Web Developer vs Software Developer: Choosing the Right Career Path in 2025
Oct 22, 2025 5 Min Read 1774 Views
(Last Updated)
The tech industry is growing at a rapid pace, and there’s a huge need for talented workers. If you’re new to the field, you’ve wondered: Should I become a Web Developer or a Software Developer?
Both jobs are thrilling, in-demand, and well-paying. However, web developers and software developers differ significantly in their skills, duties, tools, compensation, and long-term job prospects.
In this blog, we’ll take a close look at web developer vs software developer to help you choose your future career path. Whether you’re a student just starting or looking into IT jobs, this blog will show you the ins and outs of web development vs software development and help you figure out which one might suit you best.
Table of contents
- Who is a Web Developer?
- Who is a Software Developer?
- Web Developer Skills vs Software Developer Skills
- Web Developer Skills:
- Software Developer Skills:
- Web Developer vs Software Developer Tools
- Web Developer Tools:
- Software Developer Tools:
- Web Developer vs Software Developer Education
- Web Developer Salary vs Software Developer Salary
- Choosing Between Web and Software Development: A Guide for Freshers
- Ask yourself these questions:
- Step-by-step guide: Become a Web Developer
- Step-by-step guide to becoming a Software Developer
- Web Developer vs Software Developer
- Final thoughts:
- FAQs
- What is the difference between a web developer and a software developer?
- Is web development easier than software development?
- Who gets paid well web developer or software developer?
- Do you need a degree to be a web developer?
Who is a Web Developer?
A web developer is someone who programs, designs, and manages websites and web applications. Their work revolves around the World Wide Web.

Types of Web Developers:
- Front-End Developer: Uber or ui (user interface) to build web applications and websites that are good-looking and interactive.
- Back-End Developer: Works with server-side, databases, and logic.
- Full Stack Developer: A mixture of both front-end and back-end developers to build web applications.
Basically, if you have spent time on building websites, apps or anything that a user can interact with on the World Wide Web, you are probably a web developer.
Who is a Software Developer?
A Software Developer is responsible for designing, developing, testing, and maintaining software applications that do or may not operate on a network. Software Developers generally work on desktop applications, mobile applications, embedded applications, or enterprise applications rather than exclusively on web applications or online products.

Software Development Examples:
- Mobile applications (i.e., WhatsApp or Uber)
- Desktop software (i.e., MS Word or Photoshop)
- Operating systems (i.e., Windows or Linux)
- Video games or enterprise applications.
In simple terms, If web developers are the architects of websites, Software Developers are the technicians behind all software systems.
Web Developer Skills vs Software Developer Skills
The toolkits for these roles have some overlap (like problem-solving and basic programming logic) but differ significantly in their technical arsenals.
Web Developer Skills:
- Frontend: HTML5, CSS3, JavaScript (ES6+), frameworks like React.js, Angular, or Vue.js.
- Backend: Server-side languages like Python (Django/Flask), JavaScript (Node.js), PHP, Ruby (Ruby on Rails), Java (Spring Boot).
- Database: SQL (MySQL, PostgreSQL) and NoSQL (MongoDB) databases.
- Essential Tools: Git, GitHub, web browsers’ DevTools, npm/yarn, RESTful APIs.

Software Developer Skills:
- Languages: Often more system-oriented languages like Java, C#, C++, Python, Swift (for iOS), Kotlin (for Android).
- Concepts: Strong grasp of Data Structures & Algorithms, Object-Oriented Programming (OOP), Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC), and often more low-level system design.
- Platforms: Expertise in specific environments like Windows/macOS/Linux for desktop, Android Studio/Xcode for mobile, or embedded systems IDEs.
- Tools: Git, CI/CD pipelines (Jenkins, GitLab CI), Docker, and other testing frameworks.
Web Developer vs Software Developer Tools
Web Developer Tools:
- Visual Studio Code
- Sublime Text
- Chrome DevTools
- Postman (for testing APIs)
- Figma/Sketch (for design collaboration).
Software Developer Tools:
- IntelliJ IDEA
- Eclipse
- PyCharm
- Android Studio
- Xcode
- Visual Studio (.NET stack)
Web Developer vs Software Developer Education
Compared to Software Developers, the educational path for Web Developers is more approachable, offering non-traditional education routes.
- Degrees: For both developers, a Bachelor’s degree in computer science (CS) or information technology (IT) is helpful, but for software work, especially when working with complex systems like aerospace or finance, a CS education is typically a hard requirement.
- Bootcamps and Certifications: This is where HCL GUVI comes in! Intensive coding bootcamps are enormously popular and effective in getting people job-ready for Web Developer positions. The pathway is more standardized. Bootcamps exist for software development as well (some even exclusively for mobile development), but education to get into complex system software development often requires a stricter, formal, more in-depth theoretical knowledge base.
- Self Learning: A very large number of successful self-taught developers in both of these industries have built their skills through online resources, coding scrimmages, projects, and contributing to open-source projects.
Web Developer Salary vs Software Developer Salary
| Role | Average Fresher Salary (India) | Average Experienced Salary (India) |
| Web Developer | ₹3 – 6 LPA | ₹7 – 20+ LPA |
| Software Developer | ₹3 – 8 LPA | ₹10 – 25+ LPA |
You can refer to Glassdoor or AmbitionBox for an updated salary of the above designation.
Choosing Between Web and Software Development: A Guide for Freshers
Ask yourself these questions:
- What excites you more?
- Building beautiful, interactive experiences that people use directly in their browser? → Web Development
- Solving complex logical problems and building systems that power devices or desktop applications? → Software Development
- What is your learning style?
- Do you prefer a practical, project-based approach where you can see visual results immediately? → Web Development
- Do you enjoy theory, deep dives into how things work, and don’t mind a longer learning curve? → Software Development
- What is your career vision?
- Do you want to work at a digital agency, a startup, or as a freelancer building client websites? → Web Development
- Do you aspire to work at a product-based company like Microsoft, Adobe, or a FinTech firm building its core platform? → Software Development
Step-by-step guide: Become a Web Developer
- Month 0–1: Foundations
- Learn HTML (structure), CSS (layout & visuals), and basic JavaScript (behavior).
- Practice by coding a simple personal page and a responsive layout.
- Tools: VS Code, Chrome DevTools, Git basics.
- Month 2–3: Frontend frameworks & workflow
- Pick one modern frontend library (recommend React first). Learn component model, state, props, and hooks.
- Learn CSS frameworks: Tailwind or Bootstrap.
- Start using GitHub to host projects; learn basic terminal/git workflows.
- Month 4–5: Backend basics
Learn server-side fundamentals: Node.js + Express or Python + Django/Flask.- Understand REST APIs, authentication basics, and working with databases (SQL or MongoDB).
- Build a small full-stack app (e.g., a TODO app with user login).
- Month 6: Deploy & polish
- Deploy projects using Netlify, Vercel, or simple VPS setups.
- Optimize for performance and mobile (lazy loading, responsive images).
- Build a clean portfolio site showcasing 3–5 real projects with README + code.
- Month 7–12: Deepen & specialize
- Choose a path: Frontend specialist (UI/UX + animations), Backend specialist (APIs, databases), or Full-stack.
- Add one larger project: e-commerce, chat app, or dashboard integrating third-party APIs.
- Learn testing basics (Jest, Cypress) and fundamentals of accessibility (a11y) and SEO for web.
- Job hunt & growth
- Prepare interview basics: data structures (arrays, objects), JS closures, asynchronous JS, HTTP.
- Contribute to open-source, freelance small gigs, or internships.
- Keep learning: modern patterns (PWAs, server-side rendering, static site generators).
Project ideas: Portfolio, blog CMS, e-commerce demo, real-time chat, PWA.
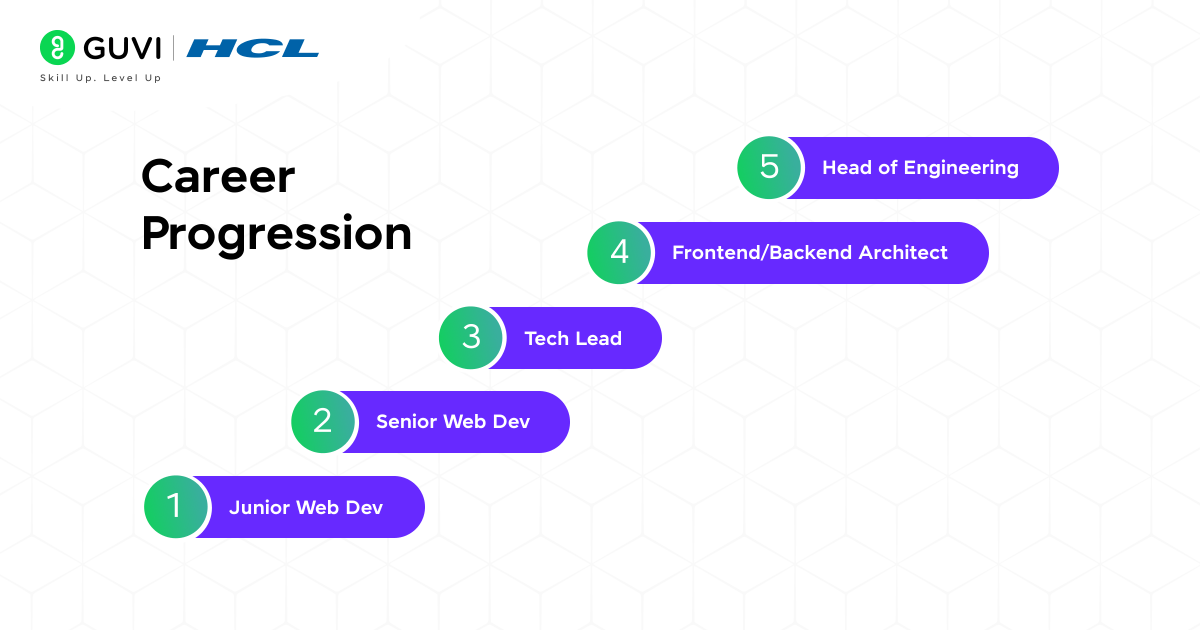
Step-by-step guide to becoming a Software Developer
- Month 0–2: Programming fundamentals
- Pick one general-purpose language (Python, Java, or C++) and master syntax, control flow, and functions.
- Practice by solving small problems and writing console apps.
- Month 2–5 : CS fundamentals
- Study data structures & algorithms (arrays, linked lists, stacks/queues, trees, hash maps, sorting, searching).
- Learn time/space complexity (Big O).
- Start solving problems on competitive/practice sites (focus on quality solutions).
- Month 5–8 : System & architecture basics
- Learn object-oriented design, basic design patterns, and software architecture principles.
- Understand databases (relational and NoSQL), transactions, and basic networking (HTTP, sockets).
- Months 8–12: Build substantial projects
- Build a medium project: desktop app, CLI tool, RESTful service, or simple mobile app.
- Add unit tests, CI basics, and use version control for team workflows.
- Month 12–18: Specialization & scaling
- Choose a specialization: Backend systems, mobile apps, embedded systems, game dev, AI/ML, or cloud engineering.
- Learn related tools: Docker, Kubernetes, cloud platforms (AWS/GCP/Azure) if targeting scalable systems.
- Study system design basics for interviews: load balancing, sharding, caching, CAP theorem.
- Job prep & growth
- Master coding interview patterns: arrays, trees, DP, graph traversal; simulate timed interviews.
- Build a GitHub repo with well-documented projects, including unit tests and design notes.
- Apply for internships, entry-level roles, and contribute to team projects to gain collaborative experience.
Project ideas: REST API with authentication, multi-module desktop app, simple mobile app, basic game, or microservice demo.
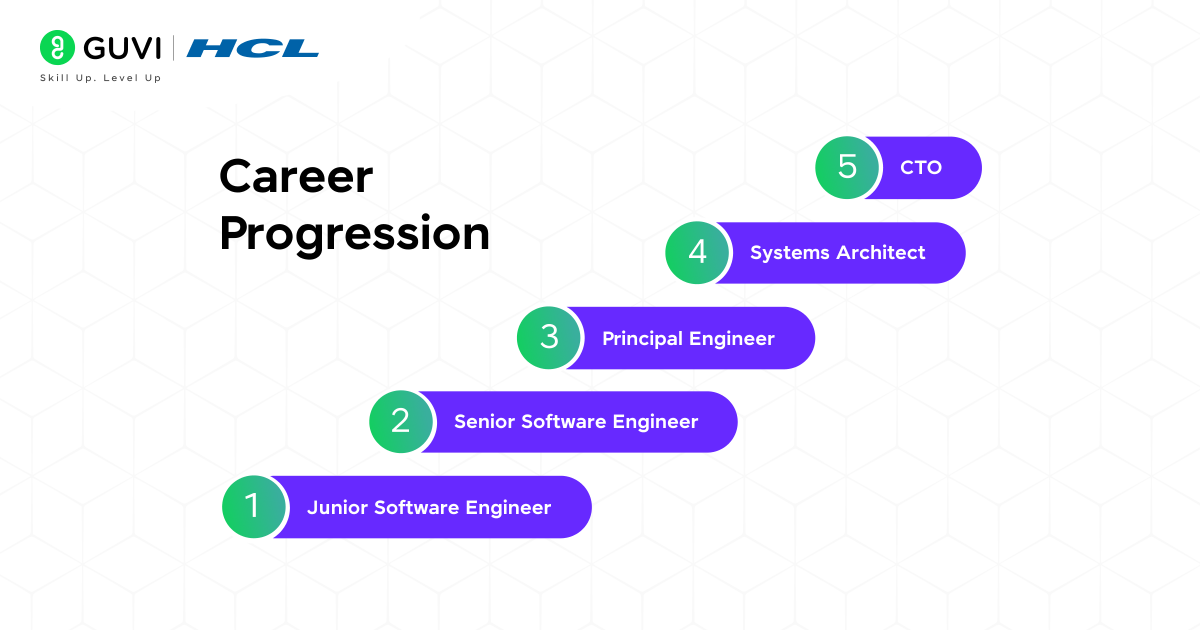
Web Developer vs Software Developer
| Factor | Web Developer | Software Developer |
| Primary Focus | Building and maintaining websites, web applications, and anything that runs in a browser. | Designing, building, and maintaining general-purpose software, including mobile, desktop, and enterprise applications. |
| Work Environment | Almost always internet-based. Their work revolves around making web apps interactive, fast, and user-friendly. | Can work both online and offline. Software may run on local machines, servers, or even embedded devices. |
| End Products | Examples include e-commerce websites like Amazon, social media platforms like Instagram (front-end), or SaaS apps like Trello. | Examples include mobile apps like WhatsApp, enterprise tools like SAP, operating systems like Linux, or games like PUBG. |
| Scope of Work | More specialized, primarily focusing on browsers and web technologies. | Much broader scope, covering apps, systems, and even hardware-integrated solutions. |
| Programming Languages | Typically uses JavaScript, HTML, CSS for front-end; Node.js, PHP, Python, or Ruby for back-end. | Works with a wider range: Java, C++, Python, C#, Swift, Go, Rust, depending on the application domain. |
| Problem-Solving Complexity | Often deals with design, interactivity, and user experience challenges. | Handles deeper system-level challenges like memory management, performance optimization, and algorithm design. |
| Collaboration | Works closely with designers, digital marketers, and product managers to make user-facing products. | Collaborates with data scientists, QA engineers, system architects, and hardware engineers depending on the project. |
| Career Opportunities | High demand in startups, freelance platforms, and digital-first companies. | Broader opportunities in fintech, healthcare, AI/ML, gaming, cybersecurity, and large-scale enterprise systems. |
If you are curious about software development and want to become a software developer, then grab the opportunity to learn with HCL GUVI’s IITM Pravartak and MongoDB Certified Online AI Software Development Course. The NSDC-endorsed course gives you a globally recognized certificate to add to your résumé, which is a significant advantage that will help you stand out in the competitive employment market.
Final thoughts:
Becoming a web developer or a software developer requires consistent building, practice, and improvement rather than rushing through tutorials. The step-by-step roadmap above provides a structured path from basics to advanced topics to prevent you from feeling lost. Whether you choose to focus on frontend, backend, or full-stack web development, or you explore software engineering and system design in depth, remember that patience and practice will teach you the most.
We hope this blog helps you plan your learning journey and gives you the clarity to start taking action today. Keep trying new things, keep writing code, and above all, enjoy the process.
Good luck and have fun on your developer journey!
FAQs
1. What is the difference between a web developer and a software developer?
Web developers specifically make websites and web applications. Software developers make software in a broader scope, including mobile apps, desktop software, or system software.
2. Is web development easier than software development?
Yes, web development has a lower barrier to entry and is more approachable for beginners. Stronger programming fundamentals are needed for software development.
3. Who gets paid well web developer or software developer?
In general, software developers have a higher upper limit on their salary. That said, experienced full-stack web developers also can make very attractive packages.
4. Do you need a degree to be a web developer?
Yes, but most web developers are self-taught through bootcamps and online courses. For software development, a CS or similar degree is preferred.




































Did you enjoy this article?