HTMX vs. React: Do You Really Need a Heavy Framework for Your First Project?
Feb 20, 2026 6 Min Read 904 Views
(Last Updated)
If you’re building your first web project, the internet probably told you to start with React. It is used by startups and enterprises alike, backed by a massive ecosystem, and packed with powerful features. But here’s the real question: do you actually need all that complexity to get started?
Here comes: HTMX, a lightweight alternative that lets you build dynamic web interfaces using plain HTML and your existing backend—no bundlers, no state libraries, no JavaScript frameworks; just markup that works.
This article isn’t about declaring a winner. It’s about helping you ask the right question: What does your project really need? We’ll break down both tools: HTMX vs React, based on performance, developer experience, scalability, and more, so you can make a decision rooted in practicality, not hype.
Let’s unpack when to go all-in on a frontend framework and when it’s smarter to stay simple.
Table of contents
- What Is HTMX?
- Key Features of HTMX
- What Is React?
- Key Features of React
- Best Use Cases
- Comparing HTMX vs. React: Key Evaluation Criteria
- Developer Experience
- Performance
- Learning Curve
- Tooling and Ecosystem
- Maintainability and Scalability
- When to Choose HTMX for Your First Project
- When to Choose React for Your First Project
- HTMX vs React: Example Comparing Code Syntax
- HTMX vs React: Comprehensive Comparison Table
- Do You Really Need a Heavy Framework for Your First Project?
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- Is HTMX better than React for beginners?
- Can I use HTMX and React together?
- Does HTMX replace JavaScript?
- What are the limitations of HTMX?
What Is HTMX?

HTMX is a lightweight library that enhances the power of HTML by allowing web pages to become interactive without writing JavaScript. It works on the idea that HTML can serve as more than a static layout language. It extends the role of HTML to handle interaction, state updates, and asynchronous communication directly from the markup.
Developers can use familiar HTML attributes to make elements respond dynamically to user actions. This design keeps the front end simple while maintaining clear communication between the browser and the server. The result is a workflow where most of the logic remains on the backend, leading to easier debugging, a cleaner structure, and faster prototyping. HTMX aligns naturally with server-rendered frameworks such as Django or Flask because it supports their existing templating systems without heavy configuration.
Key Features of HTMX
- Declarative AJAX Handling: HTMX lets developers perform asynchronous requests directly in HTML using attributes such as hx-get or hx-post. The server returns rendered HTML fragments that replace or update parts of the page without reloading it.
- Server-Side Integration: It integrates easily with backend frameworks. The server controls how data is processed and returned, which makes debugging and deployment simpler for full-stack developers.
- Real-Time Updates: Support for WebSockets and Server-Sent Events enables real-time content updates. This makes it possible to build live dashboards or notifications with minimal client-side code.
- Progressive Enhancement: HTMX adds interactivity without breaking traditional HTML rendering. Applications remain functional even if JavaScript fails or loads slowly.
- Ease of Use and Low Overhead: The setup process requires no build tools or transpilation. Developers can add the HTMX script to a page and start using it immediately.
What Is React?

React is a JavaScript library created to build user interfaces that are modular and reusable. It focuses on breaking a web application into components that manage their own logic and state. Developers describe what each component should look like based on data, and React automatically updates the interface whenever that data changes. This model simplifies the management of complex front-end behavior.
React applications run primarily on the client side, which gives users smoother transitions and faster interactions after the first load. The library is widely adopted because it supports large ecosystems, reusable patterns, and long-term scalability for interactive products such as dashboards, SaaS tools, or single-page applications.
Key Features of React
- Component-Based Architecture: Applications are built from self-contained components. Each component manages its state and rendering logic, which makes code reusable and easier to test.
- Declarative Rendering: Developers describe how the interface should appear based on the current data. React updates only the parts of the page that have changed, which improves performance and predictability.
- Virtual DOM for Efficient Updates: React maintains a lightweight representation of the Document Object Model. It compares previous and new states efficiently before applying updates to the browser.
- Hooks and State Management: Hooks allow developers to manage data flow, side effects, and context without complex class structures. This keeps code simpler and more readable.
- Rich Ecosystem and Tooling: React integrates with libraries for routing, animation, form management, and testing. Strong community support and extensive documentation make it a practical choice for large projects.
Best Use Cases
HTMX
- CRUD-based tools such as admin panels, CMS dashboards, or form-heavy apps
- Prototypes and MVPs where speed and simplicity matter
- Server-rendered apps built with Django, Flask, or Rails
- Projects that prioritize fast load times and minimal frontend dependencies
React
- Single-Page Applications that require smooth transitions and routing
- SaaS platforms and dashboards with complex state and user interactions
- E-commerce sites that demand dynamic product rendering and cart management
- Cross-team development where modularity and scalability are essential
Comparing HTMX vs. React: Key Evaluation Criteria
1. Developer Experience
HTMX provides a direct workflow that fits naturally into server-rendered architectures. Developers can add interactivity using HTML attributes without installing Node.js, configuring build tools, or managing complex dependencies. This makes it appealing for backend or full-stack developers who prefer working close to HTML and server logic.
React introduces a more complex environment. Developers must set up Node.js, bundlers like Webpack or Vite, and often rely on JSX for templating. Many projects also integrate libraries such as Redux or Zustand for state management. These tools create flexibility but require more setup and ongoing maintenance.
2. Performance
HTMX operates with a server-first approach. It loads minimal JavaScript and relies on the backend for rendering updates. This structure reduces the initial bundle size and improves time-to-first-byte performance. Since the browser only receives HTML fragments, load times remain consistent even on limited networks.
React uses client-side rendering, which allows interfaces to update quickly after the initial load. However, its bundle size and dependency graph are heavier. Applications may take longer to become interactive, especially on low-end devices, although optimization techniques such as code splitting and lazy loading can reduce these issues.
3. Learning Curve
HTMX is approachable for developers already familiar with backend frameworks. It uses simple HTML attributes rather than custom syntax, which shortens onboarding time. Backend engineers can extend their existing workflows to include interactivity without needing deep JavaScript knowledge.
React requires understanding component lifecycles, hooks, and state flow. Developers must also learn JSX syntax and modular design patterns. The learning curve is higher but valuable for those aiming to specialize in modern frontend development or contribute to large-scale web systems.
4. Tooling and Ecosystem
HTMX focuses on minimalism. It integrates easily into existing backend environments but offers fewer third-party tools or community plugins. Debugging often happens within the browser’s native developer tools. This simplicity keeps the stack predictable but limits flexibility for large-scale UI development.
React has one of the richest ecosystems in web development. It includes libraries for routing, animation, form validation, and testing. Tools such as React DevTools, Storybook, and Jest improve debugging, UI consistency, and testing coverage. The ecosystem supports both small and enterprise-scale applications.
5. Maintainability and Scalability
HTMX works best in small to medium projects where server-rendered pages and limited interactivity are sufficient. Its monolith-friendly structure keeps everything in one place, reducing coordination overhead across services. However, scaling to highly interactive interfaces may become cumbersome as client-side logic grows.
React supports scalability through modular design. Components can be reused across projects and updated independently. Its architecture aligns with microfrontend and API-driven models, which makes it suitable for distributed teams and applications that evolve continuously.
Master both simplicity and scalability with our Full Stack Development Course, certified by IIT-M Pravartak. Learn to build responsive, high-performance web applications using tools that fit your project’s goals, whether it’s lightweight HTML-driven interfaces with HTMX or dynamic, component-based architectures with React. Through hands-on projects, mentor-led guidance, and placement support, you
When to Choose HTMX for Your First Project
- You are building a CRUD or form-based application, such as an admin panel or feedback system.
- You prefer server-rendered HTML and want minimal dependency on frontend frameworks.
- You want to avoid JavaScript fatigue and boilerplate while maintaining clean templates.
- You are working under tight timelines or limited deployment resources.
- You aim to prototype quickly without complex infrastructure or build processes.
HTMX helps developers focus on logic and content delivery instead of configuration. It’s ideal for first projects where reliability and simplicity matter more than heavy interactivity.
When to Choose React for Your First Project
- You plan to build a highly interactive or real-time single-page application.
- You aim to gain deep experience in modern frontend development practices.
- You need client-side routing and stateful interactions such as modals, animations, or dashboards.
- You expect the project to scale in complexity or team size over time.
- You want to take advantage of a mature ecosystem with active community support.
React rewards long-term investment. Its component-based design supports rapid iteration once the initial setup is complete. It is a strong choice for projects that emphasize interactivity and continuous growth.
HTMX vs React: Example Comparing Code Syntax
Below is a simple example showing how HTMX and React handle the same functionality, a button that fetches and displays user data from the server.
HTMX Example (HTML + Backend)
<!-- index.html -->
<button hx-get="/user" hx-target="#result" hx-swap="innerHTML">
Load User Info
</button>
<div id="result"></div>
# Flask backend example
@app.route("/user")
def get_user():
return "<p><strong>User:</strong> Alice, Age: 28</p>Explanation:
HTMX uses HTML attributes like hx-get and hx-target to make asynchronous requests. The server returns HTML that replaces the content inside the target element. No JavaScript or frontend build setup is needed.
React Example (JavaScript + Component)
// UserInfo.jsx
import { useState } from "react";
function UserInfo() {
const [data, setData] = useState(null);
const loadUser = async () => {
const res = await fetch("/user");
const html = await res.text();
setData(html);
};
return (
<div>
<button onClick={loadUser}>Load User Info</button>
<div dangerouslySetInnerHTML={{ __html: data }} />
</div>
);
}
export default UserInfo;
Explanation: React handles the same task using client-side logic. It fetches data via JavaScript, stores it in state, and updates the UI dynamically. This approach offers greater flexibility but requires a build setup and more code.
HTMX vs React: Comprehensive Comparison Table
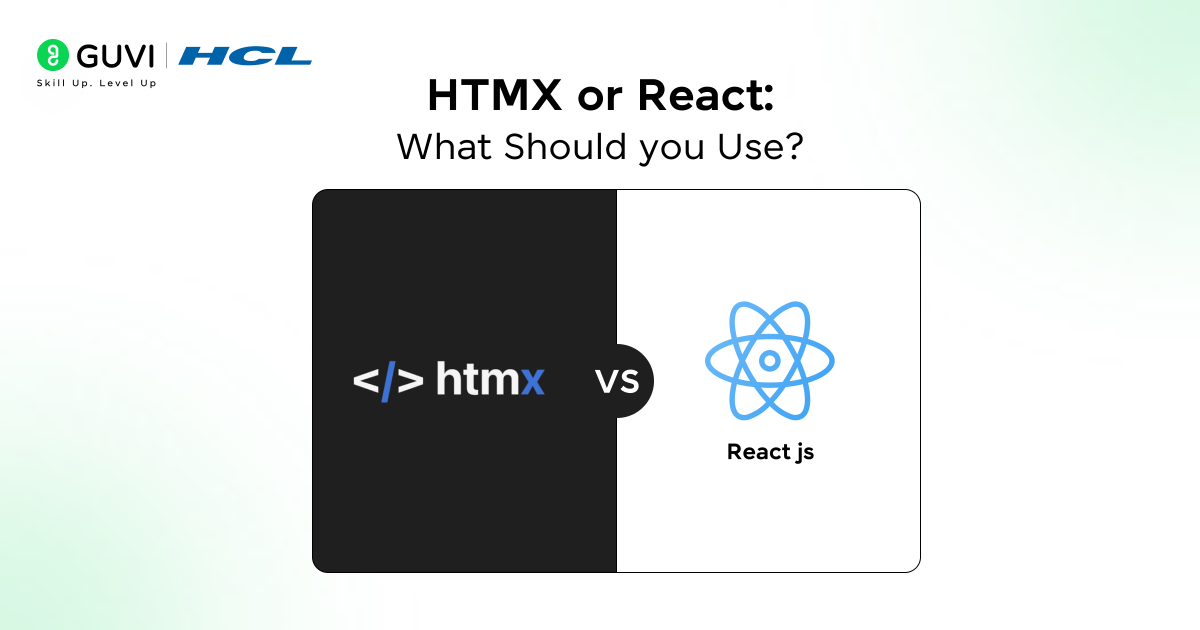
| Factor | HTMX | React |
| Definition | Extends HTML for interactivity without custom JavaScript | Builds reusable, state-driven UI components |
| Setup | Simple, no build tools required | Needs Node.js, JSX, and bundlers |
| Core Logic | Server-rendered updates via HTML fragments | Client-side rendering with virtual DOM |
| Performance | Fast initial load, minimal JS footprint | Fast UI updates, heavier initial bundle |
| Learning Curve | Easy for backend and full-stack developers | Steep, requires JavaScript and state management |
| Tooling | Lightweight with limited integrations | Rich ecosystem with libraries for routing, testing, and UI |
| Scalability | Best for small to mid-sized apps | Suited for large, complex applications |
| Use Cases | CRUD apps, dashboards, CMS, prototypes | SPAs, SaaS, real-time apps, data-driven dashboards |
| Ecosystem Size | Small community, limited third-party tools | Large ecosystem with active community support |
| Maintainability | Simple and backend-friendly | Modular but needs consistent tooling upkeep |
| Real-Time Support | Built-in WebSockets and SSE support | Requires libraries like Socket.io |
| Limitations | Less suited for heavy client-side logic | Higher complexity and dependency overhead |
| Best For | Fast, server-driven projects | Interactive, scalable, and modern UIs |
Do You Really Need a Heavy Framework for Your First Project?
For most first-time developers, the answer is no. You do not always need a heavy framework like React to build a functional and engaging web application. Frameworks introduce complexity through build configurations, state management, and dependency handling that can distract from learning core concepts. Starting with a lightweight approach such as HTMX or plain HTML and server rendering helps you focus on the essentials: clean structure and user interaction. Once those fundamentals are strong, adopting frameworks becomes easier and more meaningful for scaling complex applications.
Conclusion
Choosing between HTMX and React depends on the project’s goals, scope, and your comfort with tooling. HTMX favors simplicity and server-driven development, which makes it ideal for small or backend-heavy projects. React excels when applications demand complex interactivity, modular scalability, and long-term flexibility.
Beginners often find HTMX faster to learn and more productive initially, while React rewards deeper investment with greater control and ecosystem support. Instead of chasing popularity, evaluate what your project truly requires. The best framework is the one that helps you build efficiently, maintain clarity, and deliver meaningful user experiences without unnecessary complexity.
FAQs
1. Is HTMX better than React for beginners?
HTMX is easier for beginners who understand basic HTML and backend logic. It removes the need for complex build tools or JavaScript frameworks. React is more powerful but requires learning JSX, component structure, and state management, which can feel overwhelming for a first project.
2. Can I use HTMX and React together?
HTMX and React can coexist in the same project. You can use HTMX for server-rendered pages and React for isolated, highly interactive components. This hybrid setup helps balance simplicity and interactivity without forcing a full migration to a single framework.
3. Does HTMX replace JavaScript?
HTMX does not replace JavaScript. It reduces the need to write custom JavaScript for common tasks such as form submission or dynamic updates. Developers can still add JavaScript for advanced interactivity or client-side logic when required.
4. What are the limitations of HTMX?
HTMX works best in small or medium projects. It becomes less practical for applications that require heavy client-side state management or offline functionality. It also has a smaller ecosystem, which limits access to third-party libraries and specialized tooling.




































Did you enjoy this article?