
Unlocking the Secrets of Digital Success: Top 10 Digital Marketing Metrics and KPIs
Sep 15, 2025 10 Min Read 2747 Views
(Last Updated)
What defines the success of a digital marketing strategy? Some would argue it lies in creativity, others point to the budget, but the truth often emerges through numbers. Metrics and KPIs provide evidence of what works and what wastes resources. They show how campaigns affect brand awareness and revenue growth. Without them, even the most ambitious strategy risks being built on assumptions. With them, businesses gain a clear view of progress and the ability to adjust before small issues become larger setbacks.
The following list of the top ten digital marketing metrics and KPIs highlights the measures that matter most for understanding performance and guiding smarter decisions.
- 70% of organizations produce more content, but only 21% can measure if it’s profitable.
- The average e-commerce site converts less than 2% of visitors into customers.
- 89% of marketers say SEO delivers strong results.
- 86% of companies create video content, and 92% call it a vital strategy.
- Passive ad exposure generates 6.7× more value per dollar than active engagement.
- Companies with strong customer success programs see +12% revenue, +19% higher margins, and +15% retention.
Table of contents
- What are Digital Marketing Metrics and KPIs?
- Top 10 Digital Marketing Metrics and KPIs
- Website Traffic
- Bounce Rate
- Organic Search Traffic
- Click-Through Rate (CTR)
- Cost per Click (CPC)
- Social Media Engagement
- Email Open Rate
- Pages per Session
- Average Session Duration
- New vs. Returning Visitors
- Tools for Tracking Digital Marketing Metrics
- Top 10 Digital Marketing Key Performance Indicators
- Conversion Rate
- Cost per Acquisition (CPA)
- Return on Investment (ROI)
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
- Marketing Qualified Leads (MQLs)
- Sales Qualified Leads (SQLs)
- Customer Retention Rate
- Net Promoter Score (NPS)
- Customer Churn Rate
- Lead-to-Customer Rate
- Top Tools for Tracking Digital Marketing KPIs
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- What is the main difference between a metric and a KPI?
- Why should businesses track both metrics and KPIs instead of focusing on one?
- How often should digital marketing metrics and KPIs be reviewed?
- Can metrics and KPIs change depending on the stage of a business?
- What tools can help track digital marketing metrics and KPIs effectively?
What are Digital Marketing Metrics and KPIs?

Digital marketing metrics and KPIs are measurable values that show how well marketing efforts perform against defined objectives. Metrics represent the raw data, such as clicks, impressions, or conversions, which indicate activity and engagement. KPIs stand apart because they connect directly to business goals, such as cost per acquisition or customer lifetime value. Together, they provide a framework that turns performance data into meaningful insights, which helps teams understand impact and align strategies with measurable outcomes.
Top 10 Digital Marketing Metrics and KPIs

1. Website Traffic
Definition:
Website traffic measures the flow of visitors to a site over a specific time frame. It acts as the entry point to evaluating digital performance and reflects how well marketing channels attract attention. It is one of the most vital components for reinforcing Search Engine Optimization parameters for your site.
Importance of Website Traffic:
Traffic is more than a simple count of visitors. It signals brand reach, reveals the strength of campaigns, and highlights the balance between different acquisition sources. A sudden spike can point to a successful campaign, but without relevant engagement, the spike offers little long-term value. Consistent and high-quality traffic provides a stronger base for conversions and supports reliable forecasting of future growth.
Tips to Improve Website Traffic:
- Focus on creating content that answers real customer questions, which improves organic visibility and builds trust
- Strengthen relationships across social platforms where your audience already spends time, which encourages referral traffic beyond paid channels
- Analyze underperforming pages and restructure them with stronger calls-to-action, which helps convert passive visits into active exploration
- Maintain a regular publishing rhythm so that visitors return, which stabilizes recurring traffic rather than relying on occasional spikes
Formula:
- Website Traffic = Number of unique and repeat visitors during a defined period
Also Read: 10 Best Digital Marketing Projects in 2025
2. Bounce Rate
Definition:
Bounce rate represents the percentage of visitors who leave a site after viewing only one page. It highlights the immediate reaction of users and reflects how relevant or engaging the landing experience is.
Importance of Bounce Rate:
A high bounce rate does not always mean poor performance, but it signals areas worth examination. Visitors leaving quickly can point to slow load times or content that does not match their expectations. On the other hand, a single-page session might mean the visitor found the exact answer they needed. The real value comes from analyzing bounce rate alongside traffic sources and page purpose to understand whether the exit reflects satisfaction or a missed opportunity.
Tips to Improve Bounce Rate:
- Improve loading speed, since even a short delay can cause visitors to abandon the page before engaging further
- Align landing page content with the intent behind ads or keywords, which creates continuity between the promise and the experience
- Add clear next steps such as related articles, product recommendations, or a compelling call-to-action, which encourages deeper exploration
- Review mobile usability to make sure design and navigation guide visitors smoothly across the site
Formula:
- Bounce Rate = (Single-page sessions ÷ Total sessions) × 100
3. Organic Search Traffic
Definition:
Organic Search Traffic measures the number of visitors who arrive at a website through unpaid search engine results. It reflects how well a site ranks for relevant queries without relying on ads.
Importance of Organic Search Traffic:
This metric highlights the effectiveness of SEO efforts in attracting consistent, high-quality visitors. Unlike paid traffic, organic traffic compounds over time, delivering long-term value. A steady increase in organic traffic often signals that a brand is building authority and trust with both users and search engines.
Tips to Improve Organic Search Traffic:
- Conduct keyword research to target terms with both volume and intent
- Optimize on-page elements such as titles, meta descriptions, and headings
- Produce high-quality content that answers audience questions in depth
- Strengthen backlinks from authoritative sites to boost domain credibility
Formula:
Organic Search Traffic = Total visitors from unpaid search results in a period
4. Click-Through Rate (CTR)
Definition:
Click-through rate measures the percentage of users who click on a link, ad, or call-to-action after viewing it. It reflects how persuasive and relevant the message is to the audience.
Importance of CTR:
A strong CTR shows that content resonates and grabs attention, while a weak CTR often signals poor targeting or uninspiring copy. High CTRs in ads reduce wasted spend and improve Quality Scores on platforms like Google Ads, which lowers overall costs. Monitoring CTR also helps marketers understand whether their campaigns spark curiosity and move users into deeper stages of the funnel.
Tips to Improve CTR:
- Craft headlines and ad copy that directly address user needs and highlight clear benefits
- Use compelling visuals or rich snippets that stand out in crowded feeds and search results
- Test variations of calls-to-action to identify which wording encourages clicks most effectively
- Segment audiences so messages feel tailored rather than generic, which increases engagement
Formula:
- CTR = (Number of clicks ÷ Number of impressions) × 100
5. Cost per Click (CPC)
Definition:
Cost per Click represents the average amount paid each time a user clicks on a digital ad. It is a vital part of performance marketing and reflects the efficiency of paid campaigns in generating interest.
Importance of CPC:
CPC reveals how competitive your target keywords or audience segments are. A lower CPC means campaigns attract clicks at a more affordable rate, which stretches advertising budgets further. Tracking CPC alongside CTR and conversion rate creates a clearer view of whether paid campaigns are both cost-effective and impactful. Without this balance, campaigns may generate traffic but fail to deliver profitable outcomes.
Tips to Improve CPC:
- Target long-tail keywords with lower competition, which often cost less while attracting higher-quality clicks
- Improve ad relevance and landing page experience to increase Quality Score, which directly reduces CPC in auction-based platforms
- Refine negative keyword lists to avoid paying for irrelevant clicks
- Adjust bidding strategies based on performance data so that spend is concentrated on the most effective segments
Formula:
- CPC = Total ad spend ÷ Total number of clicks
6. Social Media Engagement
Definition:
Social Media Engagement measures the level of interaction users have with a brand’s content across platforms. It includes likes, shares, comments, mentions, and saves, which reflect how audiences connect with posts beyond passive viewing.
Importance of Social Media Engagement:
Engagement signals the strength of the community around a brand. High engagement shows that content resonates enough to spark conversation or sharing, which extends reach organically. It also builds credibility, since audiences are more likely to trust and respond to brands that inspire interaction. Tracking engagement trends helps identify what type of content encourages dialogue and loyalty over time.
Tips to Improve Social Media Engagement:
- Create content that invites responses, such as polls or interactive visuals
- Post consistently at times when the audience is most active to increase visibility
- Respond promptly to comments and messages to build trust and encourage ongoing interaction
- Collaborate with influencers or industry voices to reach new audiences and spark meaningful conversations
Formula:
- Social Media Engagement Rate = (Total interactions ÷ Total followers) × 100
7. Email Open Rate
Definition:
Email Open Rate measures the percentage of recipients who open an email campaign. It reflects the effectiveness of subject lines, sender reputation, and timing.
Importance of Email Open Rate:
A strong open rate means the subject line captures attention, and the audience sees value in receiving communication from the brand. Low open rates often signal weak targeting or declining subscriber trust. Since opens are the first step toward clicks and conversions, tracking this metric ensures email marketing strategies remain relevant and persuasive.
Tips to Improve Email Open Rate:
- Write subject lines that are concise, clear, and focused on the benefit for the reader
- Segment email lists so content feels tailored to specific audience groups
- Maintain a healthy subscriber base by removing inactive addresses and avoiding spam triggers
- Test sending times to identify when subscribers are most likely to open messages
Formula:
- Email Open Rate = (Emails opened ÷ Emails delivered) × 100
8. Pages per Session
Definition:
Pages per Session shows the average number of pages a visitor views during one website visit. It reflects how engaging and interconnected the site’s content is.
Importance of Pages per Session:
A higher number suggests that visitors explore multiple areas of the site, which often signals a strong interest. Low numbers can point to shallow engagement or ineffective internal linking. Tracking this metric helps reveal whether content structure encourages deeper browsing.
Tips to Improve Pages per Session:
- Strengthen internal links to guide visitors naturally across related content
- Add “related posts” or “recommended products” to keep users engaged
- Use clear navigation menus that help users find content of interest quickly
- Ensure pages load quickly to encourage continued browsing
Formula:
Pages per Session = Total page views ÷ Total sessions
9. Average Session Duration
Definition:
Average Session Duration measures the average length of time users spend on a website during a single visit. It highlights how well content holds attention.
Importance of Average Session Duration:
A longer duration often indicates meaningful engagement and strong content relevance. Short sessions may reveal weak content, poor user experience, or unmet expectations. Tracking this metric alongside Pages per Session gives deeper insight into how effectively the site retains attention.
Tips to Improve Average Session Duration:
- Create longer-form content that delivers real depth and value
- Add multimedia like videos or infographics to keep visitors engaged
- Break content into scannable sections with clear subheadings
- Ensure page design supports readability across devices
Formula:
Average Session Duration = Total session time ÷ Total sessions
Explore: Why Digital Marketing is the Skill of the Future (+ Free 5-Day Email Course to Get You Started)
10. New vs. Returning Visitors
Definition:
This metric tracks the ratio of first-time visitors compared with those who return. It reflects both reach and loyalty.
Importance of New vs. Returning Visitors:
A balanced ratio indicates that marketing efforts bring in fresh traffic while also keeping existing audiences engaged. A skew heavily toward new visitors may reveal weak retention, while too much reliance on returning visitors might show stagnant reach. Both perspectives are crucial for evaluating growth potential.
Tips to Improve New vs. Returning Visitors:
- Use retargeting and remarketing campaigns to encourage return visits
- Deliver ongoing content updates that give audiences reasons to come back
- Offer subscription options or email signups to retain interest
- Expand SEO and ad strategies to capture new audiences regularly
Formula:
New vs. Returning Visitors = (New visitors ÷ Returning visitors) ratio over time
Tools for Tracking Digital Marketing Metrics
| Tool | Primary Use for Metrics | Why It’s Effective |
| Google Analytics 4 (GA4) | Website traffic, bounce rate, pages/session, session duration | Provides detailed insights into user behavior and site performance. |
| SEMrush / Ahrefs | Impressions, clicks, and CTR for organic search | Strong SEO tracking to measure visibility and ranking. |
| Google Search Console | Email open rate, CTR, and unsubscribes | Direct insights from Google on search performance and indexing. |
| Hootsuite / Buffer | Social media engagement metrics (likes, shares, comments) | Centralized dashboard for managing and measuring multiple platforms. |
| Mailchimp / HubSpot Email | Heatmaps, session recordings, and on-page behavior | Tracks campaign engagement at the inbox level with automation. |
| Hotjar / Crazy Egg | Heatmaps, session recordings, on-page behavior | Visualizes how users interact with web pages for UX optimization. |
Top 10 Digital Marketing Key Performance Indicators
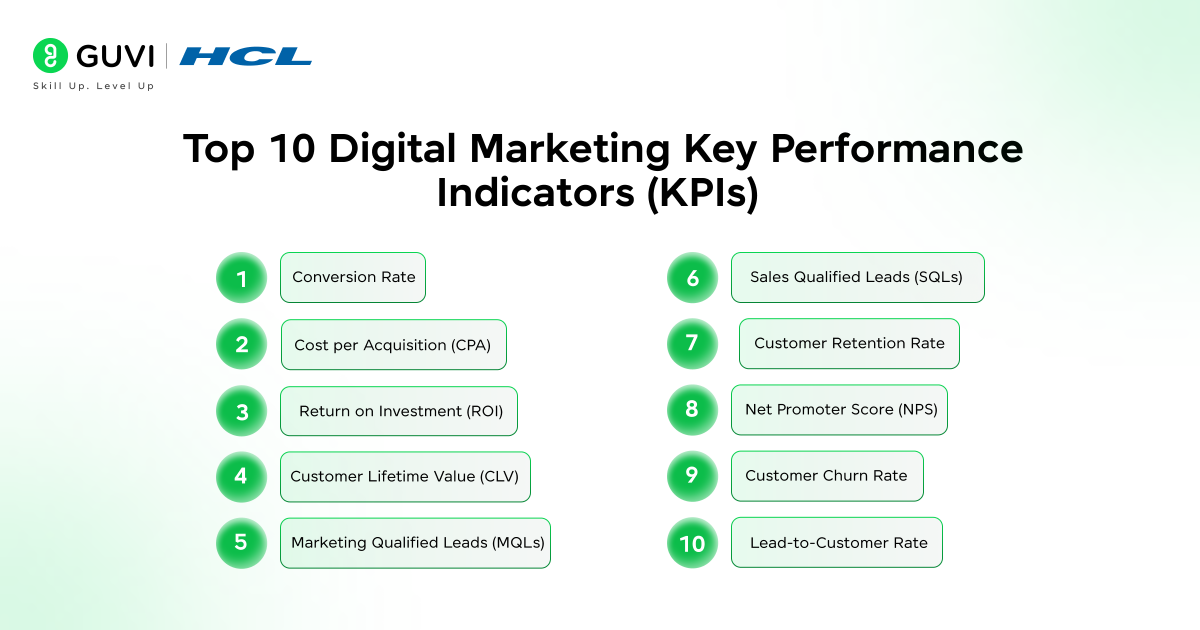
1. Conversion Rate
Definition:
Conversion rate measures the percentage of visitors who take a desired action, such as signing up for a newsletter, completing a purchase, or filling out a form. It connects website activity directly to business outcomes.
Importance of Conversion Rate:
A steady flow of traffic means little without conversions. This metric shows whether marketing efforts attract the right audience and whether the website experience supports decision-making. A low rate often signals friction points such as confusing navigation, weak messaging, or lack of trust signals. Tracking conversion rate across different channels and campaigns also clarifies which investments deliver the highest return.
Tips to Improve Conversion Rate:
- Simplify forms and checkout processes so visitors can complete actions without unnecessary steps
- Use clear and persuasive calls-to-action that guide visitors toward the next step
- Test variations of headlines, images, and layouts to identify what resonates best with the audience
- Strengthen trust with reviews, testimonials, and security badges that reduce hesitation before committing
Formula:
- Conversion Rate = (Number of conversions ÷ Total visitors) × 100
2. Cost per Acquisition (CPA)
Definition:
Cost per Acquisition measures the average expense required to gain a new customer. It includes advertising spend, campaign costs, or other direct investments tied to conversions.
Importance of Cost per Acquisition:
CPA reveals how efficiently marketing budgets translate into paying customers. A low cost indicates that campaigns attract the right audience with strong conversion potential, while a rising CPA can highlight issues with targeting, bidding, or message relevance. Comparing CPA with Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) helps determine whether growth is sustainable or whether acquisition costs outweigh long-term returns.
Explore More: Top 10 Conversion Rate Optimization Techniques for 2025
Tips to Improve CPA:
- Refine targeting criteria to reach audiences most likely to convert, which reduces wasted impressions
- Use remarketing strategies to re-engage users already familiar with your brand, which lowers acquisition costs
- Test ad creatives and landing pages in parallel to identify which combinations deliver the best performance
- Monitor campaign spend closely across platforms and shift budget toward the highest-yielding channels
Formula:
- CPA = Total campaign cost ÷ Number of acquisitions
3. Return on Investment (ROI)
Definition:
Return on Investment measures the profitability of marketing efforts by comparing the revenue generated to the total costs incurred. It is one of the most direct ways to evaluate campaign effectiveness.
Importance of ROI:
Positive ROI shows that campaigns deliver more value than they cost, while negative ROI signals a drain on resources. Tracking ROI across different channels highlights where budget produces the greatest impact. It also helps leadership make confident decisions about scaling efforts or reallocating spend. A strong ROI is essential for proving marketing’s contribution to overall business growth.
Tips to Improve ROI:
- Set clear objectives for each campaign so performance can be measured against tangible outcomes
- Optimize campaigns continuously by analyzing which ads, keywords, or audiences produce the best returns
- Invest more heavily in channels that show consistent profitability and reduce spend on underperforming ones
- Incorporate automation tools that save time and reduce wasted effort on repetitive tasks
Formula:
- ROI = (Revenue generated − Cost of investment) ÷ Cost of investment × 100
4. Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
Definition:
Customer Lifetime Value estimates the total revenue a business can expect from one customer over the entire relationship.
Importance of CLV:
A high CLV signals strong retention and loyalty, which allows businesses to invest more in acquisition with confidence. When CLV is lower than CPA, growth becomes unsustainable. Tracking CLV helps identify the long-term impact of marketing strategies and whether customer relationships truly drive profitability.
Tips to Improve CLV:
- Build loyalty programs that reward repeat purchases
- Personalize communication to encourage customers to return more often
- Improve customer support to strengthen satisfaction and retention
- Cross-sell and upsell products that extend the customer journey
Formula:
CLV = Average purchase value × Purchase frequency × Customer lifespan
5. Marketing Qualified Leads (MQLs)
Definition:
Marketing Qualified Leads are potential customers identified as more likely to convert based on specific engagement criteria such as form submissions, downloads, or interactions with content.
Importance of MQLs:
This KPI shows the effectiveness of campaigns in generating leads with genuine interest. A steady flow of MQLs supports the sales pipeline and provides insight into whether campaigns attract audiences with real intent. Weak MQL numbers may signal a need for better targeting or more relevant offers.
Tips to Improve MQLs:
- Create gated content like whitepapers or webinars that encourage form fills
- Use lead scoring systems to qualify prospects more accurately
- Align marketing and sales teams so definitions of MQLs remain consistent
- Optimize landing pages and CTAs for higher lead capture
Formula:
MQLs = Number of leads meeting qualification criteria in a period
6. Sales Qualified Leads (SQLs)
Definition:
Sales Qualified Leads are prospects that meet both marketing and sales criteria, meaning they are ready for direct outreach by sales teams.
Importance of SQLs:
This KPI demonstrates how efficiently marketing converts interest into sales opportunities. A healthy pipeline of SQLs reduces wasted sales effort and increases revenue potential. A gap between MQLs and SQLs often reveals misalignment between teams or weak lead nurturing.
Tips to Improve SQLs:
- Use lead nurturing campaigns that move prospects from interest to purchase readiness
- Refine qualification criteria with input from sales teams
- Provide case studies and testimonials that build trust during the decision stage
- Track lead behavior to prioritize the most engaged prospects
Formula:
SQLs = Number of leads approved by sales for direct engagement
7. Customer Retention Rate
Definition:
Customer Retention Rate measures the percentage of customers who continue to do business with a company over a given time period.
Importance of Retention Rate:
High retention indicates loyalty and long-term satisfaction, which reduces pressure on acquisition spending. Losing customers faster than gaining them can quickly undermine growth. Retention also has a direct impact on CLV, making it one of the most important KPIs for sustainable performance.
Tips to Improve Retention Rate:
- Maintain regular communication with personalized updates or offers
- Gather customer feedback and resolve issues quickly
- Provide value beyond the purchase, such as educational resources or exclusive benefits
- Build loyalty programs that reward long-term commitment
Formula:
Retention Rate = ((Customers at end of period − New customers during period) ÷ Customers at start of period) × 100
8. Net Promoter Score (NPS)
Definition:
Net Promoter Score measures customer loyalty by asking how likely they are to recommend a brand to others, typically on a scale from 0 to 10.
Importance of NPS:
This KPI highlights how customers feel about their overall experience. A high score signals strong advocacy, which often leads to organic referrals. Low scores reveal dissatisfaction that may hurt retention and growth. Monitoring NPS provides valuable feedback on both product quality and customer experience.
Tips to Improve NPS:
- Actively gather customer feedback and close the loop by addressing concerns
- Strengthen onboarding processes to build early satisfaction
- Deliver consistent, high-quality support that exceeds expectations
- Reward and recognize loyal customers who promote the brand
Formula:
NPS = % of Promoters (9–10) − % of Detractors (0–6)
9. Customer Churn Rate
Definition:
Churn Rate measures the percentage of customers lost during a specific time period. It directly shows how well a business retains its customer base.
Importance of Churn Rate:
High churn signals poor retention strategies, weak engagement, or product dissatisfaction. Keeping churn low is crucial for profitability, since retaining customers is usually more cost-effective than acquiring new ones. Churn also provides a direct counterbalance to retention rate.
Tips to Improve Churn Rate:
- Provide ongoing value through loyalty programs or exclusive benefits
- Use customer feedback to identify and address pain points
- Create personalized re-engagement campaigns for inactive users
- Deliver consistent communication that reminds customers of product value
Formula:
Churn Rate = (Customers lost during period ÷ Customers at start of period) × 100
10. Lead-to-Customer Rate
Definition:
Lead-to-Customer Rate tracks the percentage of leads that successfully convert into paying customers. It connects marketing efforts to actual revenue outcomes.
Importance of Lead-to-Customer Rate:
This KPI reveals how effectively the sales funnel turns interest into results. A low rate suggests gaps in lead quality, nurturing strategies, or the sales process. A strong rate shows alignment between marketing and sales teams and confirms that leads generated are truly valuable.
Tips to Improve Lead-to-Customer Rate:
- Align lead qualification criteria between marketing and sales teams
- Use nurturing campaigns that address objections and build trust
- Provide sales teams with insights from marketing about lead behavior
- Offer tailored content for different funnel stages to guide prospects toward purchase
Formula:
Lead-to-Customer Rate = (New customers ÷ Total leads) × 100
Top Tools for Tracking Digital Marketing KPIs
| Tool | Primary Use for KPIs | Why It’s Effective |
| HubSpot CRM | Conversion rate, MQLs, SQLs, lead-to-customer rate | Integrates marketing and sales for tracking customer journey KPIs. |
| Salesforce | Customer retention rate, churn, pipeline health | Enterprise-level CRM for KPI alignment across teams. |
| Google Ads Manager | Cost per acquisition (CPA), ROI, CPC | Monitors paid campaign ROI and spend efficiency. |
| Tableau / Power BI | Custom dashboards for ROI, NPS, retention | Turns raw data into visual, executive-level KPI dashboards. |
| Qualtrics / SurveyMonkey | Net Promoter Score (NPS), customer satisfaction KPIs | Captures direct customer feedback to measure loyalty and advocacy. |
| Mixpanel / Amplitude | Customer lifetime value (CLV), retention rate | Product and user journey analytics to tie activity to business outcomes. |
Unlock your digital career potential with our Digital Marketing Course! Gain industry-relevant expertise through mentor-led live sessions, hands-on projects, and a job-ready curriculum designed to make you stand out. Learn SEO, SEM, Social Media, Email Marketing, Content Strategy, and Analytics, all while receiving 1:1 mentorship from industry experts. With guaranteed placement support, globally recognized certifications, and a thriving community of learners, this course equips you with the tools and confidence to excel in today’s competitive digital landscape. Start mastering digital marketing and secure your career growth today!
Conclusion
Success and scope of digital marketing depends on more than creativity or budget, as it depends on clarity. Metrics reveal patterns in audience behavior, while KPIs connect those patterns directly to business outcomes. Together, they form the lens through which strategy becomes measurable and performance becomes actionable.
Businesses that track both avoid the trap of assumptions and base their growth on evidence instead of guesswork. Metrics show what attracts attention, and KPIs show what drives profit. The combination highlights strengths, exposes weaknesses, and guides the adjustments that keep strategies aligned with goals.
The real advantage lies in consistent monitoring and thoughtful interpretation. Numbers alone do not create progress, but the insights drawn from them direct smarter decisions, stronger campaigns, and sustainable success.
FAQs
What is the main difference between a metric and a KPI?
A metric tracks activity or behavior (like clicks or sessions), while a KPI directly ties that activity to a business goal (like conversion rate or customer retention). All KPIs are metrics, but not all metrics are KPIs.
Why should businesses track both metrics and KPIs instead of focusing on one?
Metrics show what is happening, but KPIs explain why it matters. Tracking both creates context, metrics highlight performance details, and KPIs confirm whether those details are helping the business grow.
How often should digital marketing metrics and KPIs be reviewed?
It depends on the business and campaign. Some (like CPC or CTR) should be reviewed weekly or even daily to control spend, while others (like retention or ROI) make more sense to review monthly or quarterly for long-term insights.
Can metrics and KPIs change depending on the stage of a business?
Yes. Startups might prioritize metrics like website traffic or MQLs to build awareness, while mature businesses focus on KPIs like ROI, CLV, or churn rate to maximize profitability and efficiency.
What tools can help track digital marketing metrics and KPIs effectively?
Popular tools include Google Analytics (traffic and engagement), HubSpot (leads and conversions), SEMrush (SEO performance), and CRM platforms like Salesforce (sales and retention KPIs). The right mix depends on business goals and available resources.

































Did you enjoy this article?