
Robotics and Artificial Intelligence – A Comprehensive Look
Sep 01, 2025 6 Min Read 2345 Views
(Last Updated)
Have you ever wondered how robotics and artificial intelligence are transforming the world around you? These two technologies are often mentioned together, and for good reason.
In today’s tech-driven era, robotics and artificial intelligence (AI) are changing industries and daily life in profound ways. This article will help you understand the basics of robotics and artificial intelligence, how they differ and complement each other, and why they matter.
We’ll explore what each term means, look at real-world applications, discuss benefits and challenges, and even include some fun facts and a quick quiz to test your knowledge. Let’s dive in!
Table of contents
- What is Robotics?
- Key Concepts in Robotics
- What is Robotics Used For?
- What is Artificial Intelligence?
- Key Concepts in AI
- What is AI Used For?
- Robotics and Artificial Intelligence: How Are They Different?
- Benefits of Robotics and Artificial Intelligence
- Challenges and Ethical Considerations
- Test Your Knowledge: Quick Quiz
- Answers:
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- What is the difference between robotics and artificial intelligence?
- How are robotics and AI used in everyday life?
- What are the main benefits of using robotics and AI?
- What are the challenges and risks of robotics and AI?
- What is the future of robotics and artificial intelligence?
What is Robotics?
Robotics is the field of technology that deals with the design, construction, and operation of robots. In simple terms, a robot is a programmable machine capable of carrying out a series of actions automatically.
Robotics is essentially a branch of engineering and computer science focused on creating these machines to assist humans in various tasks. Robots can be autonomous or semi-autonomous, meaning some operate entirely on their own, while others require some degree of human control.
Key Concepts in Robotics
- Physical Machines: Robots are tangible, physical entities – from robotic arms on factory floors to mobile robots like drones or rovers. They often resemble machines with moving parts (think of a robotic arm or a wheeled robot).
- Sensors and Actuators: Most robots use sensors (cameras, touch sensors, gyroscopes, etc.) to receive input from the environment. Based on this input and their programming, they use actuators (motors, hydraulics, etc.) to perform actions.
- Programming and Control: Robots must be programmed with instructions or algorithms. Traditional robots follow explicit programming – a fixed set of instructions. Modern robotics increasingly incorporates intelligent control (often powered by AI), allowing robots to make decisions or adapt to new situations.
What is Robotics Used For?
You’ll find robotics at work in many industries, often taking on tasks that are repetitive, precise, or dangerous for humans. Here are a few examples of how robotics is used today:
- Manufacturing and Industry: Industrial robots have long been used in factories for assembly, welding, painting, and material handling.
- Aerospace and Defense: Drones (unmanned aerial vehicles) are robots used for tasks like inspecting infrastructure, surveying land, or reconnaissance.
- Healthcare: In hospitals, robotic systems assist in surgeries (a famous example is the da Vinci surgical robot), allowing minimally invasive procedures with high precision.
- Everyday Life: Beyond industry, robots are increasingly found in everyday life. Home robotics like robotic vacuum cleaners, can clean your floors automatically. Social or service robots can provide customer service or information in malls and airports. There are even educational robots used as learning tools for kids.
Robots excel at tasks that require precision, endurance, or operating in environments not suitable for humans. For example, a robot can handle toxic chemicals or high-heat environments without risk, improving safety.
What is Artificial Intelligence?
While robotics is about physical machines, artificial intelligence (AI) is about smart software. Artificial intelligence refers to the simulation of human intelligence in computers and machines.
In other words, AI enables a machine or program to think and learn in a way that appears “intelligent.” Rather than a physical robot body, AI is essentially the “brain” – algorithms that can analyze data, recognize patterns, make decisions, and even improve over time.
Key Concepts in AI
- Machine Learning (ML): A major subset of AI where algorithms learn from data. Instead of being explicitly programmed for every scenario, a machine learning system can train on example data and then make predictions or decisions.
- Narrow AI vs. General AI: Most AI today is narrow AI, meaning it’s designed for a specific task (like voice assistants, recommendation engines, or image recognition). It can perform that task well, but it doesn’t possess general reasoning like a human. General AI (a machine with broad, human-like intelligence) remains largely theoretical and a topic of ongoing research.
- Cognitive Abilities: AI systems can be designed to emulate various cognitive functions – learning, problem-solving, perception, language understanding, etc. For example, natural language processing (NLP) is an AI capability that allows machines to understand and generate human language.
What is AI Used For?
AI has become pervasive across many sectors, often behind the scenes in software applications and services. You probably interact with AI every day without realizing it. Here are some common applications of artificial intelligence:
- Healthcare: AI algorithms can analyze medical images (like X-rays or MRIs) to help detect diseases. They can also assist in diagnosing illnesses and recommending treatments by analyzing patient data.
- Education: AI is used in personalized learning platforms that adapt to a student’s needs. It can power virtual tutors or chatbots that answer students’ questions.
- Finance: Banks and financial institutions use AI for fraud detection (monitoring transactions for unusual patterns), algorithmic trading, and credit scoring.
- Transportation: Self-driving cars are a hallmark example of AI in action. Autonomous vehicles use AI (specifically deep learning and computer vision) to perceive their surroundings and make driving decisions.
- Everyday Services: AI powers many everyday conveniences: voice assistants like Siri, Alexa, or Google Assistant use speech recognition and language understanding (AI technologies) to respond to your questions.
The core idea is that artificial intelligence enables computers to perform tasks that normally require human intelligence. AI systems can handle immense amounts of data and find patterns, make decisions swiftly, and even learn and improve over time.
Robotics and Artificial Intelligence: How Are They Different?
Now that we’ve defined robotics and artificial intelligence separately, you might be wondering how they relate. People often confuse the two, and it’s common to use the terms interchangeably. However, they are distinct concepts:
- Robotics is about machines; AI is about intelligence. Robotics creates physical robots that can move and act, whereas AI creates smart software and algorithms. A robot is like the body, and AI is like the brain.
- Not all robots have AI, and not all AI programs are used in robots. For example, a basic factory robot arm that repeatedly picks up parts and places them on a conveyor may not use any AI – it might just be following a precise, pre-programmed routine.
- Intersection of the two: When you combine robotics and AI, you get intelligent robots. This is where things get exciting. An intelligent robot is a robot powered by AI, meaning it can make decisions or adapt based on data. Think of a modern autonomous drone: the drone’s hardware (propellers, motors, sensors) is the domain of robotics, but the decision-making software (avoiding obstacles, plotting routes) is AI-driven.
In essence, AI acts as the “brain” and robotics provides the “body” for a system that can perceive, decide, and act.
Benefits of Robotics and Artificial Intelligence
Why are we integrating robotics and artificial intelligence into so many aspects of society? Simply put, they offer significant benefits:
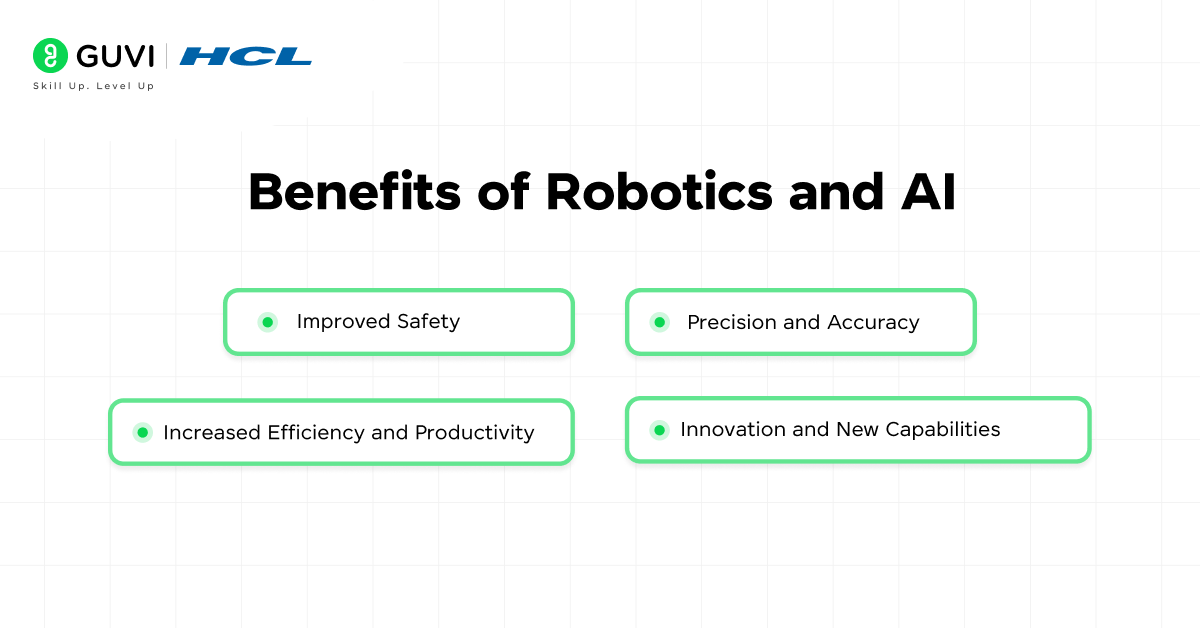
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity: Robots can work 24/7 without fatigue, speeding up production and handling tedious tasks. AI can analyze and compute far faster than a human mind, optimizing processes.
- Precision and Accuracy: Robots excel at repeatable, precise motions – a robotic arm can place components with millimeter accuracy every time. AI algorithms can detect patterns or anomalies in data that humans might miss.
- Improved Safety: One big advantage of using robots is keeping humans out of dangerous situations. In industries with hazardous conditions (mining, chemical plants, etc.), robots can take on the risky tasks – whether handling toxic substances or working in extreme temperatures – thereby reducing workplace injuries.
- Innovation and New Capabilities: AI can uncover insights from big data that lead to new solutions (for example, discovering a new drug by analyzing molecular data). Robots can be designed to do things humans can’t, like handle microscopically small components or lift extremely heavy objects.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Despite the exciting benefits, it’s important to acknowledge that robotics and artificial intelligence also bring challenges and raise important ethical questions:
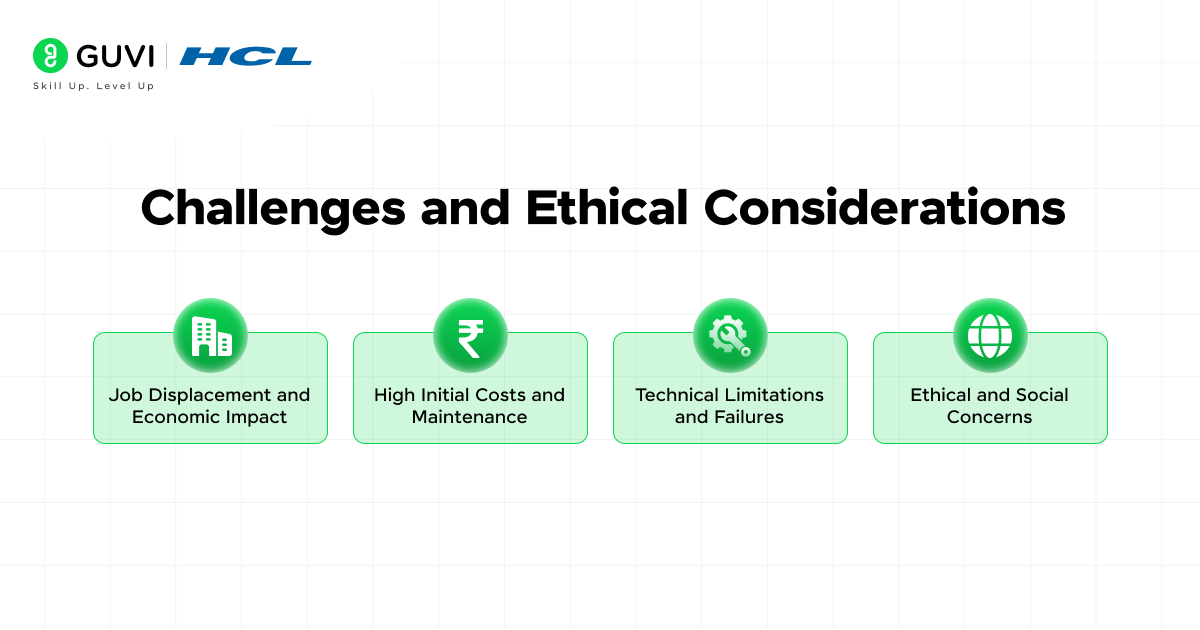
- Job Displacement and Economic Impact: Perhaps the most discussed concern is how automation will affect jobs. As robots and AI take over tasks, some jobs may become obsolete. For instance, self-checkout machines (a form of simple robotics/AI) reduce the need for cashiers. AI that automates data analysis might reduce certain administrative roles.
- High Initial Costs and Maintenance: Implementing robotics and AI systems can be expensive. Robots often require a significant up-front investment, not just to purchase the hardware but also to set up the infrastructure and training needed to use them.
- Technical Limitations and Failures: Robots can malfunction; AI systems can make mistakes or yield unexpected results. A glitch in a factory robot could halt a production line, or worse, cause an accident. AI systems are only as good as the data and algorithms behind them – if there’s a flaw, the AI might behave in undesired ways.
- Ethical and Social Concerns: AI in particular raises many ethical issues. Bias in AI is a big one: if an AI system is trained on biased data (say, for loan approvals or hiring), it could end up discriminating against certain groups. This has serious consequences for fairness and justice.
In short, while robotics and artificial intelligence offer great promise, they must be developed and deployed thoughtfully. Governments, industries, and researchers are increasingly aware of these issues. There are efforts to create ethical AI principles and safety standards for robots. For example, the OECD and United Nations have been working on AI ethics guidelines.
To lighten things up, here are some interesting tidbits about robotics and artificial intelligence that you might find surprising:
Origin of the Word “Robot”: The term “robot” comes from the Czech word “robota,” which means “forced labor” or “hard work.” It was first used in a 1920 Czech play by Karel Čapek, where mechanical beings called robots were workers.
AI as a Term Was Coined in 1956: The field of artificial intelligence got its name in the mid-1950s. In 1956, a group of scientists led by John McCarthy held a workshop at Dartmouth College, and in their proposal, they coined the term “artificial intelligence” to describe this new field of study.
These facts highlight the rich history and rapid progress in robotics and AI. From coining terms decades ago to achieving feats that once belonged only to science fiction, the journey of robotics and artificial intelligence is full of fascinating stories!
Test Your Knowledge: Quick Quiz
Ready for a quick challenge? Try answering these questions to check your understanding of robotics and artificial intelligence. This mini-quiz is just for fun – to recap some key points from the article.
- Which of the following best describes the difference between robotics and artificial intelligence?
A. Robotics is about programming software algorithms, while artificial intelligence is about building physical machines.
B. Robotics involves designing and building physical machines (robots), whereas artificial intelligence involves creating smart algorithms that can simulate thinking.
C. Robotics and artificial intelligence are actually the same field and the terms can be used interchangeably. - What is an example of an AI application that does not involve a robot?
A. An autonomous drone used for surveying crops.
B. A factory arm that assembles smartphones.
C. A voice assistant on your phone that uses speech recognition to answer questions. - Which is not an advantage of using robotics and AI?
A. They can work continuously without fatigue, improving efficiency.
B. They always make perfect decisions with no possibility of error or bias.
C. They can perform tasks dangerous to humans, improving safety in certain jobs.
(Check your answers in the answers section below to see how you did!)
Answers:
- B. Robotics focuses on physical machines (robots), and AI focuses on intelligence and algorithms. (Answer A is reversed; Answer C is incorrect – the fields are related but not identical.)
- C. A voice assistant like Siri is pure AI software without a robot body. (A and B both involve physical robots – a drone and a factory arm are robotics examples combined with AI.)
- B. It’s not true that these technologies are infallible; AI can have errors or bias, and robots can malfunction. (Options A and C are true benefits of robotics/AI.)
If you’re serious about mastering artificial intelligence and want to apply it in real-world scenarios, don’t miss the chance to enroll in HCL GUVI’s Intel & IITM Pravartak Certified Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning course. Endorsed with Intel certification, this course adds a globally recognized credential to your resume, a powerful edge that sets you apart in the competitive AI job market.
Conclusion
In conclusion, we’ve explored the basics of robotics and artificial intelligence, from what they are to how they’re used, their benefits, and their challenges. It’s clear that these technologies are already deeply embedded in our lives – and their influence is only growing.
Looking ahead, the line between robotics and AI will continue to blur as we build more intelligent machines that can learn and adapt.
Feel free to explore further, ask questions, and even get hands-on. The world of robotics and artificial intelligence is as exciting as it has ever been – and you are now better equipped to understand and be a part of it!
FAQs
1. What is the difference between robotics and artificial intelligence?
Robotics focuses on designing and building physical machines (robots) that can perform tasks, while artificial intelligence is about creating smart algorithms that enable machines to think, learn, and make decisions. AI can exist without robotics, and robotics can function without AI, but when combined, they create intelligent robots.
2. How are robotics and AI used in everyday life?
They power technologies like robotic vacuum cleaners, AI voice assistants, autonomous cars, smart appliances, and AI-powered healthcare diagnostics. From home cleaning to online recommendations, you’re likely using both in some form daily.
3. What are the main benefits of using robotics and AI?
Key advantages include higher efficiency, precision, safety, and the ability to handle repetitive or dangerous tasks. They also help in discovering new solutions through data analysis and enable innovations like personalized learning or robotic surgeries.
4. What are the challenges and risks of robotics and AI?
Challenges include job displacement, high setup costs, technical failures, and ethical issues like AI bias, data privacy concerns, and misuse (e.g., autonomous weapons). Responsible development and regulation are crucial to mitigate these risks.
5. What is the future of robotics and artificial intelligence?
Expect to see more collaborative robots (cobots) working alongside humans, smarter AI systems integrated into daily tools, humanoid robots for human-like environments, and AI-powered decision-making in industries. The future will likely involve greater synergy between AI’s “brain” and robotics’ “body.”




























Did you enjoy this article?