
When we use the internet, stream videos, send emails, or connect smart devices, everything seems to work together effortlessly. But behind this smooth experience are many networks that follow different rules, formats, and protocols. The reason they can still communicate without issues is because of an important device called a gateway. A gateway in a computer network works like a smart bridge that helps two different networks understand each other and exchange data safely and efficiently.
In this blog, we will look at what a gateway in computer network is, why it is important, how it works, and the different types you will find in real-world systems. We will also explore its functions, uses, challenges, and future trends. By the end, you will clearly understand how gateways keep modern communication running smoothly and why they are essential for both everyday users and large organizations.
Table of contents
- What Is A Gateway?
- Importance Of Gateways In Computer Networks
- Types Of Gateways
- Network Gateway
- Internet Gateway
- Cloud Storage Gateway
- VoIP Gateway
- Email Gateway
- Key Roles Of A Gateway
- Translation of Protocols
- Providing Security
- Traffic Management and Routing
- Connecting Disparate Systems
- Real-World Applications Of Gateways
- Challenges With Gateways
- Future Trends In Gateway Technology
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- Is a gateway the same as a router?
- Can a computer act as a gateway?
- What is a default gateway?
- Do gateways slow networks?
- Are gateways important in IoT?
What Is A Gateway?
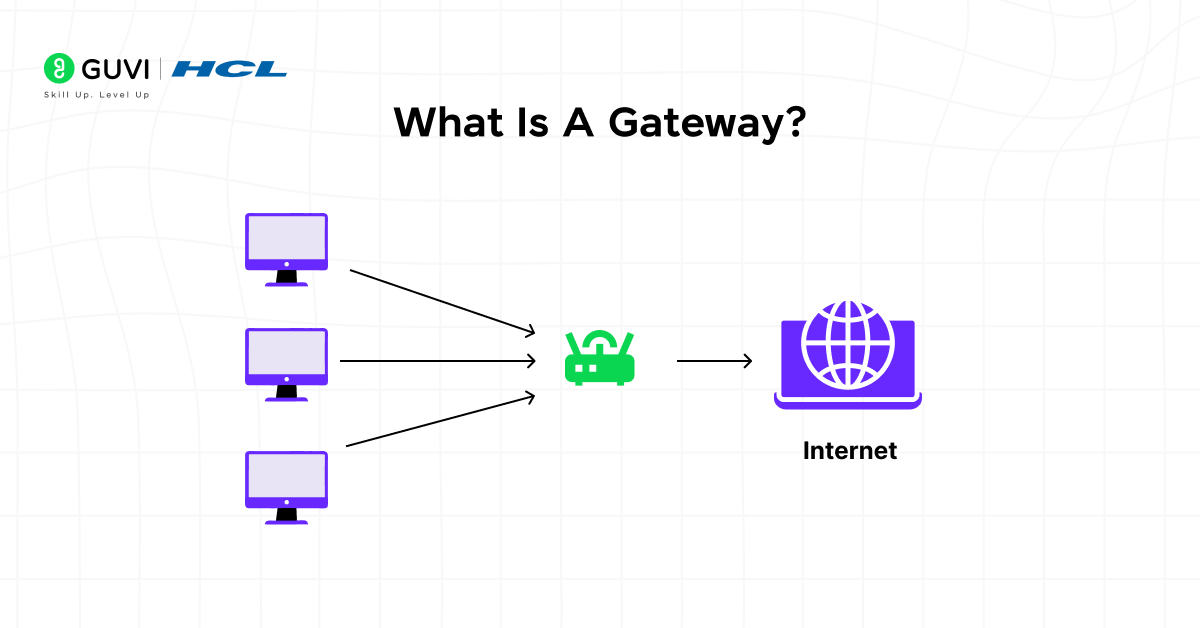
A gateway is a network device that connects two or more networks that rely on different communication protocols or data structures. It manages how information passes from one network to another by translating packet formats, applying security checks, and forwarding data appropriately. Unlike routers or switches that handle movement within similar networks, a gateway performs deeper conversions to allow incompatible systems to exchange information reliably.
Gateways act as the entry and exit points of a network, ensuring that any data leaving or entering undergoes proper transformation. They operate at multiple OSI layers depending on how complex the translation needs to be, making them one of the most versatile components in network architecture.
Importance Of Gateways In Computer Networks
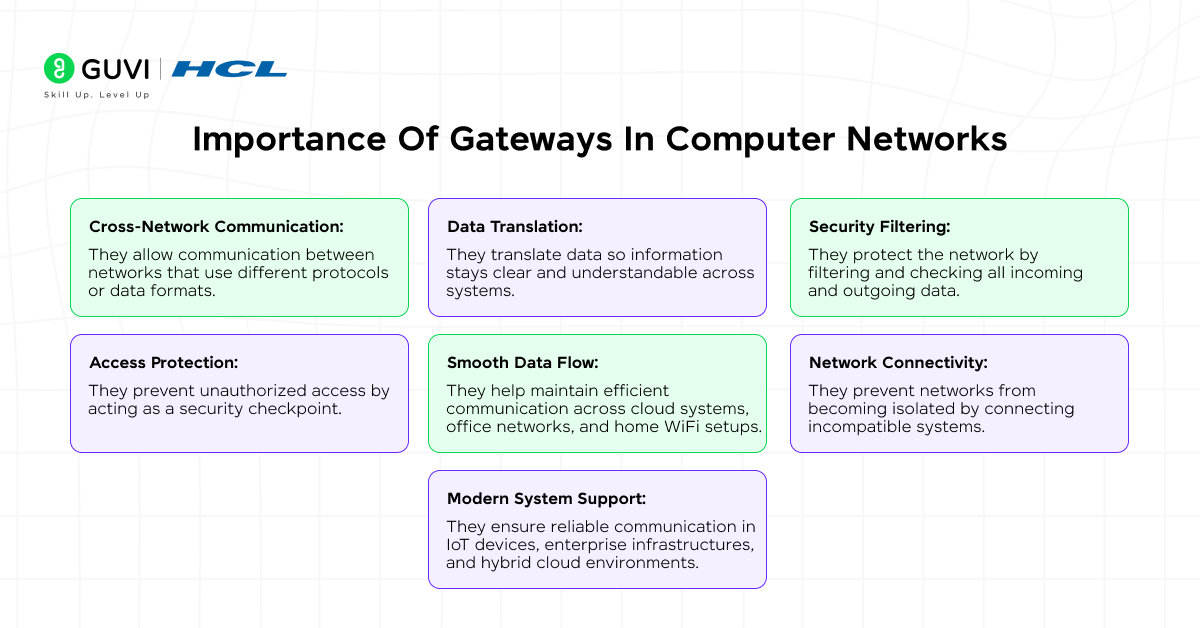
Different networks use different technologies, IP structures, and communication rules. Without a gateway in computer network setups, these networks cannot communicate smoothly. A gateway makes sure that data traveling from one network is translated into a format that another network can understand.
Here’s why gateways are important:
- Cross-Network Communication: They allow communication between networks that use different protocols or data formats.
- Data Translation: They translate data so information stays clear and understandable across systems.
- Security Filtering: They protect the network by filtering and checking all incoming and outgoing data.
- Access Protection: They prevent unauthorized access by acting as a security checkpoint.
- Smooth Data Flow: They help maintain efficient communication across cloud systems, office networks, and home WiFi setups.
- Network Connectivity: They prevent networks from becoming isolated by connecting incompatible systems.
- Modern System Support: They ensure reliable communication in IoT devices, enterprise infrastructures, and hybrid cloud environments.
A gateway ensures secure, efficient, and seamless communication even when networks operate very differently, making it a crucial part of today’s digital world.
Types Of Gateways
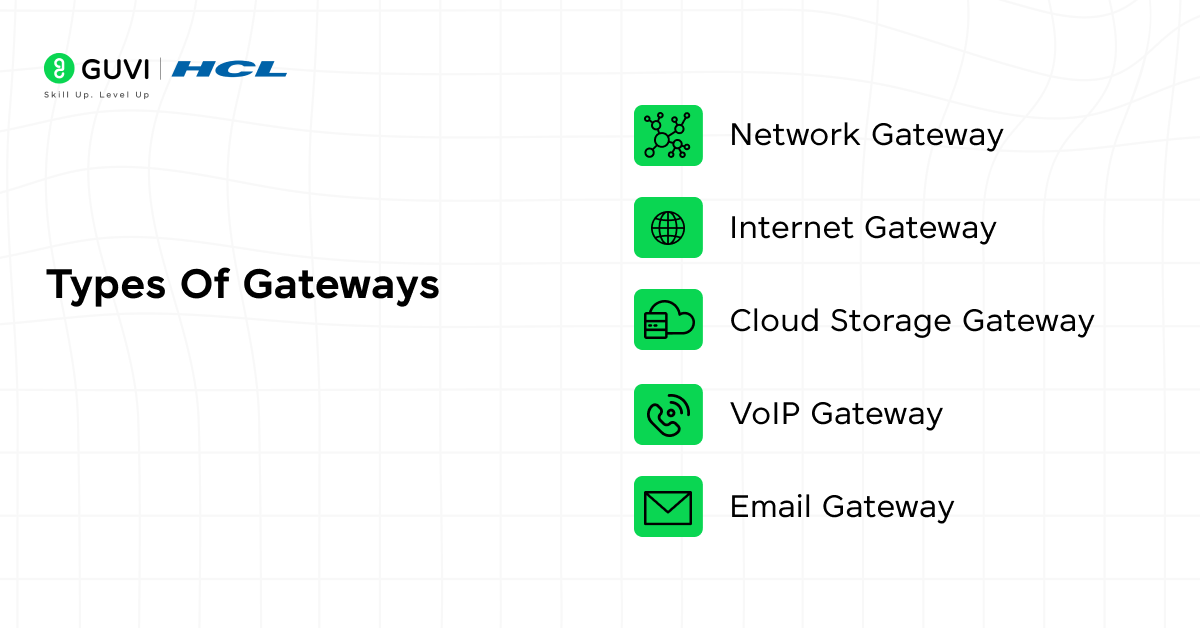
Gateways come in several types based on the kind of communication they handle and the role they play in a network. Here are the most common types of gateways you will find in real-world systems:
- Network Gateway
- Internet Gateway
- Cloud Storage Gateway
- VoIP Gateway
- Email Gateway
Each of these gateways serves a unique purpose and helps different networks communicate smoothly and securely.
1. Network Gateway
A network gateway is one of the most essential forms of a gateway in computer network environments. It connects two networks that use different communication rules or structures, ensuring they can understand each other.
What it does:
- Packet Conversion: Converts data packets from one format to another.
- Default Gateway Role: Acts as the main pathway for LAN-to-WAN communication.
- Network Interoperability: Helps different types of networks communicate seamlessly.
Example:
Your home router works as a network gateway by connecting your local devices to the internet and translating data between them.
2. Internet Gateway
An internet gateway helps a private network connect safely to the internet. It manages internet traffic while keeping internal devices secure from outside threats.
What it does:
- Traffic Management: Handles all incoming and outgoing internet traffic.
- NAT Functionality: Performs Network Address Translation to share a single public IP.
- Firewall Security: Protects the network from unauthorized access.
Example:
Cloud services like AWS use internet gateways to allow virtual machines to connect to the internet safely.
3. Cloud Storage Gateway
A cloud storage gateway connects local storage systems to cloud environments, allowing smooth data transfer between on-premise setups and cloud platforms.
What it does:
- Format Conversion: Translates local data formats into cloud-supported formats.
- Multiple Storage Support: Works with file, block, and object storage systems.
- Easy Cloud Migration: Helps organizations move or sync data to the cloud without issues.
Example:
Businesses that store files locally but automatically back them up to the cloud rely on cloud storage gateways.
4. VoIP Gateway
A VoIP gateway connects traditional telephone systems with modern internet-based voice networks, enabling smooth communication between analog and digital formats.
What it does:
- Signal Conversion: Converts voice signals from PSTN lines to digital IP packets.
- Advanced Processing: Supports echo cancellation, compression, and decompression.
- Hybrid Communication: Allows analog phones and VoIP systems to work together.
Example:
Call centers using both landline phones and VoIP services depend on VoIP gateways to connect the two systems.
5. Email Gateway
An email gateway filters, monitors, and routes email traffic between networks, ensuring safe and reliable email communication.
What it does:
- Threat Blocking: Stops spam, malware, and phishing emails.
- Policy Enforcement: Applies security rules to incoming and outgoing messages.
- Reliable Delivery: Ensures emails reach the correct destination without delays.
Example:
Corporate organizations use email gateways to scan attachments, block suspicious emails, and ensure compliance with email security standards.
Key Roles Of A Gateway
A gateway in computer network environments plays multiple critical roles that keep data flowing smoothly, securely, and intelligently between different systems. Whether it’s translating data, protecting your network, or connecting modern devices with older systems, gateways ensure seamless communication. In this blog, we will explore four major roles a gateway performs:
- Translation of Protocols
- Providing Security
- Traffic Management and Routing
- Connecting Disparate Systems
1. Translation of Protocols
When two networks use different communication rules or data formats, the gateway makes sure the information stays understandable. It converts packet structures, adjusts headers, and restructures data so both sides can communicate without errors.
Key points:
- Protocol Conversion: Converts data formats such as IPv4 ↔ IPv6.
- Data Repackaging: Restructures packets so they match the receiving network’s requirements.
- Cross-System Compatibility: Ensures smooth communication between different network types.
Example:
A device using IPv6 successfully accesses a website that still operates on IPv4 through protocol translation.
2. Providing Security
Gateways add a strong layer of protection by checking every packet that enters or leaves a network. They filter harmful data, stop unknown connections, and apply security rules to keep the network safe from attacks.
Key points:
- Deep Packet Inspection: Examines data thoroughly before allowing it inside.
- Threat Blocking: Stops untrusted or suspicious sources.
- Secure Communication: Supports encryption and authentication for safe data exchange.
Example:
An email gateway detects and blocks phishing links or malicious attachments before they reach users.
3. Traffic Management and Routing
As networks grow and handle more devices, a gateway helps manage data flow efficiently. It analyzes traffic patterns, chooses the best routes, and prevents the network from slowing down.
Key points:
- Routing Logic: Decides the most efficient path for data packets.
- Bandwidth Optimization: Balances load to avoid network strain.
- Reduced Congestion: Improves speed and reliability during high traffic.
Example:
An enterprise gateway balancing traffic between multiple internal servers and connected cloud services.
4. Connecting Disparate Systems
Modern environments use many different platforms—IoT sensors, mobile devices, cloud applications, and industrial machines. A gateway helps all these systems communicate smoothly by translating their unique formats.
Key points:
- Legacy–Modern Bridging: Connects older systems with newer digital platforms.
- API-Level Translation: Supports communication between applications using different APIs.
- Device Format Conversion: Adapts signals and data formats from specialized devices.
Example:
An IoT gateway collects data from sensors and sends it to a cloud dashboard where it can be monitored in real time.
Real-World Applications Of Gateways
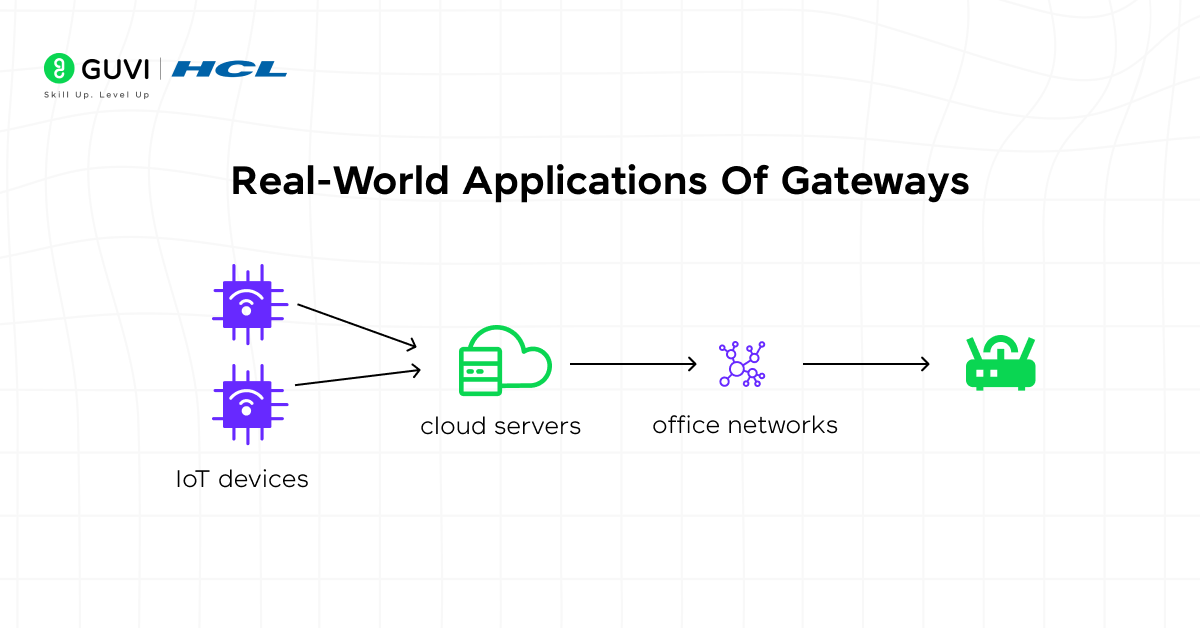
Gateways are used in many real-world situations to connect devices, secure communication, and enable smooth data exchange between different systems. Whether in offices, industries, or cloud environments, a gateway in computer network setups ensures reliable and secure communication across platforms.
- Office Branch Connectivity
Connects multiple office locations so they can share data and resources securely. - IoT–Cloud Linking
Sends data from IoT sensors to cloud dashboards for monitoring. - Enterprise Security Filtering
Blocks harmful traffic and prevents unauthorized access. - VoIP Communication Support
Converts voice signals so internet-based calling works smoothly. - Industrial System Integration
Links factory machines to monitoring systems in real time. - Secure Email Management
Filters emails to stop spam, viruses, and phishing attempts. - Hybrid Cloud Transfers
Helps move data safely between on-premise systems and cloud storage.
Challenges With Gateways
Even though gateways are essential in any gateway in computer network setup, they also come with certain challenges that can affect performance, cost, and security. Understanding these limitations helps in better planning and network management.
- Traffic Slowdown
Heavy protocol translation can reduce network speed. - Single Point Of Failure
If the gateway goes down, communication across networks stops. - High Cost
Enterprise-grade gateways are expensive to purchase and manage. - Complex Configuration
Skilled professionals are needed for setup and optimization. - Security Risks
Poor configuration can create new vulnerabilities at the network boundary. - Cloud Maintenance Issues
Managing cloud gateways often requires ongoing updates and monitoring.
To build a stronger foundation in networking concepts like gateways, routing, IP addressing, and security, you can explore HCL GUVI’s Networking Essentials Course. It offers beginner-friendly, hands-on learning that helps you understand how real-world networks operate.
Future Trends In Gateway Technology
As networking grows more advanced, gateways are evolving to handle smarter security, faster connections, and larger device ecosystems. The future of the gateway in computer network technology is moving toward automation, intelligence, and stronger protection.
- AI-Based Filtering
Gateways will use AI to detect threats and manage traffic more accurately. - Cloud-Native Gateways
Designed for distributed cloud applications to improve scalability and flexibility. - Quantum-Secure Encryption
Future gateways will use quantum-resistant security to protect sensitive data. - Ultra-Light IoT Gateways
Built for massive IoT networks with low power usage and fast device handling. - Autonomous Self-Optimizing Gateways
Gateways will automatically adjust performance, routing, and security without manual input.
Conclusion
Gateways are one of the most important components in modern network architecture, acting as the bridge that allows different systems, platforms, and technologies to communicate effortlessly. They translate protocols, filter threats, manage heavy traffic, and connect everything from cloud services to IoT devices. Without gateways, networks would remain isolated and unable to share information smoothly.
In today’s world, where businesses depend on cloud computing, smart devices, remote access, and secure communication, the role of a gateway in computer network environments has become more critical than ever. As networks continue to expand and evolve, gateways will keep adapting with smarter security, faster processing, and improved automation. Their importance will only grow as digital systems become more intelligent, integrated, and globally connected.
FAQs
1. Is a gateway the same as a router?
No. A router connects similar networks, while a gateway connects networks using different protocols.
2. Can a computer act as a gateway?
Yes. With NAT or proxy settings, a computer can perform gateway functions.
3. What is a default gateway?
It is the device that forwards data from your network to external networks like the internet.
4. Do gateways slow networks?
They may introduce delay if overloaded, but optimized gateways maintain smooth performance.
5. Are gateways important in IoT?
Yes. IoT gateways handle device communication, data conversion, and security.































Did you enjoy this article?