Types of Computer Network Architecture: An Insightful Guide
Jan 08, 2026 4 Min Read 1517 Views
(Last Updated)
“Computer Network Architecture” is a topic most of us ignore when discussing the working mechanisms of various computing devices, such as mobiles, laptops, or tablets. There is a tendency to jump directly into the step-by-step workflow of these devices without gaining a firm understanding of their architecture.
But in this blog, we will try to break out of this narrow perspective by covering all types of network architecture and how they contribute to an efficient and reliable computing environment. So, let’s begin our discussion without any further ado.
Quick Answer:
Computer network architecture comes in four key types—peer-to-peer, client-server, cloud, and hybrid—each shaping how devices connect, share resources, and power seamless communication.
Table of contents
- Computer Network Architecture: Definition
- Types of Computer Network Architecture
- Peer-to-Peer Architecture
- Client-Server Architecture
- Cloud Architecture
- Hybrid Architecture
- Types of Computer Network Architecture: Overview
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- What factors should I consider before choosing a network architecture?
- Why is the client-server model preferred for large organizations?
- How is a hybrid valuable architecture in real-world systems?
Computer Network Architecture: Definition
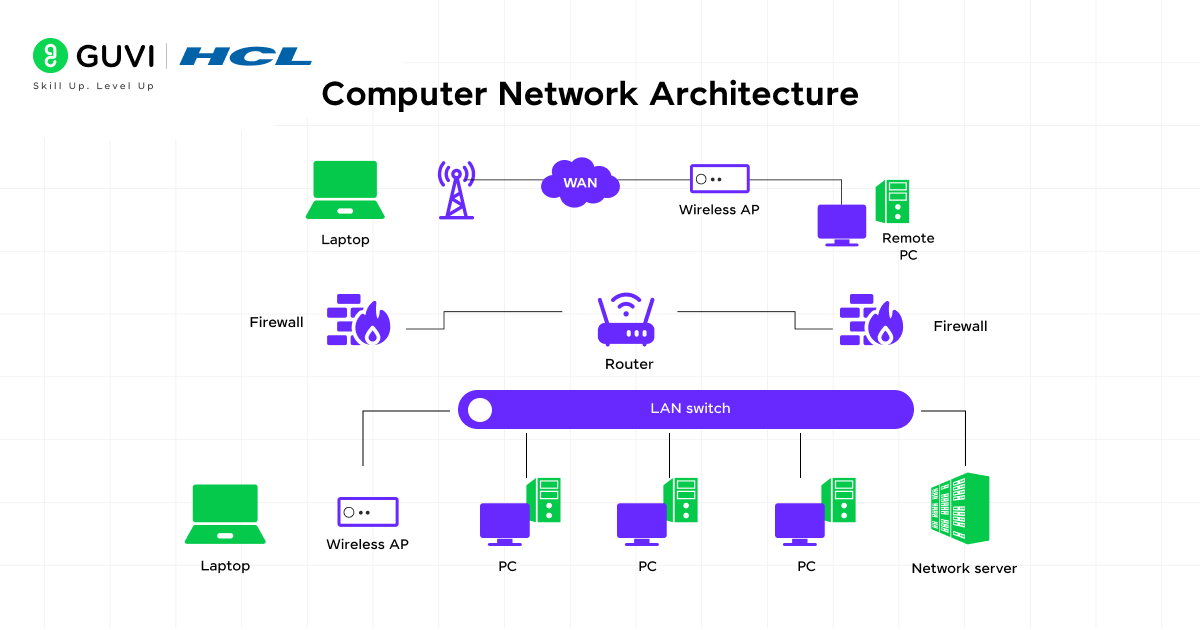
We all know that for any machine to function efficiently with minimal interruptions, it is crucial to ensure that the entity has a proper structure, with all necessary elements organized and appropriately integrated.
In this context, network architecture in computer networks is also necessary, as it defines clear paths and channels for software and hardware components to communicate. There are multiple building blocks of network architecture, such as protocols, hardware, software, network topology, communication layers, and more. These network architecture components work together in synchronization to deliver efficiency, reliability, automation, and scalability.
Most network architectures today are based on the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model, which divides network communication into 7 layers (i.e., 4 Host layers + 3 Media layers).
Moreover, this OSI model facilitates troubleshooting network issues by passing the required inputs through all 7 layers (using a top-down approach). This approach allows it to systematically identify and isolate the problem, confirming security and nominal downtime.
Types of Computer Network Architecture
These are the main types of computer network architecture, each designed to manage how devices connect and communicate. They help define the structure, control, and flow of data in a network.
1. Peer-to-Peer Architecture
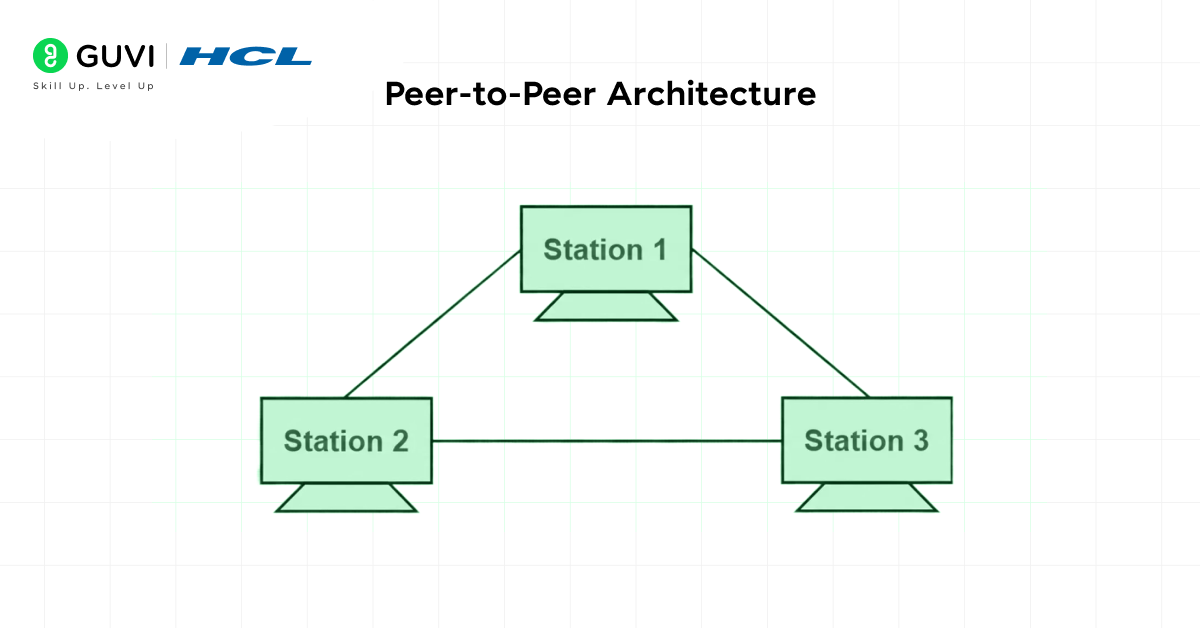
Peer-to-peer (P2P) computer network architecture is a setup in which each integrated device can function as both a client and a server. Here, each computing unit can directly share files, processing power, and other resources with other entities without depending on a single source controller.
This architecture is one of the best examples of how decentralized network systems work by providing equal roles and responsibilities. Due to its structure, it is an ideal option for smaller networks; however, it becomes ineffective for complex, scalable networks.
Pros:
- There is no requirement for a central server, so the setup is cheaper and easier to manage, as each device handles its own operations without depending on a dedicated server.
- Because data and information are shared directly between devices, communication is fast (with fewer delays).
- The communication process in this network architecture doesn’t rely solely on a central server, which is why even if one device stops operating, the others can remain active without interruption.
Cons:
- As the requirements of an organization or business expand, the network architecture needs to be scaled, and strictly adhering to a P2P architecture becomes inefficient, as managing multiple independent devices becomes challenging.
- In general, performance drops significantly when many users try to request large files or run resource-intensive programs.
- If P2P architecture is implemented for complex computing environments, monitoring issues will arise as there is no central unit to track or control the individual systems.
2. Client-Server Architecture
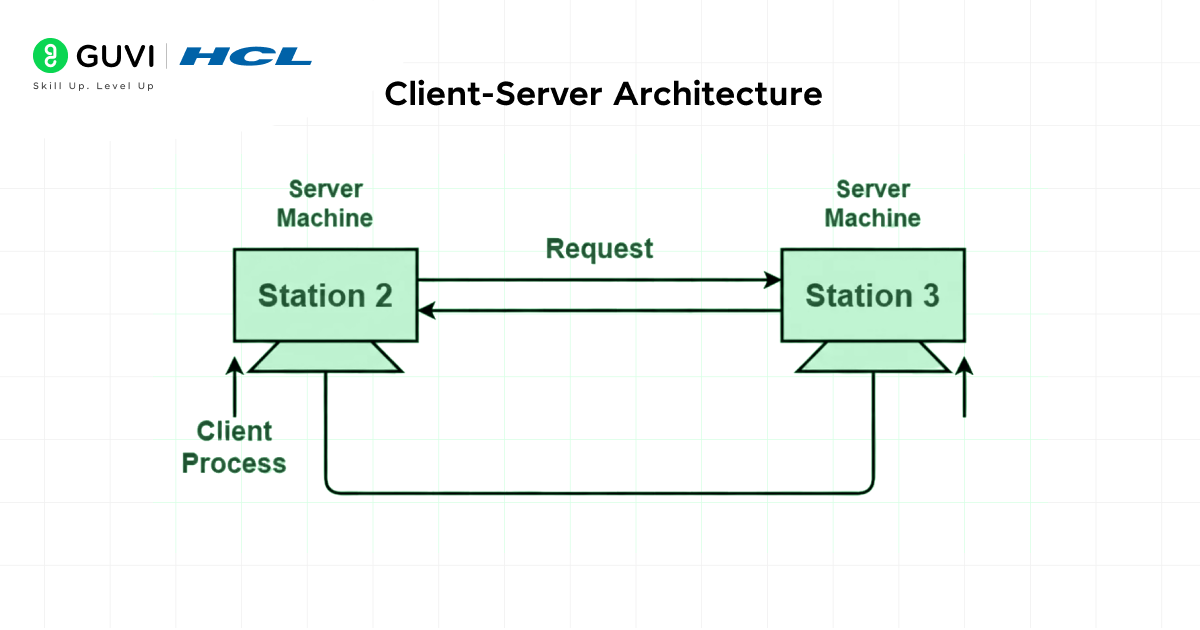
Client-server architecture is a type of centralized network architecture in which client systems (user devices) connect to a central server. This central server is responsible for storing data, managing system resources, and controlling access. In addition to these, the server also handles heavy processing tasks, enhances security, and manages data.
Since all complex and advanced functionality and tasks are executed by the server, the client systems only need to request what they require. As these architectures provide greater stability and support scalability, they are widely implemented in large organizations and enterprise-level operations.
Pros:
- The centralized server system manages the entire operation of the computer network by efficiently handling data, security policies, user access, and resources.
- Expanding the network architecture’s functionality and features is simpler than in other setups; additional users, devices, and services can be seamlessly integrated without affecting overall system performance.
- There is no need to perform redundant tasks (such as managing individual computing units separately) because all critical functions, such as storage, authorization, and updates, are handled by the central server.
Cons:
- The setup costs of the central servers are high, and maintaining them often requires deep technical knowledge.
- As the entire network architecture depends heavily on the central server, even a minor technical issue on the server side can disrupt the whole system.
- There is a significant operational dependency on proficient system administrators to manage configuration, regular updates, and security for the client-server architecture.
3. Cloud Architecture
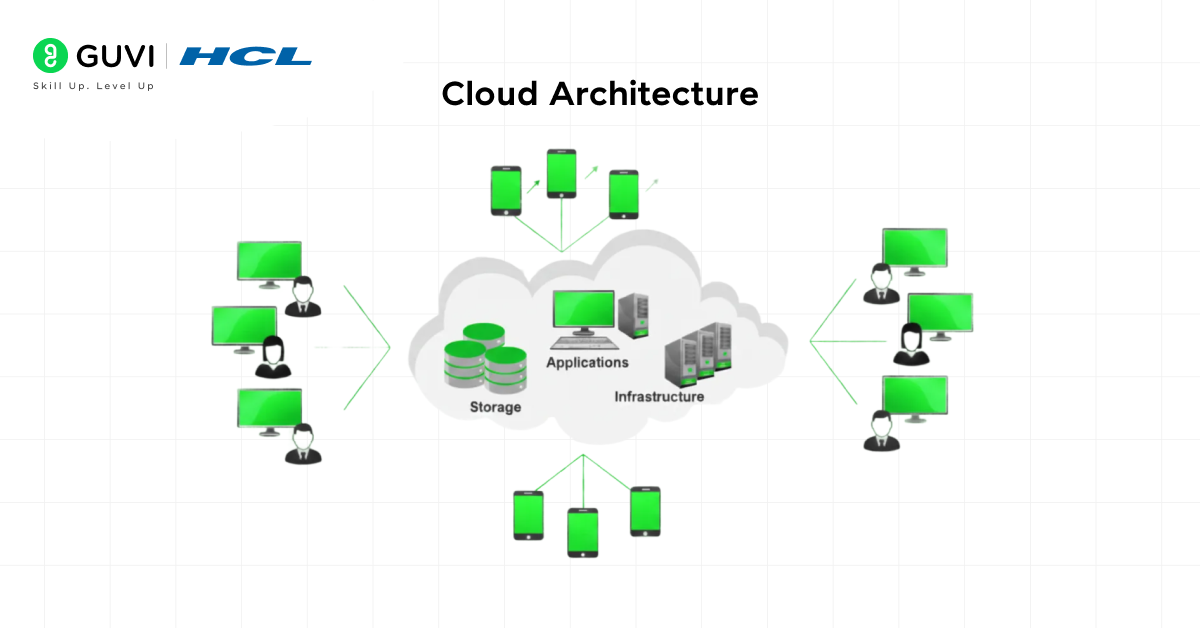
Cloud architectures are among the most advanced computing environments of modern times, providing essential services such as storage, server operations, and app and program execution over the internet rather than on a local hardware system.
All processing takes place on cloud platforms such as AWS, Azure, or GCP, which have their own massive, powerful data centers connected to the internet, and users can easily access resources on demand. This architectural setup offers flexibility, scalability, accessibility, along with minimal hardware maintenance and rapid internal operation.
Pros:
- Users can access applications, data, and services from anywhere, anytime, as long as they have an internet connection.
- As the majority of program execution and business operations take place on cloud platforms, overall hardware costs are significantly reduced.
- In response to evolving business demands, organizations can expand or reduce storage capacity and processing power without investing in new hardware.
Cons:
- Several factors, such as remote areas, network congestion, weak signal strength, or hardware issues, can cause the internet to be slow or unavailable. In situations like this, cloud services can’t be used smoothly (as connectivity is a significant dependency).
- Transferring a large amount of business data to or between cloud systems or providers can be time-consuming, expensive, and technically challenging.
- Storing sensitive data on third-party servers for extended periods can raise security and privacy concerns.
4. Hybrid Architecture
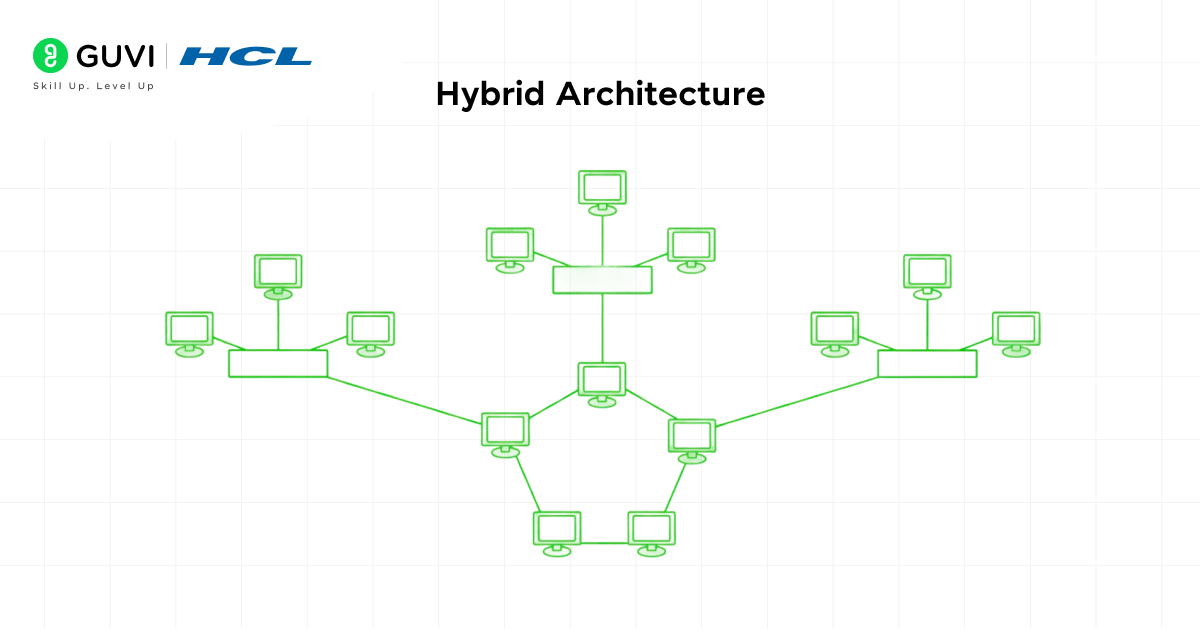
Hybrid architecture is a combination of client-server and peer-to-peer (P2P) network architectures, where overall performance is ensured by the operational efficiency of the centralized network connections and by faster data access and fault tolerance provided by distributed resource sharing.
Both architecture and combining make the entire system reliable, secure, and flexible, enabling it to easily adapt as the network evolves to meet changing needs and requirements. Hybrid network architectures are highly adopted in banking systems, healthcare platforms, automation, and IoT (Internet of Things).
Pros:
- Scalability becomes comparatively straightforward compared to other network architectures by combining the advantages of both P2P and client-server setups.
- There is high stability during the communication process, as this hybrid architecture supports spontaneous device-to-device sharing while supervising all essential operations through the central server.
- Devices can efficiently share resources directly among peers, minimizing load on the central server. This approach improves the system’s flexibility and performance.
Cons:
- Designing and managing the hybrid network architecture is a complex process that involves connecting and synchronizing multiple devices.
- The initial setup cost for this type of network architecture is very high due to the requirement of both central servers and multiple client systems.
- Ensuring uniform access to data and information across both the server and peer devices can be complex, mainly when updates occur at different times.
Types of Computer Network Architecture: Overview
| S.No | Network Architecture | Description | Real-world Examples |
| 1 | Peer-to-Peer (P2P) | Devices share resources directly without a central server. | Home networks, small offices, torrent systems |
| 2 | Client-Server | A central server handles data, security, and user requests. | Banks, schools, corporate networks |
| 3 | Cloud Architecture | Services and storage run on cloud platforms, accessible via the internet. | Google Drive, AWS apps, online CRMs |
| 4 | Hybrid Architecture | Combines client-server and P2P for flexible and balanced performance. | Healthcare systems, banking, and IoT setups |
Boost your tech journey with HCL GUVI’s IITM Pravartak Certified MERN Full Stack Development Course with AI integration. This program helps you build a strong programming base, master both front-end and back-end tzechnologies, and gain real-world experience in databases, system design, and interview preparation. Learn from industry professionals, develop the skills companies look for, and get ready to step into a full-stack development role with confidence. Join now and move closer to your career goals!
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of computer network architecture helps us see how each model handles data, communication, and control. From the simplicity of peer-to-peer networks to the structured approach of client-server systems, and from flexible cloud setups to balanced hybrid models, each architecture serves a specific purpose.
Choosing the right one depends on the network size, security needs, budget, and the level of control required. Together, these architectures form the foundation of modern communication systems and support everything from small home networks to large-scale enterprise environments.
FAQs
What factors should I consider before choosing a network architecture?
You should consider network size, security requirements, budget, performance needs, and the level of control you want over data.
Why is the client-server model preferred for large organizations?
It offers strong security, centralized management, reliable data handling, and easier scaling as the number of users increases.
How is a hybrid valuable architecture in real-world systems?
Hybrid setups provide both flexibility and control by combining multiple architectures, allowing organizations to balance speed, security, and performance.































Did you enjoy this article?