
Software Requirements Specification (SRS): Everything You Should Know
Nov 01, 2025 5 Min Read 1400 Views
(Last Updated)
In software development, a clear requirements document is essential for translating stakeholder objectives into practical solutions. Without it, developers may struggle to understand what features to build, leading to challenges for both the technical team and business stakeholders throughout the development cycle.
To avoid such unprofessional and vague situations, a Software Requirements Specification (SRS) is prepared to guide the development team and provide them with clarity on the essential elements to be developed and the additional integrations that should be implemented to enhance the project’s performance, speed, and overall quality.
In this blog, we will explore the importance of SRS documents and how they reflect the needs of clients or users, guiding developers to build the right product.
Table of contents
- What Is a Software Requirements Specification (SRS) and What is its Significance in Software Engineering?
- Purpose and Importance of Software Requirements Specification (SRS)
- Benefits of Software Requirements Specification (SRS)
- Characteristics of Software Requirements Specification (SRS)
- Types of Software Requirements Specification (SRS) Document
- Functional Requirements
- Non-Functional Requirements
- Role of Software Requirements Specification (SRS) in Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) Process
- How to Write a Software Requirements Specification (SRS) Using a Template That Includes All Essential Components
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- What exactly is a Software Requirements Specification (SRS), and why do we need it?
- Why is preparing a detailed SRS considered important before starting any software project?
- Who is responsible for creating the SRS, and how is it usually done?
What Is a Software Requirements Specification (SRS) and What is its Significance in Software Engineering?
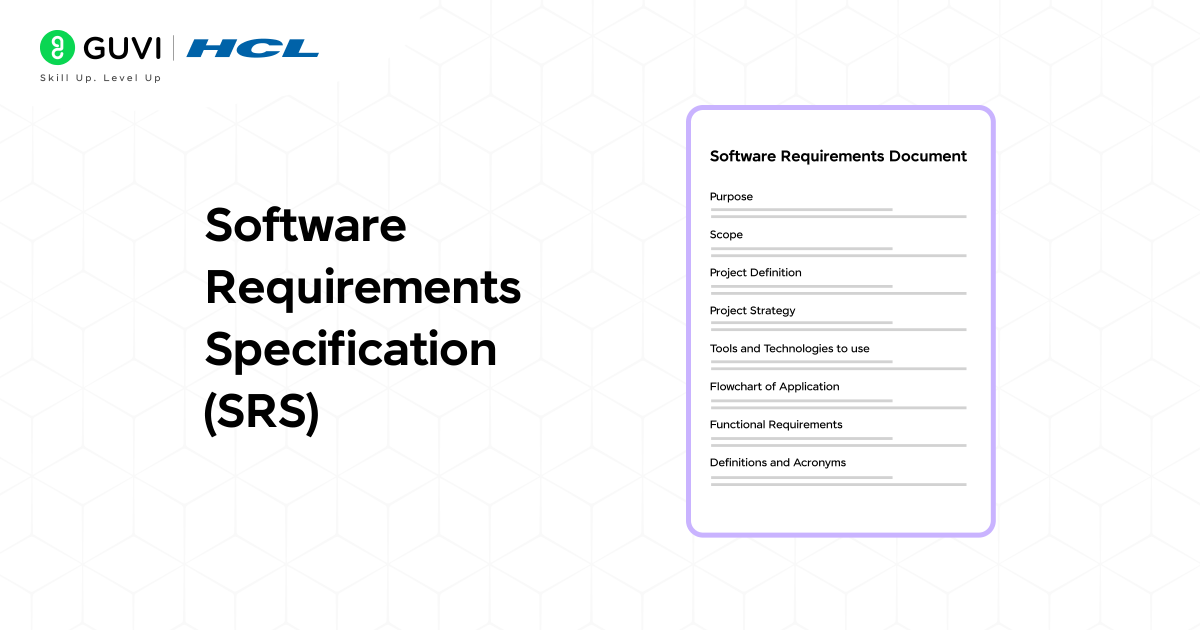
A software requirements specification (SRS) document is a descriptive document that elaborates all the essential details that are required to build a software component or a product. The purpose behind creating this document is to define the development objectives and to analyze how those objectives can meet the users’ expectations.
Before the actual product development starts, developers, testers, product consultants, and clients consider the SRS as a reference point to ensure each aspect (user interface (UI), backend system, API integration, algorithm) of the project is meticulously engineered to perfection.
By gathering and listing all relevant and requirements in a unified place, a solid development foundation is established, which helps in fostering transparent communication and avoiding misunderstandings.
(Its Significance)
The absence of a software requirements specification (SRS) document can lead to major technical issues, such as security breaches, data theft, or architectural failure due to unauthorized access. SRS is one of the most optimal ways to connect the developers and testers with the clients or end users.
While developing a project, it facilitates the developers to comprehend the desired inputs and, based on those inputs, the intended problems are solved. In software engineering, SRS also encompasses a wider scope of development that results in covering numerous capabilities and preventing ambiguities.
Furthermore, it also focuses on the vital factors such as resource allocations, project timeline, and priorities, and documents them in a well-structured fashion, in a way that is easier to grasp for both technical and non-technical individuals.
Purpose and Importance of Software Requirements Specification (SRS)
- The development goals and expectations are clearly defined for both the technical team and the stakeholders, due to which transparency is maintained during the development phase.
- It ensures productivity and efficiency of the development team by serving as a reference for functional components that are to be developed, along with allocating the optimum resources, such as the right people, technology stack, and specific timeframe to different tasks and responsibilities.
- Helps in saving time and effort by allowing the technical team to define the scope of the project. When strictly followed, scoping aids in avoiding unnecessary and repetitive tasks, which further leads to cutting down the extra development costs.
- The entire project can be segmented into smaller chunks known as sprints. In each sprint, the subtasks and milestones are set to track the regular progress and to effectively meet the deadlines.
- After the final product launch, the frequent maintenance and upgradation activities become easier to practice. As the business requirements evolve, the SRS serves as a roadmap for developers when later improvements or heavy modifications are needed.
- It also helps in designing and developing user-friendly and interactive software applications and platforms, rather than creating a sophisticated product with irrelevant features and functionalities.
- It optimizes the decision-making capabilities of professionals during the development and testing process. Accurate and precise requirements make it simpler to rely on those solutions that are suitable for fulfilling the user or business demands.
Benefits of Software Requirements Specification (SRS)
- It supports the new team members by providing them with clear project guidelines so that it is easier for them to understand every little intricacy involved in the project.
- SRS helps in knowing the exact estimation of project resources that will be integrated along with all budget and time constraints.
- It minimizes the conflicts among the team members by assigning them definite roles and responsibilities regarding the system expectations.
- It helps in managing and organizing the changes effectively during the software development life cycle (SDLC) process.
- Clients or business stakeholders get the liberty to oversee the entire project progress by referring to the SRS document, which also empowers them to communicate their feedback if the direction of the project is being diverted from the actual path.
Characteristics of Software Requirements Specification (SRS)
- Each requested task can be easily traced back to its requirements.
- Clarity is maintained throughout the document by writing in simple and comprehensible language, along with maintaining a formal tone, so that there are no complications.
- The SRS document is flexible in nature as it can be modified with respect to the changing user and business requirements and objectives.
- Each requirement mentioned in the SRS document can be validated through practical implementation, testing, prototyping, review, and analysis, to ensure its feasibility.
- Quantifiable technical information, such as response time, online traffic concentration limit, error rate, recovery timeframe, memory usage, and processing speed, is also included in the SRS document.
Types of Software Requirements Specification (SRS) Document
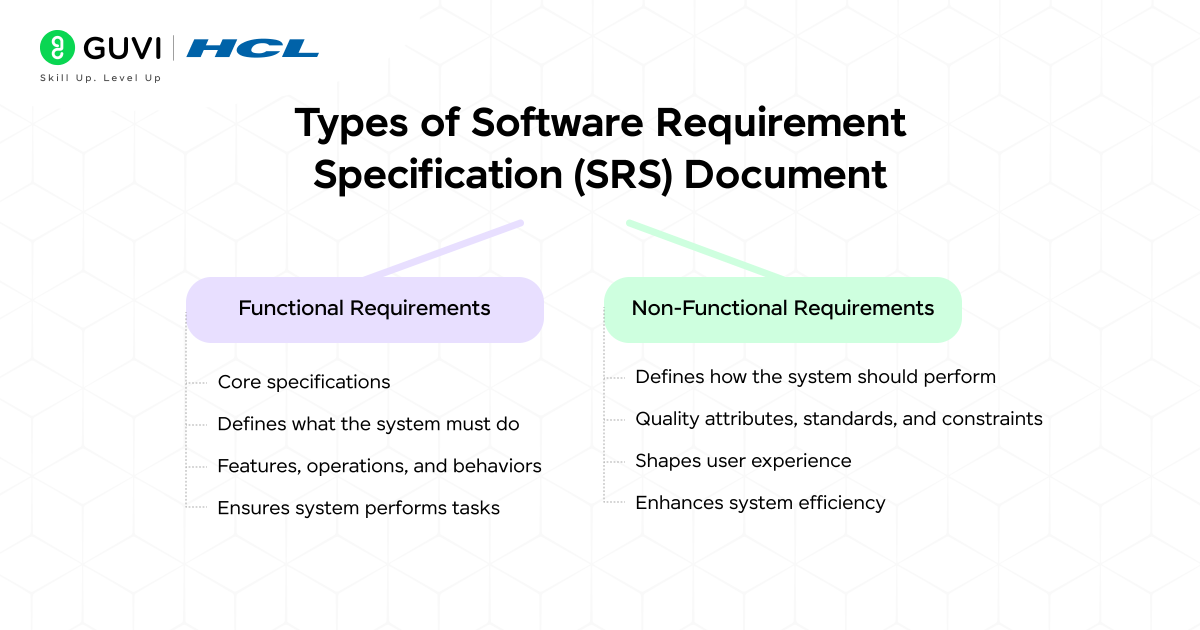
SRS can be divided into two main categories based on requirements:
1. Functional Requirements
Functional requirements are the core specifications that define what the system must do to meet business and user needs. They describe the exact features, operations, and behaviors the software should provide, ensuring the system performs its intended tasks.
These requirements focus on user interactions, system processes, and data handling, such as allowing users to register, log in, place orders, make payments, or generate reports. In short, they capture the actions and services the software is expected to deliver.
Examples:
- User login and authentication
- Payment Processing
- Report Generation System
- Notifications
2. Non-Functional Requirements
Non-functional requirements define how the system should perform rather than what it should do. They focus on the quality attributes, standards, and constraints that shape the overall user experience and system efficiency. These requirements ensure the software is secure, fast, scalable, reliable, and easy to use.
For example, they may specify response times, maximum load capacity, security measures like encryption, or uptime percentages. In short, non-functional requirements describe the qualities and conditions that make the system robust and user-friendly.
Examples:
- System handling 10,000 users concurrently
- Page load time under 2 seconds
- Data encryption using AES-256
- Availability 99.9% uptime
Role of Software Requirements Specification (SRS) in Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) Process
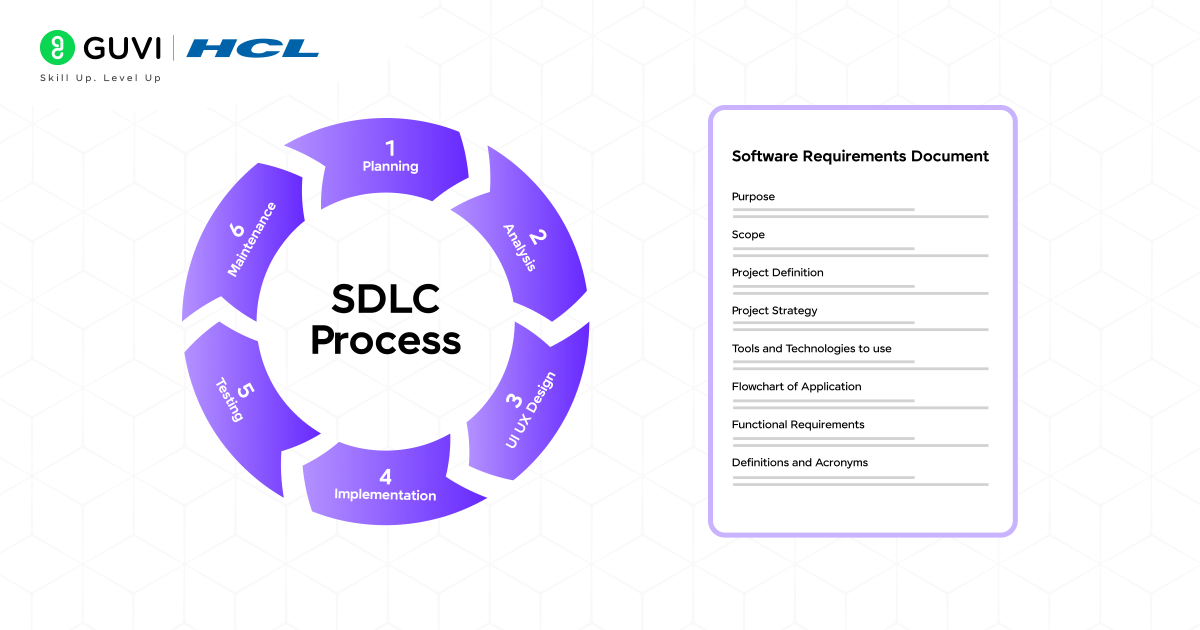
- Blueprint for the project: SRS provides a detailed plan of what the system should do and how it should perform.
- Shared understanding: Ensures developers, testers, and stakeholders are on the same page regarding system requirements.
- Reduces misunderstandings: Minimizes errors and misinterpretations during the development process.
- Prevents scope creep: Clearly defines boundaries and functionalities, avoiding unnecessary changes.
- Guides SDLC phases: Supports design, development, testing, and deployment with clear requirements.
- Baseline for validation and verification: Helps track progress and confirm the final product meets user and business needs.
- Ensures consistency and quality: Acts as a foundation for an efficient, predictable, and successful development process.
How to Write a Software Requirements Specification (SRS) Using a Template That Includes All Essential Components

- Understand the Purpose
- Understand the project goals and the reasons behind the system’s development.
- Identify the target audience for the SRS (developers, testers, clients, stakeholders).
- Gather Requirements
- Conduct meetings, interviews, and surveys with stakeholders.
- Collect functional requirements (features, tasks) and non-functional requirements (performance, security, usability).
- Organize the Structure
A typical SRS structure includes:
- Introduction – purpose, scope, definitions, acronyms.
- Overall Description – system perspective, user characteristics, constraints, assumptions.
- Specific Requirements – detailed functional and non-functional requirements.
- External Interface Requirements – UI, APIs, hardware, and communication interfaces.
- Appendices – references, supporting documents, glossary.
- Write Clear and Measurable Requirements
- Use simple, precise, and unambiguous language.
- Ensure each requirement is testable and verifiable.
- Number requirements for easy reference.
- Include Diagrams and Models
- Use flowcharts, use case diagrams, data flow diagrams, or wireframes to visualize requirements.
- Review and Validate
- Share the draft with stakeholders for feedback.
- Confirm all requirements are complete, consistent, and realistic.
- Maintain and Update
- Keep the SRS updated as the project evolves.
- Track changes to ensure everyone uses the latest version.
According to some research and studies, software companies that don’t include a Software Requirements Specification (SRS) document in their project development lifecycle find it challenging to fix requirements defects after deployment, which increases the overall cost 50 times more than catching them during the SRS phase.
Unlock a tech career full of opportunities. If you are interested in software development but have no idea how to get started on this journey, then you are not alone. Transform your aspirations into a reality by enrolling in HCL GUVI ‘s IITM Pravartak & MongoDB certified AI Software Development course. This is a next-generation learning program that combines the core fundamentals of software development with Artificial Intelligence to build real-world projects that have a tangible impact. Don’t wait—contact us today and we’ll prioritize your needs!
Conclusion
After discussing all the essential aspects of the Software Requirements Specification (SRS) document, we can conclude that for planning a project and executing the plan to solve a real-world problem successfully, a well-structured descriptive roadmap is a must. We also understood the purpose, importance, characteristics, and key advantages of the SRS document.
Apart from this, we also understood how functional and non-functional requirements are required to fulfill the needs of users and other stakeholders. After going through every section of this specific blog, if you feel you gained some insights, then don’t forget to explore more such engaging content on HCL GUVI’s blog pages.
FAQs
What exactly is a Software Requirements Specification (SRS), and why do we need it?
An SRS is a document that clearly defines what a software system should do and how it should perform. It serves as a guide for developers, testers, and stakeholders throughout the project.
Why is preparing a detailed SRS considered important before starting any software project?
A detailed SRS ensures everyone understands the requirements, reduces mistakes, and saves time and money by avoiding confusion during development.
Who is responsible for creating the SRS, and how is it usually done?
Business or system analysts usually prepare the SRS, working closely with clients, developers, and testers to capture all requirements accurately.



































Did you enjoy this article?