
Selenium vs RPA: Battle Of The Best Automation Technologies
Oct 30, 2025 6 Min Read 1493 Views
(Last Updated)
Have you ever wondered why some automation tools seem tailor-made for web testing, while others promise to streamline entire business processes? Automation is a necessity for efficiency and accuracy in the modern and digitized world. Yet, choosing between Selenium and Robotic Process Automation (RPA) usually leaves professionals scratching their heads.
Both drive automation, but their goals, scopes, and capabilities couldn’t be more different. If you’ve ever been curious about where Selenium ends and RPA begins, this blog will walk you through the key differences that truly set them apart.
Table of contents
- What is Selenium?
- What is RPA?
- Key Components of Selenium
- Key Components of RPA
- Top Benefits of Selenium
- Top Benefits of RPA
- Top Applications of Selenium
- Top Applications of RPA
- Robotic Process Automation Life Cycle
- Analysis
- Bot Development
- Testing
- Support and Maintenance
- Selenium Life Cycle
- Test Plan
- Generating Basic Tests
- Enhancing Tests
- Running and Debugging Tests
- Analyzing Test Results and Reporting Defects
- Is it platform-dependent or independent?
- Knowledge of coding is required?
- Similarities Between Selenium and RPA
- Comparison Between Selenium and RPA
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- Can Selenium be used for business process automation like RPA?
- How does RPA differ from Selenium in terms of purpose and functionality?
- Which tool should organizations choose between Selenium and RPA?
What is Selenium?

Selenium is an open-source automation framework used for testing web applications across different browsers and platforms. It operates through scripts that interact with web elements such as buttons, forms, and links to verify whether a web application functions as expected. The framework supports several programming languages, including Java, Python, and C#, which allows developers and testers to integrate it into existing technology stacks with ease. Selenium focuses on browser-level automation that replicates user actions, making it a valuable tool for regression and functional testing.
What is RPA?
Robotic Process Automation, or RPA, is a technology that uses software robots to perform repetitive and rule-based tasks that humans typically handle through digital systems. These robots interact with various applications and user interfaces to complete structured workflows such as data entry or report generation. RPA tools operate at the user interface level, which means they can work across multiple systems without requiring deep integration or changes in the underlying code. The primary goal of RPA is to improve operational efficiency by reducing manual workload and minimizing human errors. Businesses use RPA to automate processes across departments like finance and human resources, where accuracy and speed hold high importance.
Key Components of Selenium
- Selenium WebDriver: This is the core component that automates browser actions by communicating directly with the browser’s native automation API. It supports multiple browsers and allows execution of scripts written in languages such as Java, Python, or C#.
- Selenium IDE: It is a record-and-playback tool designed for creating test cases quickly. Users can record their actions within a browser and replay them to verify functionality. It is helpful for beginners and for creating prototypes of test scenarios.
- Selenium Grid: This component allows parallel execution of tests across multiple browsers, devices, and operating systems. It helps reduce test execution time and supports distributed testing environments.
- Selenium Client Libraries: These libraries provide language bindings for interacting with Selenium WebDriver. They allow developers to write scripts in their preferred programming languages without changing the framework’s behavior.
Key Components of RPA
- Bot Creator: This is the environment where developers design and build automation workflows. It includes tools for defining steps and triggers that guide the bot’s actions across various applications.
- Bot Runner: It executes the workflows designed in the creator environment. Bot Runners operate on virtual or physical machines to perform tasks such as data entry, validation, and system updates without human intervention.
- Control Room: This component functions as the central management hub. It monitors, schedules, and controls the execution of bots, providing insights into performance, errors, and audit logs.
- Recorder: It captures user actions on different applications and converts them into automation steps. This simplifies bot creation, especially for non-technical users who rely on visual cues rather than coding.
- Analytics Dashboard: It offers a visual representation of bot performance, process efficiency, and error trends. This helps organizations track the value generated by automation and identify areas that require improvement.
Top Benefits of Selenium
- Cross-Browser Compatibility: Selenium supports major browsers such as Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge. This helps testing teams confirm that web applications perform consistently across multiple environments.
- Support for Multiple Languages: Developers can write automation scripts in several programming languages, including Java, Python, and C#. This flexibility allows integration with different technology stacks.
- Open-Source Framework: Selenium is free to use, which reduces software testing costs. Its large community contributes libraries, plugins, and frequent updates that keep the framework relevant and reliable.
- Parallel Test Execution: Selenium Grid enables concurrent test execution, which helps reduce testing time and accelerates release cycles.
- Integration with CI/CD Tools: Selenium works smoothly with tools such as Jenkins, Maven, and Docker. This supports continuous testing and helps maintain product quality in agile development environments.
Top Benefits of RPA
- Improved Efficiency: RPA automates repetitive and rule-based tasks, which helps teams complete high-volume work faster and with fewer errors.
- Enhanced Accuracy: Software robots follow defined rules without deviation, which reduces human errors and maintains consistency in process execution.
- Scalability: Organizations can deploy additional bots to handle increased workloads. This flexibility allows automation to expand as business needs grow.
- Cost Reduction: Automating manual processes lowers labor costs and minimizes the need for rework caused by human mistakes.
- Audit and Compliance Support: Every action performed by bots is logged and traceable. This provides transparency for compliance audits and process reviews.
- 24/7 Availability: Bots can operate continuously without breaks, which increases productivity and supports round-the-clock business operations.
Top Applications of Selenium
- Web Application Testing: Selenium is primarily used to automate testing of web-based applications. It interacts directly with browsers to verify user interfaces, validate navigation, and confirm that each element functions as intended.
- Regression Testing: It is widely applied in regression testing, where existing functionalities must be revalidated after software updates. This maintains reliability through continuous development cycles.
- Cross-Browser Validation: Selenium helps confirm consistent performance across browsers such as Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge. This ensures that end users experience uniform behavior regardless of platform.
- Performance Verification in CI/CD Pipelines: It integrates into continuous integration and continuous delivery environments. Automated scripts run with every build to detect issues early, which improves product stability before deployment.
- Data-Driven Testing: Selenium supports testing with external datasets from Excel or CSV files. This approach verifies how applications handle various input conditions and boundary values.
Top Applications of RPA
- Invoice and Payment Processing: RPA bots handle invoice validation and data extraction into accounting systems. They cross-check details and post transactions without human involvement, which increases speed and accuracy.
- Customer Onboarding: Bots gather client information from multiple sources in service sectors. They update CRM platforms and trigger welcome emails. This reduces onboarding time and improves record accuracy.
- Data Migration Between Systems: Bots transfer data from legacy systems to modern applications. They move large volumes of structured information while maintaining format consistency and audit trails.
- Employee Attendance and Payroll Management: Bots calculate working hours, process leaves, and prepare payroll summaries. This removes manual intervention in repetitive HR processes and minimizes processing errors.
- Compliance Reporting: RPA automates report generation for audits and regulatory submissions. It compiles data from several systems and formats reports according to compliance standards.
Robotic Process Automation Life Cycle
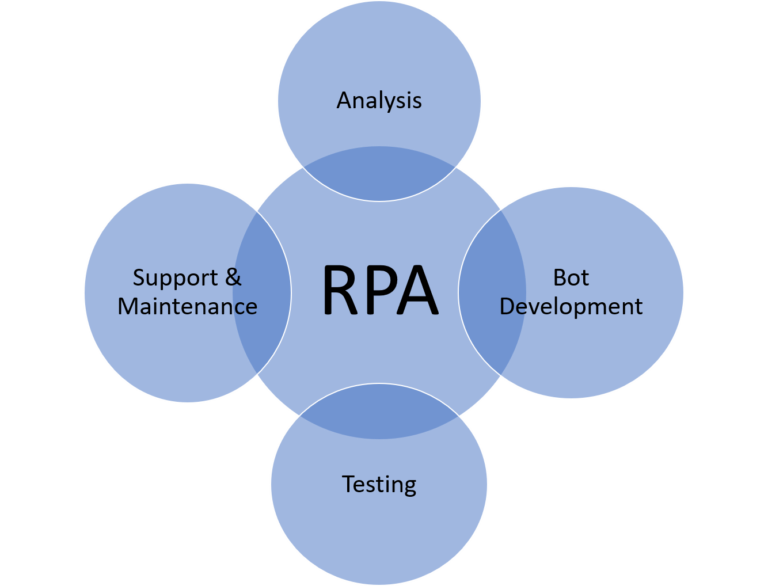
1. Analysis
The RPA life cycle begins with analyzing business processes that can be automated. Each process is evaluated for volume, frequency, stability, and error rate. Analysts identify rule-based activities that follow predictable patterns and involve structured data. This stage results in a detailed process definition document that outlines every step, decision point, and exception to help developers understand how the automation will operate.
2. Bot Development
After the analysis phase, developers start building the bot based on the approved process design. Using RPA tools such as UiPath, Automation Anywhere, or Blue Prism, they map each step into executable commands. Bots are configured to interact with applications, handle data, and follow logic that mirrors human decision-making patterns. Developers also include features for handling exceptions and security control so that the automation remains stable and auditable.
3. Testing
Testing ensures that the bot performs exactly as designed. Developers verify its ability to execute every workflow step under real conditions and confirm that it produces consistent results. Functional, exception, and performance tests are conducted to check data accuracy and reliability. If any deviation appears, the workflow is refined before moving to deployment. A properly tested bot ensures accuracy and confidence in production environments.
4. Support and Maintenance
Once deployed, bots are continuously monitored to confirm that they operate as expected. Any changes in source systems, user interfaces, or process rules require prompt updates in the automation logic. Maintenance involves fine-tuning workflows and adapting bots to evolving business requirements. Continuous support helps sustain process efficiency and extends the lifespan of automation initiatives across the organization.
Step into the world of automation and unlock new career paths with our RPA (Robotic Process Automation) Course. Learn to design, build and deploy software bots using UiPath, streamline repetitive tasks in any business process, and gain the skills employers are actively seeking in the automation era!
Selenium Life Cycle
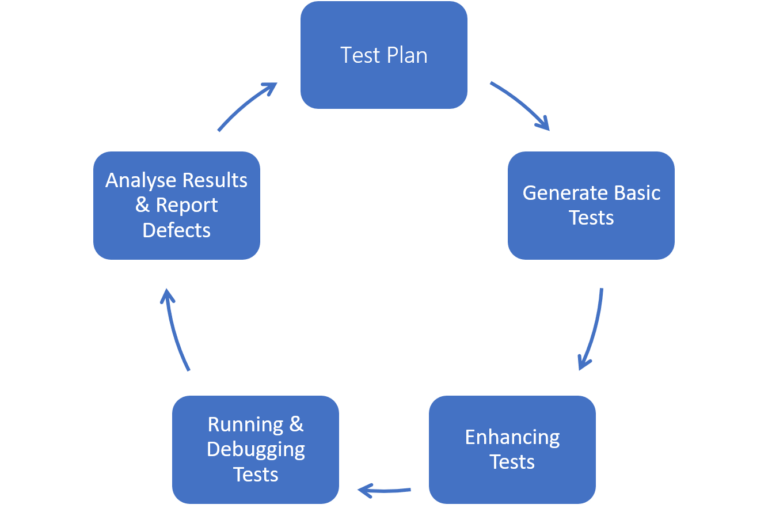
1. Test Plan
The process begins with defining a clear test plan. Teams outline what parts of the web application need to be automated, which browsers will be used, and what goals each test should achieve. The plan aligns testing objectives with project requirements so that coverage includes all critical user journeys. This foundation helps determine timelines, resources, and measurable quality targets.
2. Generating Basic Tests
Once the plan is ready, basic tests are created to verify core functionalities of the application. These initial scripts focus on actions such as logging in, submitting forms, and verifying responses. Selenium IDE is often used at this stage for quick recording and playback of user actions. The outcome provides an early validation of the test environment and confirms that automation scripts interact correctly with web elements.
3. Enhancing Tests
After the initial scripts work correctly, they are refined for better accuracy and maintainability. Developers introduce logic for handling conditions, input variations, and reusable methods. They also organize scripts into modular structures to simplify updates and extend coverage to complex user workflows. At this stage, integration with test data files and configuration management begins to support broader test execution.
4. Running and Debugging Tests
The enhanced scripts are executed through Selenium WebDriver or Selenium Grid across different browsers and platforms. Execution logs and console outputs are monitored to detect errors or failures. Debugging involves analyzing failed test steps, adjusting locators, and modifying scripts where elements or behaviors have changed. Parallel testing helps reduce time and validate application consistency across environments.
5. Analyzing Test Results and Reporting Defects
After execution, test outcomes are collected and analyzed. Reports highlight the number of passed, failed, and skipped cases along with execution logs. Defects identified during this stage are documented with clear evidence, such as screenshots or console traces. These reports are shared with the development team for resolution. Continuous tracking of defect trends helps improve both testing efficiency and product quality over time.
Explore the power of automation testing with our Selenium Java Course, where you’ll master web-driver frameworks, build reliable test suites, and understand why Selenium remains foundational even as RPA technologies rise. Gain hands-on experience, build automation skills, and decide which path: Selenium or RPA fits your career best.
Is it platform-dependent or independent?
Selenium is an open-source tool that is platform-independent and can be used on any browsing platform.
In RPA, the user can use processes that can run on any of the web, desktop, and mobile applications. It is platform independent.
Knowledge of coding is required?
- If you are working with Selenium, basic knowledge of Java is required.
- RPA requires minimal coding knowledge.
Consider a scenario where you order something on any of the e-commerce websites.
- RPA helps in capturing the order details.
- Streamlines the process by simplifying the order entry.
- Integrates the details with the data entered. This reduces the discrepancies & simplifies the view of order status.
Using Selenium,
- One can create a Webdriver instance.
- Navigate to the corresponding webpage, and find a particular element on the current web page.
- Perform actions like login, sign up, and so on.
- Initiate a browser response, run the tests, and record the test results using a test framework.
Similarities Between Selenium and RPA
| Feature | Selenium | RPA | Common Ground |
| Automation Objective | Automates web application testing tasks | Automates rule-based business processes | Both aim to reduce manual effort and increase operational efficiency |
| Script-Based Control | Uses programming scripts for test execution | Uses scripts or workflows to define bot behavior | Both rely on defined sets of instructions to execute actions |
| Cross-Platform Functionality | Works across various browsers and operating systems | Works across multiple enterprise applications and systems | Both are platform-independent to a large extent |
| Error Reduction | Automates repetitive actions to avoid human mistakes in testing | Performs repetitive tasks accurately without fatigue | Both reduce the likelihood of human error |
| Reusability | Test scripts can be reused across projects | Bot workflows can be reused for similar processes | Both promote reusability, which saves time and resources |
| Integration Capabilities | Integrates with CI/CD tools and reporting frameworks | Integrates with business applications and analytics platforms | Both can connect with external tools to enhance automation outcomes |
| Community and Support | Supported by a large open-source developer community | Backed by strong vendor and community ecosystems | Both have strong support structures for maintenance and growth |
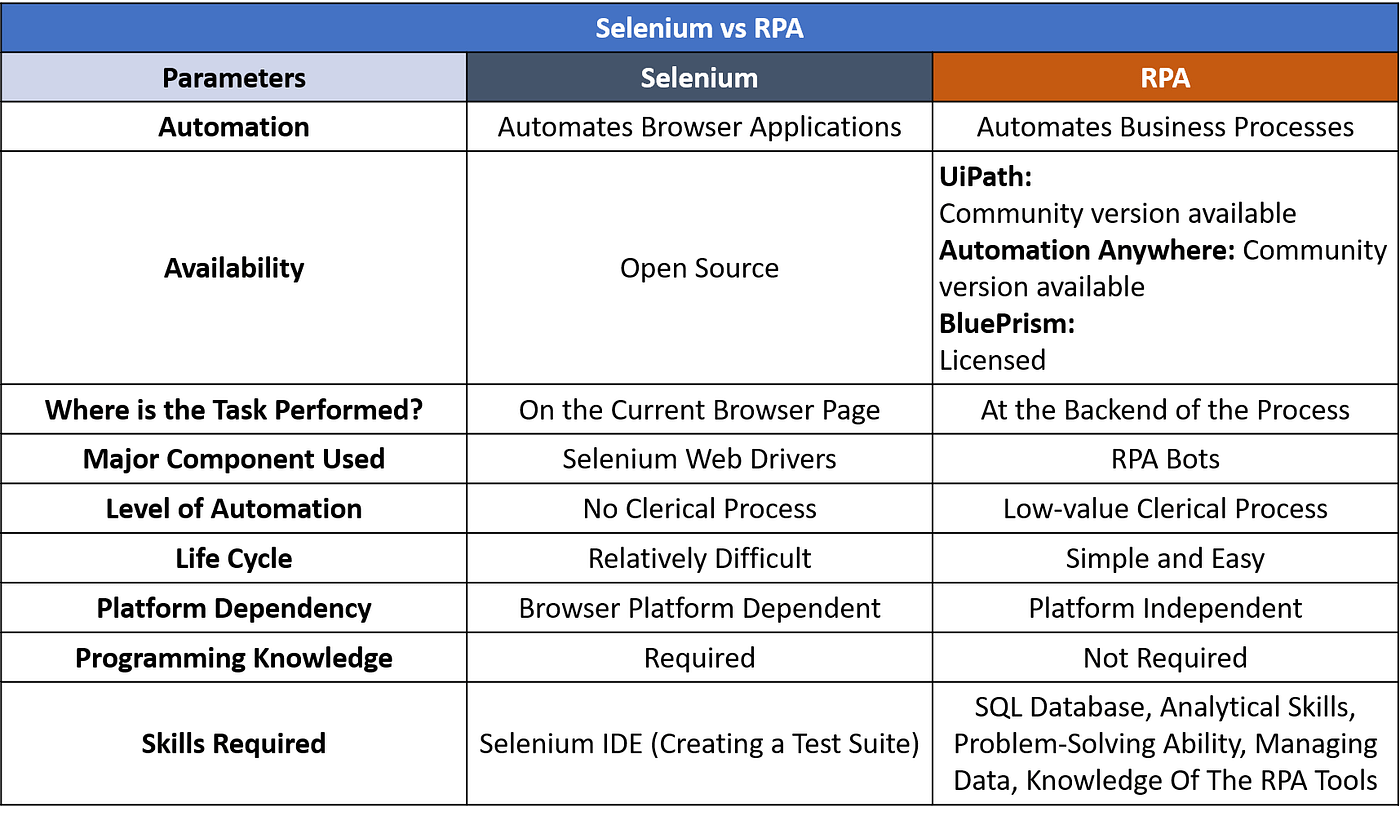
Comparison Between Selenium and RPA
Conclusion
Selenium and RPA represent two distinct directions in automation. Selenium strengthens software testing through browser-based validation, while RPA reshapes business efficiency by handling structured operational tasks. Both serve unique goals that complement modern digital workflows. Understanding their differences helps professionals select the right tool for their objectives and move toward smarter, more consistent automation practices.
FAQs
1. Can Selenium be used for business process automation like RPA?
Selenium focuses on browser-based automation for testing web applications. It does not interact with desktop or enterprise systems the way RPA does. RPA works across multiple applications and handles structured business workflows, while Selenium remains limited to validating web interfaces and test conditions.
2. How does RPA differ from Selenium in terms of purpose and functionality?
Selenium is built for testing and quality assurance in software development. It validates how a web application behaves under different conditions. RPA automates operational tasks such as data entry, invoice handling, or report generation. Selenium serves the needs of testers, whereas RPA supports business users who handle repetitive processes.
3. Which tool should organizations choose between Selenium and RPA?
The choice depends on the goal. Selenium suits teams that focus on software testing and continuous integration workflows. RPA fits organizations aiming to automate business operations and reduce manual workloads. Each serves a distinct domain and delivers value within its specific area of automation.



















Did you enjoy this article?