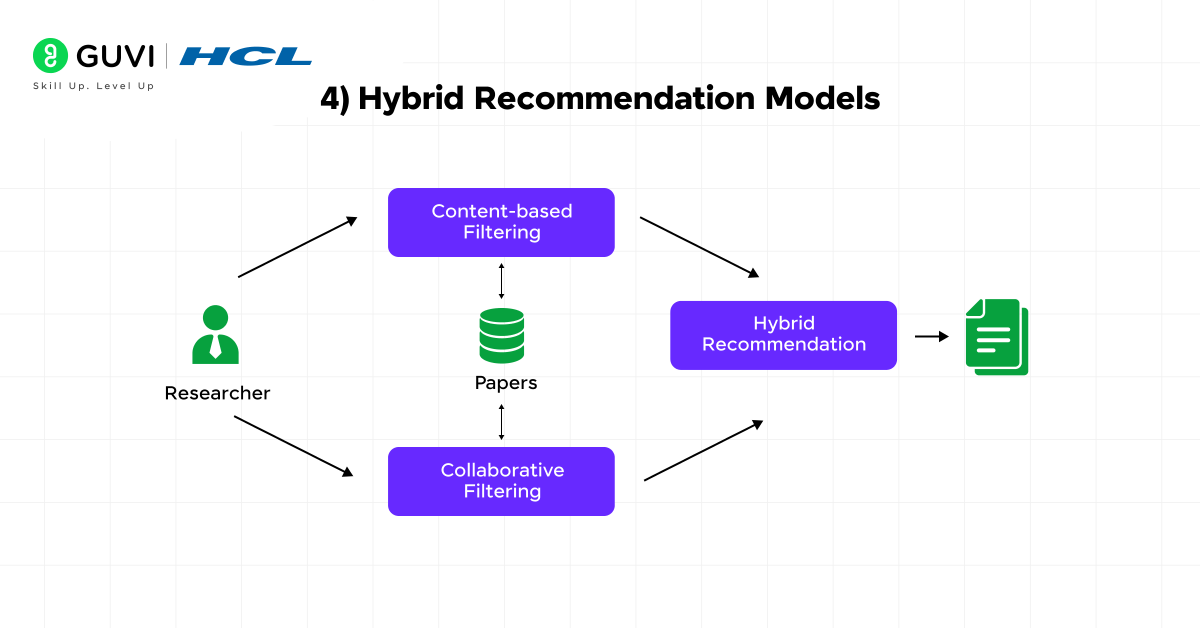
These sophisticated systems:
- Leverage collaborative data to understand user similarities
- Utilize content features to understand item relationships
- Apply various combination strategies to produce better recommendations
Companies like Netflix implement hybrid approaches that blend collaborative filtering, content-based filtering, and additional techniques to deliver more accurate and diverse suggestions. Hybrid models can be implemented through various strategies, including weighted combinations, switching between methods based on context, or using one method to refine results from another.
Recommendation engines power much of what you see online — from your movie list to your shopping cart! Here are some fascinating facts you might not know:
Netflix Saves $1 Billion a Year: Thanks to its highly accurate recommendation system, Netflix reduces customer churn and boosts engagement — saving nearly $1 billion annually!
Amazon’s Secret Revenue Driver: Around 35% of Amazon’s total sales come directly from its product recommendation algorithms.
Spotify’s “Discover Weekly” Uses Machine Learning Magic: Every Monday, over 400 million playlists are uniquely generated for listeners — all through AI-powered personalization models.
These facts show just how much recommendation engines silently shape your digital world — guiding your choices, saving you time, and keeping you engaged every day.
Benefits of Using Recommendation Engines
Businesses across industries are rapidly adopting recommendation engines for one simple reason: they deliver measurable results for both companies and customers alike. These intelligent systems create value through multiple channels that benefit the entire digital ecosystem.
1) Improved user experience
- Recommendation engines save you precious time by eliminating endless scrolling through thousands of options. Instead of manual searching, these systems present relevant choices immediately, making your digital journey smoother and more enjoyable.
- In fact, approximately 80% of what viewers watch on Netflix comes from automated recommendations rather than manual searches, demonstrating how much users rely on these suggestions.
- When platforms understand your preferences, they create a sense that the service truly “gets” you. This personalization leads to a 20% increase in customer satisfaction according to McKinsey research. As a result, your relationship with these platforms becomes more meaningful as they consistently deliver content aligned with your interests.
2) Higher engagement and retention
- Well-designed recommendation systems keep you coming back for more. By consistently suggesting relevant content, these engines boost your engagement with the platform. Personalization through recommendations directly improves loyalty, as users who receive tailored suggestions tend to spend more time on a service and return more frequently.
- Notably, 56% of individuals are more likely to return to retailers that remember their preferences. This increased loyalty translates into reduced customer churn – a critical metric for subscription-based businesses. When users see that a service consistently finds content they enjoy, they develop trust and stay connected longer.
3) Increased conversions and revenue
Recommendation engines drive impressive business results through several mechanisms:
- Increasing conversion rates by 10-15% through personalized customer experiences
- Boosting average order values by approximately 25% when showing relevant offers
- Contributing 30-35% of total revenue on major platforms like Amazon
These systems effectively encourage additional browsing, clicks, and ultimately purchases by showcasing items you’re likely to want. Even in non-commerce settings like streaming platforms, recommendations keep users active and subscribed, protecting revenue streams.
4) Scalable personalization
- Perhaps most importantly, modern recommendation engines enable personalization at scale. These systems can process vast amounts of user data and transform it into actionable insights. As your business grows, recommendation engines adapt to handle increasing data volumes while maintaining performance.
- The scalability of these systems allows companies to extend personalized experiences to millions of users simultaneously, something impossible through manual curation. At the same time, these engines continuously learn and evolve based on new interactions, ensuring recommendations stay relevant as user preferences change.
Challenges and Limitations
Even with their impressive capabilities, recommendation engines face several critical challenges that limit their effectiveness. Let’s examine these limitations that developers must address to create truly useful systems.
1) Cold start problem
The cold start problem occurs whenever a recommendation engine lacks sufficient data to make relevant suggestions. This happens primarily in two scenarios:
- When new users join with no interaction history
- When new items are added with no ratings or reviews
Without historical data, engines struggle to understand preferences, often resulting in generic recommendations that can frustrate users and increase churn rates by up to 30%.
2) Data sparsity and bias
Data sparsity emerges when users interact with only a tiny fraction of available items, creating a sparse matrix of user-item interactions. This sparsity reduces recommendation accuracy and can lead to popularity bias, where already-popular items receive excessive visibility while niche content remains undiscovered.
3) Scalability and speed
As platforms grow, recommendation engines must handle exponentially larger datasets while maintaining real-time performance. Processing recommendations for millions of users simultaneously requires sophisticated computing infrastructures and techniques like distributed processing.
4) Privacy and compliance concerns
Recommendation engines necessarily collect substantial user data, raising significant privacy risks. This includes potential data misuse, unauthorized profiling, and re-identification risks even with anonymized data. Furthermore, systems must comply with regulations like GDPR, carefully balancing personalization with protection of user information.
Want to build your own recommendation engine — or go deeper into AI/ML? This IITM-Pravartak & Intel powered Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning course by HCL GUVI gives you hands-on experience across Generative AI, MLOps, neural networks and more — designed to take you from basics to real-world deployment fast.
Concluding Thoughts…
Recommendation engines have fundamentally transformed how you discover products, content, and services online. Throughout this article, we’ve seen how these sophisticated systems analyze your behavior patterns and preferences to create personalized experiences.
Next time you discover a perfect product suggestion or find yourself enjoying content you never specifically searched for, you’ll recognize the recommendation engine working quietly behind the scenes. As this technology advances, the personalized experiences you encounter online will become increasingly intuitive, making your digital interactions more meaningful and efficient than ever before.
FAQs
Q1. How do recommendation engines improve user experience?
Recommendation engines enhance user experience by saving time, providing personalized content, and introducing users to items they might not have discovered on their own. They analyze user behavior and preferences to offer relevant suggestions, making digital interactions more intuitive and enjoyable.
Q2. What are the main types of recommendation engines?
The main types of recommendation engines are user-based collaborative filtering, item-based collaborative filtering, content-based filtering, and hybrid models. Each type uses different approaches to analyze user preferences and item characteristics to generate personalized recommendations.
Q3. How do businesses benefit from using recommendation engines?
Businesses benefit from recommendation engines through increased revenue, higher engagement rates, improved customer retention, and the ability to offer scalable personalization. These systems can boost conversion rates by 10-15% and contribute to 30-35% of total revenue on major platforms.
Q4. What challenges do recommendation engines face?
Recommendation engines face several challenges, including the cold start problem for new users or items, data sparsity and bias, scalability issues when handling large datasets, and privacy concerns related to data collection and usage.
Q5. How do recommendation engines learn and improve over time?
Recommendation engines improve through a continuous feedback loop. They analyze user interactions with recommendations, incorporate new data, and often use A/B testing to compare different models. This iterative process allows the system to refine its understanding of user preferences and enhance the accuracy of future recommendations.





























Did you enjoy this article?