
CAD Designer Career in India: Salary, Job Roles & Skills
Oct 10, 2025 4 Min Read 5371 Views
(Last Updated)
India is rapidly emerging as a hotspot for skilled CAD designers. With massive government-led projects like national industrial corridors, smart cities, railways, and the Make in India initiative, CAD designers are in high demand for planning, structural modeling, and BIM-led infrastructure design.
Adding to that, India’s CAD drafting services are scaling fast, from $5.65 billion in 2023 to $5.95 billion in 2024 (a 5.3% increase), and are projected to reach $7.26 billion by 2028.
This surge is driven by rising needs in manufacturing, architecture, electronics, civil engineering, and automotive industries, all of which depend on precision design, 3D modeling, and digital workflows.
If you’re unsure how to begin your CAD designer career or are stuck midway in your CAD designer career path, this blog breaks it all down, from education and skills to roles, growth paths, and real-world opportunities.
Table of contents
- What Does a CAD Designer Do?
- CAD Designer Career Path: Required Education to Get Started
- Key Responsibilities of a CAD Designer
- CAD Designer Career Path & Salary in India (2025)
- Must-Have Skills to Grow in the CAD Designer Career Path
- How to Start Your CAD Designer Journey Today
- Learn the Basics
- Get Certified with Job-Focused Training
- Apply Your Skills on Projects
- Build a Strong Portfolio
- Start Gaining Work Experience
- Wrapping it together
- FAQs
- Is CAD a good career path?
- Are CAD designers in demand?
- Is CAD a stressful job?
- Is CAD an IT skill?
- What are the highest-paid CAD jobs?
What Does a CAD Designer Do?
A CAD Designer (Computer-Aided Design Designer) creates detailed and precise technical drawings for various design projects using 2D and 3D modeling software. Their core responsibility is to translate ideas, concepts, and specifications into visual designs that can be accurately manufactured or constructed.
They play a crucial role in bridging the gap between creative concepts and real-world execution by producing drawings that meet functional, aesthetic, and engineering requirements.
For example, let’s say an interior designer is planning the layout for a modular kitchen. The CAD designer works alongside the interior designer, starting with rough sketches or verbal ideas. Using software like AutoCAD, SketchUp, or SolidWorks, the CAD designer develops a 2D floor plan showing the exact placement and dimensions of cabinets, plumbing lines, electrical outlets, and ventilation systems.
From there, they move on to building a 3D model, which helps visualize the spatial arrangement, finishes, and how different components interact. Throughout the process, the CAD designer ensures all measurements are accurate, the design aligns with safety standards, and that it’s practical for fabrication or installation.
In essence, a CAD Designer:
- Converts design briefs and sketches into technical blueprints
- Prepares 2D drafts and 3D models using industry-standard CAD tools
- Collaborates with architects, engineers, or product designers to refine and iterate on designs
- Ensures technical drawings meet project specifications, codes, and manufacturability requirements
- Identifies potential design or production issues early through digital simulation or clash detection
- Maintains version control and organizes drawing files for seamless project coordination
CAD Designer Career Path: Required Education to Get Started
The first step in your roadmap to becoming a CAD designer starts from a solid educational foundation. A bachelor’s degree, typically in engineering, is the minimum qualification required to pursue a CAD-focused career. Courses like Mechanical Engineering, Civil Engineering, Architecture, or Industrial Design are most relevant. These programs introduce the core principles of design, geometry, physics, and material science that serve as the backbone of CAD work.
Once you have a foundational understanding, the next step is gaining proficiency in industry-standard software tools like AutoCAD, SolidWorks, CATIA, and Revit. These tools aren’t usually taught in depth during undergraduate programs, which is why pursuing add-on certification courses becomes essential. Specialized training, such as HCL GUVI’s Mechanical or Civil CAD Zen Classes, can help you build practical skills, work on real-world projects, and create a strong portfolio that employers look for.
If you’re aiming for a CAD designer career path that goes beyond just academic knowledge, this combination of formal education and hands-on tool expertise is non-negotiable.
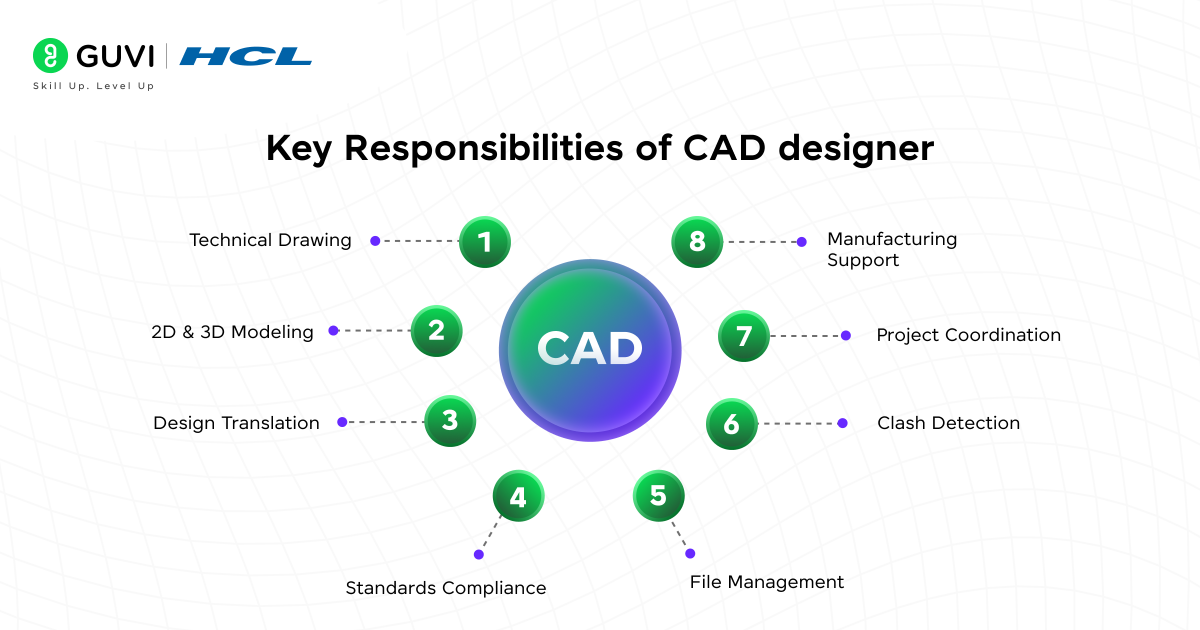
Key Responsibilities of a CAD Designer
A CAD Designer is responsible for creating precise 2D and 3D technical drawings based on design concepts, engineering inputs, or client specifications.
Using software like AutoCAD, SolidWorks, or Revit, they translate sketches or verbal ideas into digital formats that guide construction, manufacturing, or product development.
Their role includes ensuring dimensional accuracy, adhering to industry standards, and regularly updating designs based on feedback or project changes. CAD Designers work closely with engineers, architects, and project teams to resolve design conflicts and ensure feasibility.
They also manage file documentation, version control, and may support prototyping or simulation processes, especially in fields like mechanical, civil, or product design.
Their outputs are often used in CNC machining, 3D printing, or BIM workflows, making them a critical link between design vision and real-world execution.
CAD Designer Career Path & Salary in India (2025)
| Job Role | Avg. Annual Salary (INR) | Experience | Key Skills | Industries |
| Junior CAD Designer | ₹1.4–4 Lakhs | 0–2 years | AutoCAD, 2D drafting, basic 3D modeling | Construction, Manufacturing, Engineering |
| CAD Engineer | ₹3–6 Lakhs | 2–5 years | SolidWorks/CATIA, GD&T, assembly design | Automotive, Aerospace, Product Design |
| Senior CAD Draftsman | ₹5–9 Lakhs | 5–8 years | Mastercam, CNC programming, and toolpath generation | Infrastructure, MEP, Heavy Engineering |
| Product Design Specialist | ₹6–12 Lakhs | 5–10 years | Fusion 360, design thinking, prototyping, rendering | Consumer Electronics, Startups |
| BIM Modeler | ₹4.5–10 Lakhs | 3–8 years | Revit, Navisworks, clash detection, BIM standards | Smart Cities, Construction, Architecture |
| Tooling Engineer | ₹5–12 Lakhs | 4–10 years | Mastercam, CNC programming, toolpath generation | Aerospace, Tooling, Manufacturing |
| CAD Design Engineer | ₹3.5–8 Lakhs | 3–8 years | STAAD.Pro, FEA, structural analysis | Civil, Energy, Design Consultancies |
| CAD Trainer/Instructor | ₹3–7 Lakhs | 4+ years | Teaching, curriculum development, certification programs | EdTech, Training Centers |
Must-Have Skills to Grow in the CAD Designer Career Path
To find your path in a crowded and competitive job market, CAD designers need more than just software knowledge. A balanced mix of technical expertise and interpersonal skills is what truly shapes a successful CAD designer career.
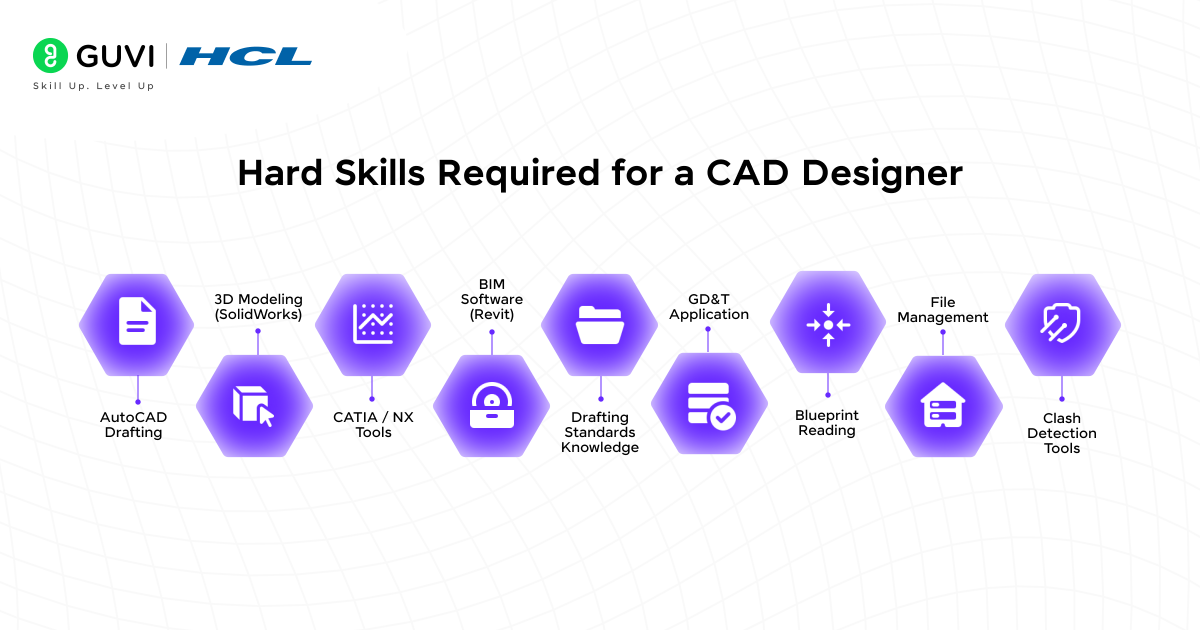
Hard skills:
These are the core tools and competencies you need to become industry-ready and move beyond just academic knowledge:
- AutoCAD – 2D drafting, annotation, dimensioning, layout creation
- SolidWorks – 3D modeling, assemblies, motion simulation
- CATIA / Siemens NX – Surface modeling, sheet metal, advanced assemblies (used in aerospace/automotive)
- Revit Architecture / AutoCAD Civil 3D – BIM tools used in civil and architectural design
- Drafting Standards – Knowledge of ISO, ASME, or BIS standards
- Geometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing (GD&T) – Essential for manufacturing-ready designs
- Technical Drawing Interpretation – Reading and generating blueprints
- File Management – Exporting, converting, and organizing formats (.DWG, .DXF, .STEP, etc.)
- Simulation & Clash Detection Tools – Especially useful in BIM and mechanical design
- Basic CAM Understanding – Knowing how designs transition into manufacturing adds depth to your profile
Soft skills
Often underestimated, soft skills are what set you apart in real project environments. These traits ensure smoother teamwork, project execution, and long-term career growth:
- Attention to Detail – Precision is everything in CAD. Even minor mistakes can cost time and money
- Problem-Solving – Ability to spot design inefficiencies or clashes and correct them independently
- Communication – Explaining technical details to engineers, clients, or vendors in simple language
- Collaboration – Working with cross-functional teams including architects, engineers, and technicians
- Time Management – Balancing multiple revisions, deadlines, and project phases efficiently
- Adaptability – Learning new tools or workflows as technologies and client needs evolve
- Analytical Thinking – Understanding how each design impacts real-world production or usability
- Version Control & Organization – Keeping drawings updated, named, and structured for easy access
How to Start Your CAD Designer Journey Today
Starting your CAD designer career doesn’t have to feel overwhelming. With the right approach and tools, you can build a strong foundation that leads to real job opportunities, especially in high-demand sectors like mechanical and civil design.
Here’s a step-by-step path to get started:
Learn the Basics
Begin by understanding 2D drafting, 3D modeling, and how geometry, scale, and measurements are applied in design software. Grasping these fundamentals sets the tone for everything that follows.
Get Certified with Job-Focused Training
To work professionally, just knowing software isn’t enough. You need guided, practical learning. HCL GUVI’s CAD Zen Classes are designed to bridge this gap with hands-on training and placement support:
These programs teach tools like AutoCAD, SolidWorks, CATIA, and Revit through real-world projects.
Apply Your Skills on Projects
Practice with real or mock design briefs. Build mechanical components, create building layouts, or draft detailed models. The more practical exposure you gain, the more confident and hire-ready you become.
Build a Strong Portfolio
Document your work—show your 2D plans, 3D models, and completed assignments in an organized, visual portfolio. A well-crafted portfolio helps recruiters quickly evaluate your capability.
Start Gaining Work Experience
Look for internships, freelance gigs, or junior CAD roles. On-the-job experience is the fastest way to refine your skills and grow into higher-level positions.
Wrapping it together
Becoming a successful CAD designer is a work in progress. The demand is high, but so is the competition. What sets you apart is a strong foundation in design principles, hands-on software expertise, and the ability to think and build like a professional. When you understand how design translates to real-world functionality across industries like manufacturing, construction, and product development, your skills begin to stand out where it matters most.
Learn, build, and keep refining your skills. With the right training, real-world practice, and a solid portfolio, your CAD designer career can move from entry-level to expert faster than you think.
If you’re ready to begin, HCL GUVI’s CAD Zen Classes are a great place to start, because industry-ready learning is what truly gets you hired.
FAQs
1. Is CAD a good career path?
Yes, CAD is a solid career path with applications in architecture, engineering, manufacturing, and construction. It offers long-term growth, creative satisfaction, and steady demand across global industries.
2. Are CAD designers in demand?
CAD designers are in high demand, especially in industries like automotive, civil infrastructure, aerospace, and electronics, where 2D drafting, 3D modeling, and BIM workflows are essential for modern project execution.
3. Is CAD a stressful job?
CAD jobs are typically low to moderately stressful. Pressure can arise from tight deadlines, design revisions, or project coordination, but clear briefs and experience usually reduce day-to-day stress levels.
4. Is CAD an IT skill?
CAD is not strictly an IT skill, but it overlaps with tech. It falls under design and engineering technology, involving software proficiency, digital modeling, and technical problem-solving, not traditional IT tasks.
5. What are the highest-paid CAD jobs?
Senior CAD Designers, BIM Managers, CAD Engineers in aerospace, and Product Design Specialists earn the highest salaries. Roles requiring both design and engineering expertise tend to offer the best compensation.































Did you enjoy this article?