
Software Development Life Cycle Phases: A Complete Guide
Sep 05, 2025 4 Min Read 2393 Views
(Last Updated)
Have you ever thought about how your favorite software applications, whether it’s Instagram and banking applications or your favorite game, are developed and maintained?
Every successful application has a process that is outlined and organized to help the developers, product manager, and stakeholders convert the idea into a functioning, reliable product. This process is known as the software development life cycle (SDLC).
Software development life cycle is a series of processes that are used to build, develop and test high-quality software that meets the user requirements.
This blog will cover everything related to the Software Development Life Cycle phases. You will also learn what the SDLC process is and why and how each step is a critical step to building a software product.
Table of contents
- What is the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)?
- The Main phases of the Software Development Life Cycle
- Phase 1: Planning
- Phase 2: Requirements analysis
- Phase 3: Design
- Phase 4: Implementation (coding)
- Phase 5: Testing
- Phase 6: Deployment
- Phase 7: Maintenance
- Importance of Software Development Life Cycle Phases
- Common SDLC Models
- Waterfall Model:
- Agile Model:
- Spiral Model:
- The V-Model (Verification and Validation):
- Conclusion: Why Understanding SDLC Phases is Crucial
- FAQs
- What are the main Software Development Life Cycle phases?
- Why is the Requirements phase in SDLC important?
- Which SDLC model should organizations use?
- What are common challenges in SDLC?
- What part of SDLC is most critical?
What is the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)?
The software development life cycle is a systematic approach used by software developers to build and maintain a high-quality software product. Imagine it as a blueprint for managing the entire development process, ensuring the end product aligns with the user requirements as well as the business goals.
In other words, SDLC establishes a clear framework for communication and collaboration between the stakeholders, from developers and testers to project managers and clients. This planned structure helps minimize errors, manage potential risks, and streamline workflows, allowing the teams to deliver a faster and more reliable product.
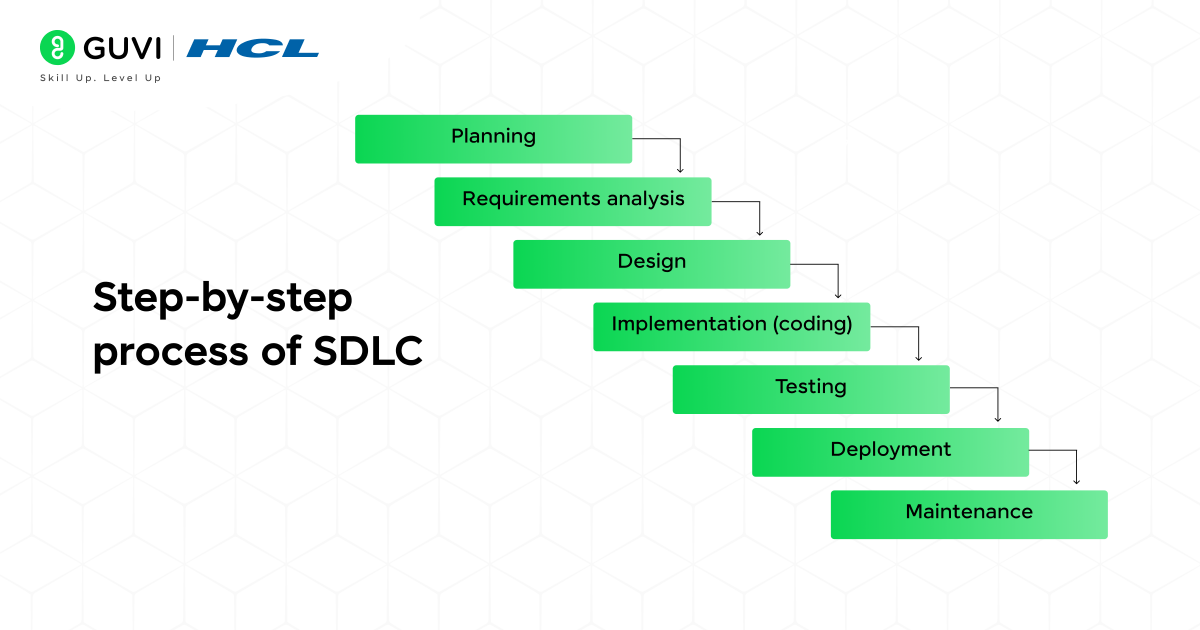
The Main phases of the Software Development Life Cycle
Though different model follows SDLC process steps, here are the seven most commonly used software development life cycle phases:
- Planning
- Requirements analysis
- Design
- Implementation (coding)
- Testing
- Deployment
- Maintenance
Phase 1: Planning
The software development process always starts with the Planning phase of SDLC. The planning phase is the starting point in the process, as it creates a clear path, states deliverables, and evaluates feasibility.
The main actions in the Planning phase are:
- Determine business needs or problems to be solved with software
- Determine project feasibility (Feasibility = Technical, Operational, Financial)
- Estimate time, budget, and resources to complete the project
- Clearly define the project scope and objectives
- Develop the project plan and project schedule
Phase 2: Requirements analysis
The Requirements phase in SDLC involves gathering detailed information about what the software should do. This phase is critical because unclear or incomplete requirements often lead to project failure.
The main actions in the Requirements phase are:
- Interacting with stakeholders (clients, users, managers)
- Collecting functional requirements (features and functions)
- Gathering non-functional requirements (performance, security)
- Documenting requirements in a Software Requirements Specification (SRS)
- Validating and approving the requirements
A recent study revealed that poor requirements management accounts for nearly 78% of software project failures. This striking statistic highlights the critical role of the Requirements Analysis phase in ensuring project success.
Phase 3: Design
The Design phase in SDLC translates requirements into blueprints for construction. This phase defines the system architecture, user interfaces, data models, and other technical specifications.
The main actions in the Design phase are:
- Creating high-level design (system architecture and modules)
- Developing detailed design (database design, interface design)
- Choosing a technology stack and tools
- Preparing design documents for developers
Phase 4: Implementation (coding)
The Implementation phase in SDLC, also called the coding phase, is where the actual software is developed.
The main actions in the Implementation phase are:
- Writing source code based on design documents
- Following coding standards and best practices
- Integrating different modules and components
- Conducting initial code reviews
Phase 5: Testing
The testing phase in SDLC is critical for ensuring software quality. Here, the software is rigorously verified against requirements and checked for bugs.
The main actions in the Testing phase are:
- Creating and executing test plans and test cases
- Performing various tests: unit testing, integration testing, system testing, acceptance testing
- Identifying, reporting, and fixing defects
- Validating that software meets requirements and quality standards
Phase 6: Deployment
The Deployment phase in SDLC involves releasing the software to the end-users or production environment.
The main actions in the Deployment phase are:
- Preparing deployment documentation and user manuals
- Installing software on user machines or servers
- Training users and providing support
- Collecting feedback for improvements
Today, many organizations rely on DevOps pipelines, CI/CD pipelines, and automation tools like Jenkins, Docker, or Kubernetes. This reduces manual errors, speeds up release cycles, and ensures software is deployed consistently across environments.
Phase 7: Maintenance
The Maintenance phase in SDLC ensures that software continues to operate smoothly after deployment. It involves fixing issues, making updates, and adding new features.
The main actions in the Maintenance phase are:
- Monitoring software performance and user feedback
- Addressing reported bugs and errors
- Providing regular updates and patches
- Enhancing software with additional features as needed
Importance of Software Development Life Cycle Phases
The importance of SDLC phases cannot be overstated. By breaking down software development into clear, manageable steps, organizations can:
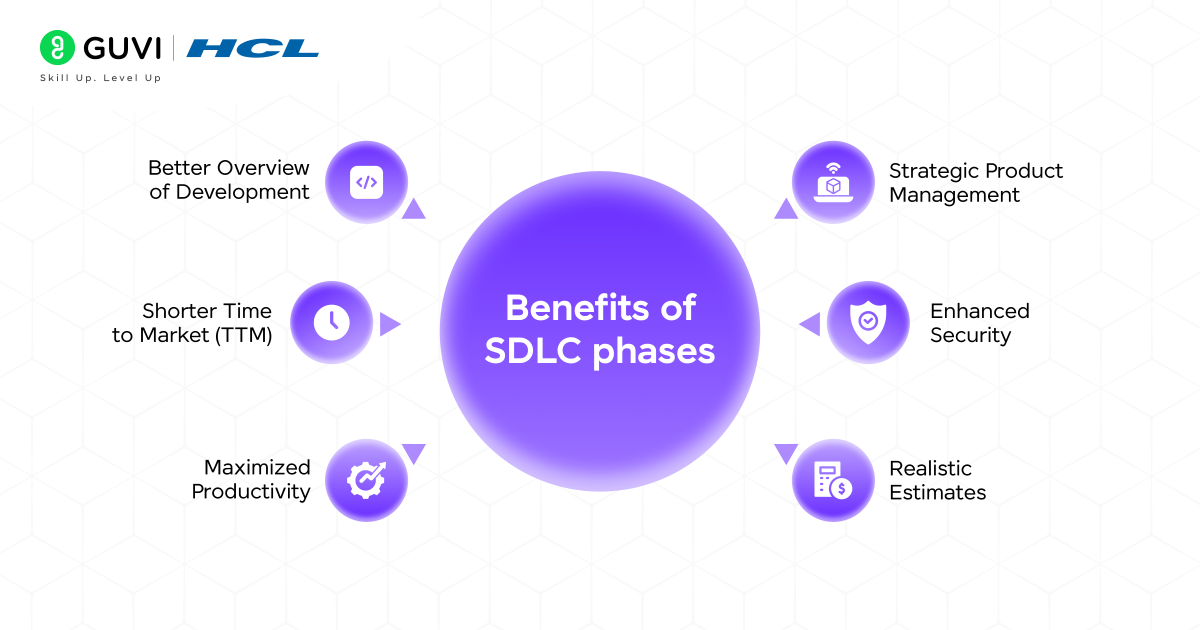
- Minimize the risk of project failure.
- Improve project planning and control over schedule and resources.
- Facilitate better communication between project stakeholders.
- Allow better quality software through testing and validation.
- Create a process for maintenance and updates once the software is live.
Common SDLC Models
Many organizations use various software development life cycle models depending on the type of project, timeframe, and objectives. Each SDLC model has different benefits and drawbacks, so using one based on project needs will be necessary.
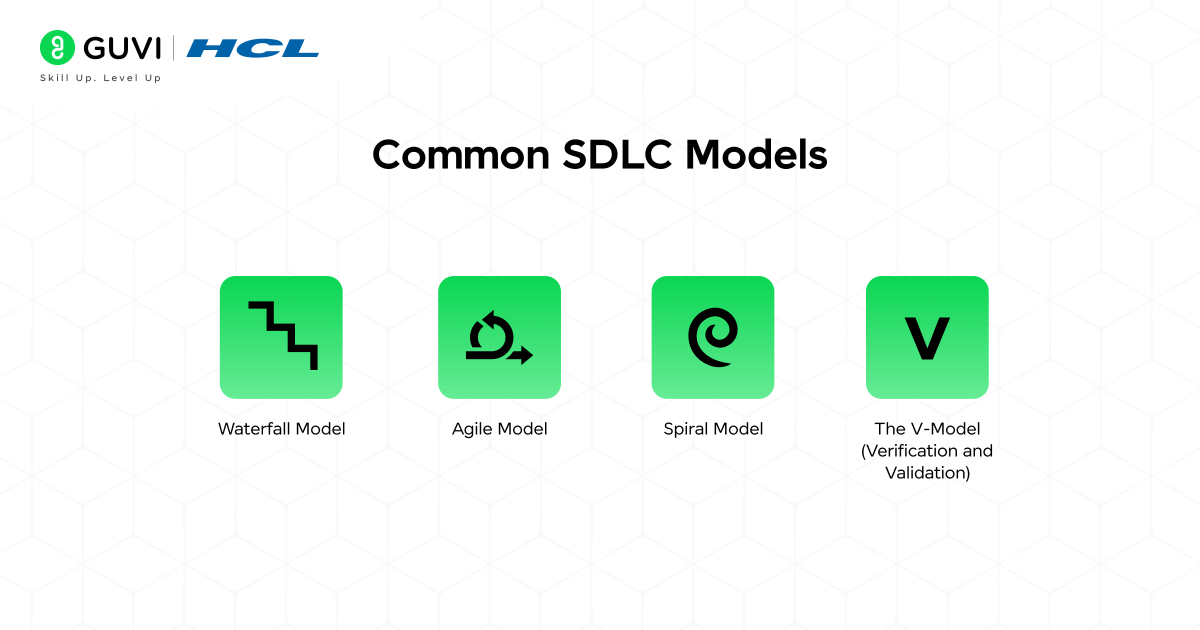
1. Waterfall Model:
The Waterfall model is a linear sequential software development process where at least one phase (planning, requirements, design, coding, testing, documentation, and maintenance) must be finished before entering the next phase. The Waterfall model is helpful for projects that have clear and specific requirements with minimal expected changes. This model is often used for government or healthcare systems.
2. Agile Model:
Agile is an iterative, flexible model where the software is delivered in very small, workable increments. Agile emphasizes work and feedback from stakeholders, the ability to deliver faster, and the constant ability to shape changing needs. The Agile model is often preferred by startups and product-based companies where the requirements are always evolving.
3. Spiral Model:
The Spiral model emphasizes risk evaluation through iterative development cycles (spirals), which allow developers to evaluate risks at an early point of the development cycle and make adjustments to solutions. This model is well-suited to large, complex, and high-risk projects, such as software for defense or aerospace.
4. The V-Model (Verification and Validation):
This model is very test-focused; testing is performed at each level. Each phase of development has a corresponding testing phase to ensure reliability and quality. It is commonly used in safety-critical applications such as medical devices.
No matter the model, the fundamental SDLC phases explained remain largely the same.
If you are genuinely excited about software development and want to pursue a career as a software developer, then you are in luck. HCL GUVI’s IITM Pravartak and MongoDB Certified Online AI Software Development Course is a great way to learn! One of the most significant advantages that will set you apart from other candidates in the job market is that you will receive a recognized, globally NSDC-endorsed certificate, which can be uploaded quickly onto your resume.
Conclusion: Why Understanding SDLC Phases is Crucial
It is critical for every group member, including developers, project managers, and stakeholders, to know the Software Development Life Cycle. It allows planning in a structured way that helps create as good software as possible, but can also help assure it is delivered on time, complete, and to a standard of quality.
If teams regularly follow SDLC phases, from planning and requirements to design, implementation, testing, deployment, and maintenance, they can eliminate increasing numbers of errors, risk, and ultimately assure users get a software solution that meets their requirements.
The first step on the road to successful software development is understanding what the SDLC phases are. And by reading this blog, you now have a clear idea of how each stage contributes to building reliable software.
FAQs
1. What are the main Software Development Life Cycle phases?
The main SDLC phases are Planning, Requirements, Design, Implementation (Coding), Testing, Deployment, and Maintenance. Some variations of SDLC models may add or combine phases, but these core steps remain constant.
2. Why is the Requirements phase in SDLC important?
The Requirements phase in SDLC ensures all project needs are clearly defined. Without accurate requirements, developers may build software that doesn’t meet user expectations, leading to wasted resources and costly rework.
3. Which SDLC model should organizations use?
The choice of the SDLC model depends on project requirements:
The Waterfall Model is best for projects with fixed, clear requirements.
Agile Model works well for dynamic projects requiring flexibility and continuous feedback.
The Spiral Model is suitable for large, complex, and high-risk projects.
4. What are common challenges in SDLC?
The common challenges in SDLC are unclear requirements, scope creep, communication gaps, testing delays, and a lack of stakeholder involvement. These can lead to a delay in project delivery, increased costs, and unhappy users. Teams should select the appropriate SDLC model, foster regular feedback, and follow DevOps practices such as automation and continuous integration to ease these challenges.
5. What part of SDLC is most critical?
While every task of the Software Development Life Cycle is critical, the Requirements Analysis phase is the most important phase. The project will most certainly fail if the requirements are not clear or incomplete, despite good design or coding.



































Did you enjoy this article?