
Spring Boot 3.x Interview Prep: Latest 50 Questions for Backend Engineers
Aug 19, 2025 6 Min Read 2204 Views
(Last Updated)
Are you preparing for backend interviews and feeling overwhelmed by the new features in Spring Boot 3.x? You’re not alone. With the shift to Java 17+, Jakarta EE, and native image support, Spring Boot has evolved significantly, and so have the interview questions.
Spring Boot is a powerful framework for building Java-based enterprise applications quickly and efficiently. This guide brings you 50 of the most relevant and frequently asked Spring Boot 3.x interview questions, covering everything from core concepts and auto-configuration to security, caching, microservices, and performance tuning.
Table of contents
- A. Core Spring Boot Questions
- What is Spring Boot?
- What are the key features of Spring Boot?
- What is the difference between Spring and Spring Boot?
- What is the latest version of Spring Boot?
- What are the system requirements for Spring Boot 3.x?
- B. Spring Boot Auto-Configuration & Starters
- What is Spring Boot Auto-Configuration?
- How does Spring Boot Auto-Configuration work?
- What are Spring Boot Starters?
- How to exclude auto-configuration classes?
- C. Spring Boot Annotations
- What is @SpringBootApplication?
- What is @RestController vs @Controller?
- What is @RequestMapping vs @GetMapping/@PostMapping?
- What is @Autowired?
- What is @Bean?
- D. Spring Boot Properties & Configuration
- What is application.properties/application.yml?
- How to read custom properties in Spring Boot?
- What are Spring Boot Profiles?
- How to activate a profile?
- E. Spring Boot Actuator
- What is Spring Boot Actuator?
- How to enable the Actuator?
- F. Spring Boot Database & JPA
- How to configure a database in Spring Boot?
- What is spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto?
- What is @Entity?
- What is @Repository?
- G. Spring Boot Security
- How to secure a Spring Boot application?
- H. Spring Boot Testing
- What is @SpringBootTest?
- What is @MockBean?
- I. Spring Boot REST API
- How to create a REST API in Spring Boot?
- What is ResponseEntity?
- J. Spring Boot Exception Handling
- How to handle exceptions in Spring Boot?
- K. Spring Boot Caching
- How to enable caching in Spring Boot?
- L. Spring Boot Deployment
- How to deploy a Spring Boot application?
- M. Spring Boot Microservices
- What is Spring Cloud?
- N. Spring Boot Best Practices
- What are Spring Boot's best practices?
- O. Advanced Spring Boot Questions
- What’s new in Spring Boot 3.x?
- P. Spring Boot Transactions
- What is @Transactional in Spring Boot?
- What are the propagation behaviors in @Transactional?
- Q. Spring Boot AOP (Aspect-Oriented Programming)
- What is Spring AOP?
- What are the key AOP annotations?
- R. Spring Boot Caching
- How to enable caching in Spring Boot?
- What are the different cache providers supported?
- S. Spring Boot Testing
- What is @WebMvcTest?
- What is @DataJpaTest?
- T. Spring Boot Security (OAuth2 & JWT)
- How to implement JWT authentication in Spring Boot?
- What is OAuth2 in Spring Boot?
- U. Spring Boot Monitoring & Observability
- What is Micrometer in Spring Boot?
- How to integrate Prometheus with Spring Boot?
- V. Spring Boot Native Image (GraalVM)
- What is Spring Native?
- W. Spring Boot Best Practices
- How to improve Spring Boot performance?
- What are the common pitfalls in Spring Boot?
- Conclusion
A. Core Spring Boot Questions
1. What is Spring Boot?
Spring Boot is an open-source Java-based framework used to create stand-alone, production-grade Spring applications with minimal configuration. It simplifies Spring application development by providing auto-configuration, embedded servers, and starter dependencies.
2. What are the key features of Spring Boot?
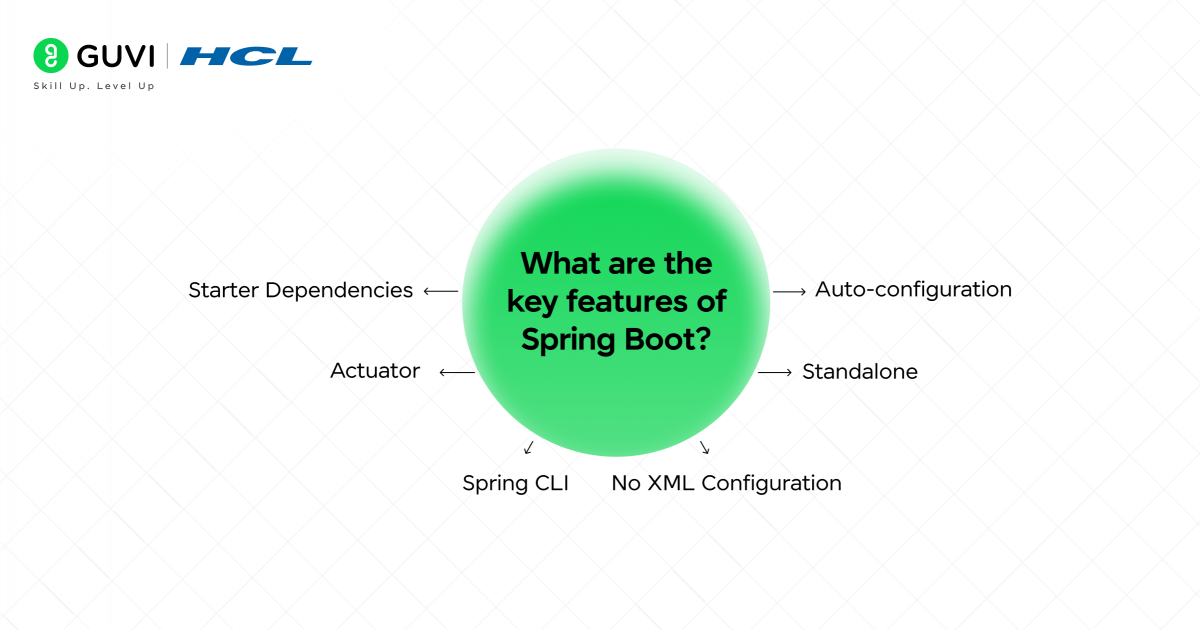
- Auto-configuration – Automatically configures Spring applications based on dependencies.
- Standalone – No need for external servers; includes embedded Tomcat, Jetty, or Undertow.
- Starter Dependencies – Simplifies dependency management (e.g., spring-boot-starter-web).
- Actuator – Provides production-ready features like health checks and metrics.
- Spring CLI – Allows rapid development using Groovy scripts.
- No XML Configuration – Uses Java-based or annotation-based configuration.
3. What is the difference between Spring and Spring Boot?

| Spring | Spring Boot |
| Requires manual configuration. | Provides auto-configuration. |
| No embedded server; needs external setup. | Comes with embedded servers. |
| Developers must define dependencies manually. | Starter POMs simplify dependency management. |
| More boilerplate code. | Reduces boilerplate code. |
4. What is the latest version of Spring Boot?
As of 2025, Spring Boot 3.x is the latest stable release, based on Spring Framework 6.x and Java 17+.
5. What are the system requirements for Spring Boot 3.x?
- Java 17+ (mandatory)
- Spring Framework 6.x
- Compatible with Jakarta EE 9+ (replaces javax with jakarta packages)
B. Spring Boot Auto-Configuration & Starters
6. What is Spring Boot Auto-Configuration?
Auto-configuration automatically configures the Spring application based on the dependencies present in the classpath. For example, if the H2 database is in the classpath, Spring Boot auto-configures an in-memory database.
7. How does Spring Boot Auto-Configuration work?
- It scans the classpath for dependencies.
- Uses @Conditional annotations (e.g., @ConditionalOnClass, @ConditionalOnMissingBean) to decide which beans to configure.
- Defined in META-INF/spring/org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports (Spring Boot 3.x).
8. What are Spring Boot Starters?
Starters are dependency descriptors that bundle common dependencies. Examples:
- spring-boot-starter-web – For web applications.
- spring-boot-starter-data-jpa – For JPA and Hibernate.
- spring-boot-starter-test – For testing.
9. How to exclude auto-configuration classes?
Use @SpringBootApplication(exclude = {DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class}) or in application.properties:
spring.autoconfigure.exclude=org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration
C. Spring Boot Annotations
10. What is @SpringBootApplication?
It is a combination of:
- @Configuration – Marks the class as a configuration class.
- @EnableAutoConfiguration – Enables auto-configuration.
- @ComponentScan – Scans for components in the package.
11. What is @RestController vs @Controller?
- @Controller – Used for traditional Spring MVC (returns view names).
- @RestController = @Controller + @ResponseBody (returns JSON/XML responses directly).
12. What is @RequestMapping vs @GetMapping/@PostMapping?
- @RequestMapping – Generic mapping (supports all HTTP methods).
- @GetMapping, @PostMapping – Shortcut annotations for specific HTTP methods.
13. What is @Autowired?
Used for dependency injection. Spring automatically injects the required beans.
14. What is @Bean?
Used in configuration classes to define a Spring bean:
@Bean
public RestTemplate restTemplate() {
return new RestTemplate();
}D. Spring Boot Properties & Configuration
15. What is application.properties/application.yml?
Files used to configure Spring Boot applications. Example:
server.port=8081
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:mem:testdb
16. How to read custom properties in Spring Boot?
Using @Value:
@Value("${custom.property}")
private String customProperty;
Or using @ConfigurationProperties:
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "app")
public class AppConfig {
private String name;
// Getters & Setters
}17. What are Spring Boot Profiles?
Profiles allow different configurations for different environments (e.g., dev, prod). Use application-{profile}.properties.
18. How to activate a profile?
In application.properties:spring.profiles.active=devVia command line:java -jar app.jar --spring.profiles.active=prod
E. Spring Boot Actuator
19. What is Spring Boot Actuator?
A module that provides production-ready features like:
- Health checks (/actuator/health)
- Metrics (/actuator/metrics)
- Environment details (/actuator/env)
20. How to enable the Actuator?
Add the dependency:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
Configure endpoints in application.properties:
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*F. Spring Boot Database & JPA
21. How to configure a database in Spring Boot?
Use application.properties:
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=root
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update22. What is spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto?
- None – No schema generation.
- Update – Updates schema if needed.
- create – Creates schema on startup (drops old data).
- create-drop – Creates on startup, drops on shutdown.
23. What is @Entity?
Marks a class as a JPA entity (maps to a database table).
24. What is @Repository?
Used in DAO classes for database operations. Extends JpaRepository.
G. Spring Boot Security
25. How to secure a Spring Boot application?
Add spring-boot-starter-security:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>Configure security in a @Configuration class extending WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter (deprecated in Spring Boot 3.x) or using SecurityFilterChain.
H. Spring Boot Testing
26. What is @SpringBootTest?
Used for integration testing (loads the full application context).
27. What is @MockBean?
Used to mock a bean in the Spring context (useful in testing).
I. Spring Boot REST API
28. How to create a REST API in Spring Boot?
- Use @RestController.
- Define endpoints (@GetMapping, @PostMapping).
- Use @RequestBody for POST/PUT requests.
29. What is ResponseEntity?
A wrapper for HTTP responses (status code, headers, body).
J. Spring Boot Exception Handling
30. How to handle exceptions in Spring Boot?
- Use @ControllerAdvice for global exception handling.
- Use @ExceptionHandler to handle specific exceptions.
K. Spring Boot Caching
31. How to enable caching in Spring Boot?
Add @EnableCaching and use @Cacheable on methods.
L. Spring Boot Deployment
32. How to deploy a Spring Boot application?
- As a JAR (embedded server): java -jar app.jar.
- As a WAR (external server like Tomcat).
M. Spring Boot Microservices
33. What is Spring Cloud?
A set of tools for building microservices (e.g., Eureka, Zuul, Config Server).
N. Spring Boot Best Practices
34. What are Spring Boot’s best practices?
- Use DTOs instead of entities in APIs.
- Follow layered architecture (Controller → Service → Repository).
- Use proper logging (SLF4J with Logback).
- Validate inputs (Bean Validation).
- Secure APIs (OAuth2, JWT).
O. Advanced Spring Boot Questions
35. What’s new in Spring Boot 3.x?
- Java 17+ baseline.
- Jakarta EE 9+ (replaced javax with jakarta).
- Improved Native Image Support (GraalVM).
- Enhanced Observability (Micrometer, OpenTelemetry).
P. Spring Boot Transactions
36. What is @Transactional in Spring Boot?
@Transactional ensures that a method executes within a database transaction. If an exception occurs, the transaction rolls back.
Example:
@Transactional
public void transferMoney(Account from, Account to, double amount) {
from.debit(amount);
to.credit(amount);
}37. What are the propagation behaviors in @Transactional?
- REQUIRED (Default) – Uses existing transactions or creates a new one.
- REQUIRES_NEW – Always creates a new transaction.
- SUPPORTS – Runs in a transaction if one exists, else non-transactional.
- NOT_SUPPORTED – Executes non-transactionally.
- MANDATORY – Must run within an existing transaction (else throws an exception).
- NEVER – Must not run within a transaction (else throws an exception).
- NESTED – Creates a nested transaction (if supported by the database).
Q. Spring Boot AOP (Aspect-Oriented Programming)
38. What is Spring AOP?
Spring AOP allows cross-cutting concerns (logging, security, transactions) to be modularized using aspects.
39. What are the key AOP annotations?
- @Aspect – Declares a class as an aspect.
- @Before – Runs before a method.
- @After – Runs after a method (success or failure).
- @Around – Wraps a method (can modify input/output).
- @AfterReturning – Runs after successful execution.
- @AfterThrowing – Runs if an exception occurs.
Example:
@Aspect
@Component
public class LoggingAspect {
@Before("execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..))")
public void logBefore(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("Method called: " + joinPoint.getSignature());
}
} R. Spring Boot Caching
40. How to enable caching in Spring Boot?
- Add spring-boot-starter-cache:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>Enable caching with @EnableCaching.
Use @Cacheable on methods:
@Cacheable("products")
public Product getProductById(Long id) {
return productRepository.findById(id).orElse(null);
} 41. What are the different cache providers supported?
- Caffeine (Default in Spring Boot 3.x)
- EhCache
- Redis
- Hazelcast
S. Spring Boot Testing
42. What is @WebMvcTest?
Used for testing Spring MVC controllers (without loading the full application context).
Example:
@WebMvcTest(ProductController.class)
public class ProductControllerTest {
@Autowired
private MockMvc mockMvc;
@MockBean
private ProductService productService;
@Test
public void testGetProduct() throws Exception {
when(productService.getProduct(1L)).thenReturn(new Product(1L, "Laptop"));
mockMvc.perform(get("/products/1"))
.andExpect(status().isOk());
}
} 43. What is @DataJpaTest?
Used for testing JPA repositories (configures an in-memory database).
Example:
@DataJpaTest
public class ProductRepositoryTest {
@Autowired
private TestEntityManager entityManager;
@Autowired
private ProductRepository productRepository;
@Test
public void testFindById() {
Product product = new Product(1L, "Laptop");
entityManager.persist(product);
assertThat(productRepository.findById(1L)).isPresent();
}
} T. Spring Boot Security (OAuth2 & JWT)
44. How to implement JWT authentication in Spring Boot?
- Add dependencies:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.jsonwebtoken</groupId>
<artifactId>jjwt-api</artifactId>
<version>0.11.5</version>
</dependency> 2. Configure SecurityFilterChain:
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain securityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.csrf().disable()
.authorizeHttpRequests(auth -> auth
.requestMatchers("/auth/login").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated())
.sessionManagement(sess -> sess.sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS))
.addFilterBefore(jwtAuthFilter, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class);
return http.build();
} 45. What is OAuth2 in Spring Boot?
OAuth2 is an authorization framework that allows third-party apps to access user data without exposing credentials.
Key components:
- Resource Server (e.g., REST API)
- Authorization Server (e.g., Keycloak, Okta)
- Client (e.g., Web/Mobile App)
U. Spring Boot Monitoring & Observability
46. What is Micrometer in Spring Boot?
Micrometer is a metrics instrumentation library used for monitoring (supports Prometheus, Grafana, etc.).
Example:
@RestController
public class MetricController {
private final Counter requestCounter;
public MetricController(MeterRegistry registry) {
requestCounter = registry.counter("api.requests.count");
}
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
requestCounter.increment();
return "Hello!";
}
} 47. How to integrate Prometheus with Spring Boot?
- Add dependencies:
<dependency>
<groupId>io.micrometer</groupId>
<artifactId>micrometer-registry-prometheus</artifactId>
</dependency> 2. Enable Prometheus endpoint in application.properties:
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=prometheus,health,metrics
V. Spring Boot Native Image (GraalVM)
48. What is Spring Native?
Spring Native allows compiling Spring Boot apps into native executables (using GraalVM) for faster startup (~100ms).
How to use it?
- Add dependency:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.experimental</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-native</artifactId>
<version>0.12.1</version>
</dependency>2. Build a native image:
mvn spring-boot:build-image W. Spring Boot Best Practices
49. How to improve Spring Boot performance?
- Use connection pooling (HikariCP).
- Enable caching (@Cacheable).
- Use Lombok to reduce boilerplate code.
- Avoid circular dependencies.
- Use asynchronous processing (@Async).
50. What are the common pitfalls in Spring Boot?
- Using @Autowired on fields (prefer constructor injection).
- Ignoring transaction management (leads to DB inconsistencies).
- Not handling exceptions properly (use @ControllerAdvice).
- Hardcoding configurations (use @ConfigurationProperties).
If you want to learn more about Full-stack development and become well-versed in Backend Development, consider enrolling in GUVI’s IIT-M Pravartak certified Full-Stack Development Course with AI Tools, which provides you with all the resources and guidance to have a successful full-stack career!
Conclusion
In conclusion, mastering Spring Boot 3.x means more than just knowing how to build an API—it’s about understanding how the framework works under the hood, how it’s changing with modern Java, and how to architect scalable, secure applications.
Whether you’re a junior developer brushing up or a seasoned engineer targeting senior roles, these questions cover the depth and breadth you’ll need to walk into your next backend interview with confidence.

































Did you enjoy this article?