Understanding LLMs (Large Language Models): A Complete Beginner’s Guide
Dec 03, 2025 4 Min Read 1231 Views
(Last Updated)
What you are reading is not a pre-written script. This sentence, or the sentence before this, is well-crafted in real time by a writer. But what if I told you this blog can be generated by a machine that has never felt curiosity, never struggled for the right word, and never had an original thought?
This is the power of LLMs (Large Language Models) . The technology that enables machines to use language as humans do: they learn patterns, tone, and meaning from large amounts of text so that they can respond with nearly perfect accuracy and fluency.
In this blog, we will explore how LLMs work, what enables them to be so effective, and why they are considered the foundation of the AI revolution.
Table of contents
- What Are LLMs (Large Language Models)?
- The Process of How an LLM Works
- Training on Massive Data
- Tokenization
- The Transformer architecture
- Fine-tuning and optimization
- Responding (Inference)
- Evolution of Large Language Models
- Why Are LLMs So Powerful?
- Learning Scale
- Contextual Awareness
- Multitasking Ability
- Few-Shot and Zero-Shot Learning
- Applications of LLMs (Large Language Models)
- Challenges and Limitations of LLMs
- Wrapping it up:
- FAQs
- What does LLM stand for?
- How do LLMs learn?
- Are LLMs intelligent or conscious?
- Can LLMs replace humans?
What Are LLMs (Large Language Models)?
Large Language Models (LLMs), an advanced application of AI, are created to understand and generate human language. To learn the interrelationships, structures, and meanings of words and sentences in human language, LLMs are “trained” on extensive amounts of text data, which can include: books, websites, research papers, articles, and other codified texts.
The goal is a very simple but profound one to enable machines to understand context and produce plausible, coherent, and meaningful output. Whereas traditional programs are bound to specific human-generated rules, LLMs, through statistical learning and deep neural networks, “predict” the next word or phrase with probability based on examples established through training.
A Simple Analogical Reference
Imagine when a parent teaches a child to talk. The parent might have the child listen to them or read multiple iterations of sentences or stories before the child begins to understand grammar, tone, and meaning in the language. LLMs are used for instructional purposes in the same manner, although on a scale that human capacity cannot comprehend.
Also read: 7 Exciting Project Ideas Using Large Language Models (LLMs)
The Process of How an LLM Works
At first glance, it may simply seem as though LLMs (Large Language Models) simply “know” things; they write essays, translate languages, summarize text, and answer questions like humans do. However, behind this intelligence, there is a compelling combination of data, mathematics, and deep learning.
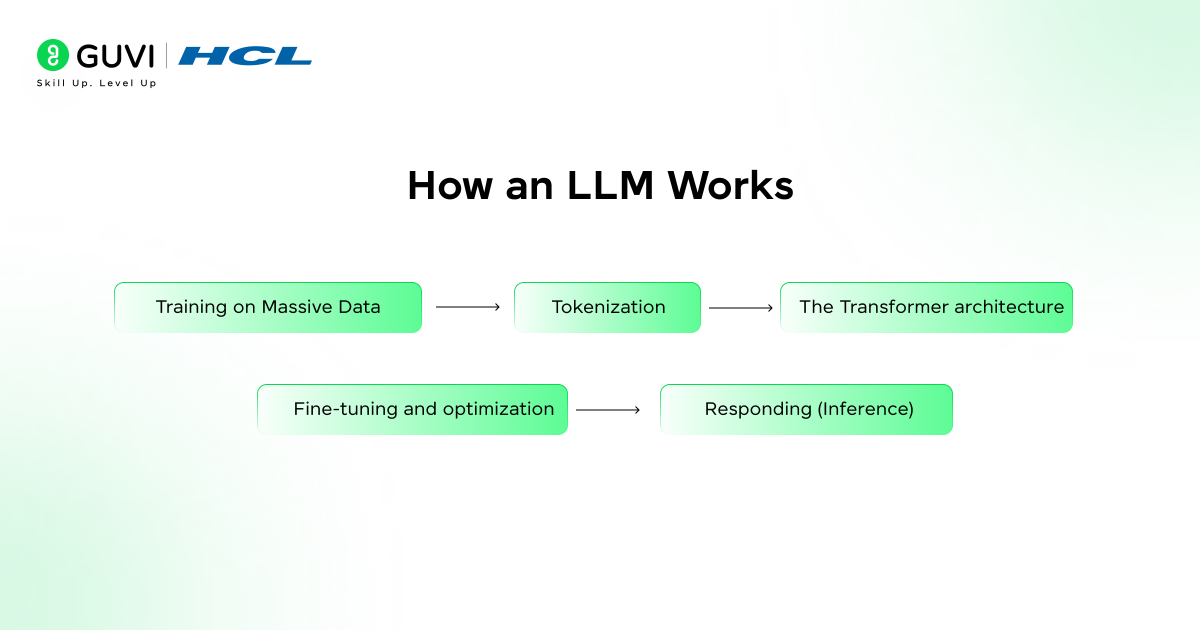
1. Training on Massive Data
LLMs are trained on extremely large amounts of text, everything from books, newspaper articles, and research papers to code repositories. Through reading such text, the model learns grammar, facts, reasoning patterns, and even emotional tone.
This training phase enables the model to better understand how words and phrases relate to one another while coding the model to understand the context of words instead of just the individual word.
2. Tokenization
Before processing text to a model, text is segmented into smaller elements, or tokens. These tokens can take the form of words or subwords or even characters. Tokenization allows the model to process and understand language efficiently and is capable of processing text that includes words that the model has never seen before.
Also read: AI Meets Edge: Building Smart Applications with LLMs on Edge Devices
3. The Transformer architecture
The true power of modern LLMs comes from the Transformer architecture, a method described by Google in 2017.
Transformers use a mechanism called self-attention, which allows a model to focus on the most relevant words in a sentence. For example, in the sentence “The cat sat on the mat because it was tired,” the model can understand that “it” refers to “the cat,” not “the mat.”
This mechanism enables the model to get the meaning and relationships across long pieces of text.
4. Fine-tuning and optimization
After the base model is trained, developers perform a fine-tune step on the model to optimize it on datasets and/or instructions. This allows LLMs to perform and generalize for different use cases; i.e., writing, question answering, and code generation.
5. Responding (Inference)
Once you type a prompt, the LLM does not “search” for an answer. The model’s output depends on predicted next-word probabilities learned during the training process. In addition, the model generates fluent and contextualized writing based on predicted probabilities.
Evolution of Large Language Models
Large Language Models did not grow overnight: here is how they have evolved over the years.
| Year | Model | Key Innovation |
| 2017 | Transformer (Google) | Introduced attention mechanism |
| 2018 | GPT (OpenAI) | First large-scale generative model |
| 2019 | BERT (Google) | Improved understanding of context using bidirectionality |
| 2020 | GPT-3 (OpenAI) | 175 billion parameters; human-like text generation |
| 2022 | PaLM, OPT, BLOOM | Open and multilingual large models |
| 2023–2024 | GPT-4, Claude, Gemini | Multimodal reasoning (text, image, and code) |
Why Are LLMs So Powerful?

1. Learning Scale
LLMs (Large Language Models) are trained on billions of words from different domains science, history, pop culture, etc. Because of this, they learn from a large data that allows them to address almost any subject.
2. Contextual Awareness
In contrast to previous models, LLMs can remember the previous context of your conversation. They keep track of much longer threads, remember previous prompts and ideas, and generate answers that sound more natural.
3. Multitasking Ability
The Large Language Models can summarize an article, translate a paragraph, generate code, and even write a poem, all without changing the fundamental architecture of the LLM.
4. Few-Shot and Zero-Shot Learning
LLMs can perform tasks for which they were never explicitly trained, by observing examples and understanding (few-shot), or even without examples (zero-shot). This quality makes the LLM easily and broadly adaptable to new tasks.
Enroll in HCL GUVI’s AI & ML Email Course and explore how real AI models learn, think, and evolve.
- The term “transformer” in LLMs refers to how the model transforms sequences of words into meaningful patterns.
- GPT-3 was trained on over 570GB of text data — that’s equivalent to millions of books!
- OpenAI’s GPT-4 can process text and images together, enabling powerful multimodal reasoning.
- Training a single Large Language Model (LLM) can cost millions of dollars in computing resources.
Applications of LLMs (Large Language Models)
Let’s explore some of the most transformative use cases:
- Text and Content Generation: LLMs (Large Language Models) can produce human-quality text on nearly any topic, including blog posts, emails, marketing copy, poetry, and screenplays. This article may have been generated by one.
- Summarization and Distillation: Models can take a long and complex document, such as a legal contract, research paper, or long news article, and generate an accurate and concise summary, capturing the major themes and points throughout.
- Translation: While they are not explicitly trained for this task, the sheer size of their knowledge means they will correctly translate between dozens of languages, often with a level of fluency that is superior to dedicated systems, including idiomatic expressions.
- Code Generation and Explanation: Applications like GitHub Copilot (using OpenAI’s Codex) can write code in response to described programs in plain natural English, debug existing code, and explain what a complicated function is doing in everyday language, such as English.
- Question Answering and Reasoning: Large Language Models can respond to factual questions, but they can also engage in the more impressive step-by-step reasoning of chains of thought. When prompting the model to “think step by step” they can delegate a multi-step problem (like a math word problem or logic puzzle) in a way that appear to engage in a kind of logical deduction.
Challenges and Limitations of LLMs
While LLMs are revolutionary, they aren’t perfect. Understanding their challenges is key to using them responsibly.

- Hallucination: Large Language Models can, on occasion, produce false or misleading information conveyed confidently. This phenomenon is known as AI hallucination, and it continues to create major obstacles in important areas.
- Bias in Data: LLMs learn from data available on the internet; thus, they may unintentionally reflect the human biases that exist in the data, such as gender, cultural, or racial biases.
- Computational Cost: Both training and running Large Language Models require significant computing power, electricity, and hardware, which raises concerns regarding sustainability.
- Lack of True Understanding: LLMs do not “understand” language like humans do. LLMs simulate understanding of language through statistical prediction and not reasoning or consciousness.
- Security Risks: Malicious use cases on text (deepfake text), misinformation campaigns, and the risk of automated phishing raise ethical or cybersecurity concerns.
Also, check out Join HCL GUVI’s IITM Pravartak Certified Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning Course, designed by industry experts and backed by NSDC, to build your career in the world of intelligent systems from foundational ML concepts to hands-on LLM projects.
Wrapping it up:
Large language models (LLMs) have revolutionized the world of technology by changing how humans engage with it. LLMs create a clear distinction between information and understanding through conversations that mimic real human interaction. There are still roadblocks associated with bias, accuracy, and energy demands for LLMs, but it doesn’t take away from the obvious possibilities that exist for LLMs to change education, business, and communication.
I hope this blog was useful in providing you with a better understanding of how LLMs (Large Language Models) function. Stay curious and keep exploring the exciting world of AI!
FAQs
1. What does LLM stand for?
LLM refers to Large Language Model, which is a class of AI systems that is trained to learn and generate human language.
2. How do LLMs learn?
They learn by ingesting massive datasets of text and calibrating their parameters to estimate patterns in human language.
3. Are LLMs intelligent or conscious?
No. LLMs generate the appearance of intelligence by discerning patterns, but they are not conscious and do not possess understanding.
4. Can LLMs replace humans?
They can assist in automating functions; however, even though machines may be able to replicate an accomplished human worker’s actions, the potential for creativity or ethics will always require some human oversight.





























Did you enjoy this article?