
30 Blockchain Developer Interview Questions and Answers
Dec 29, 2025 6 Min Read 5743 Views
(Last Updated)
With the world moving towards technology, one prominent field that is turning the tide is Blockchain. It has revolutionized industries from finance to supply chain management, and the demand for skilled blockchain developers is on the rise.
If you’re preparing for that role, you need to master blockchain developer interview questions and answers. It’s essential to brush up on key concepts, technical know-how, and coding skills.
To make this easier, we’ve compiled a list of 30 blockchain developer interview questions and answers designed for three levels: fresher, intermediate, and advanced. Whether you’re new to the field or have hands-on experience, these questions will give you a solid foundation to confidently tackle your interview. Let us get started!
Table of contents
- Quick Answer
- Top 30 Blockchain Developer Interview Questions and Answers
- Freshers Level
- Intermediate Level
- Advanced Level
- Bonus section: Scenario-Based Blockchain Interview Questions
- 💡 Did You Know?
- Conclusion
Quick Answer
Blockchain developer interview questions assess your knowledge of blockchain fundamentals, smart contracts, consensus algorithms, cryptography, security practices, and hands-on technical skills across fresher, intermediate, and advanced levels.
Top 30 Blockchain Developer Interview Questions and Answers

Preparing for a blockchain developer interview requires a solid understanding of both fundamental concepts and advanced technical skills.
This article presents 30 carefully curated blockchain developer interview questions and answers, to help you navigate interviews at various levels of expertise.
Freshers Level
1. What is Blockchain? Explain it in simple terms.
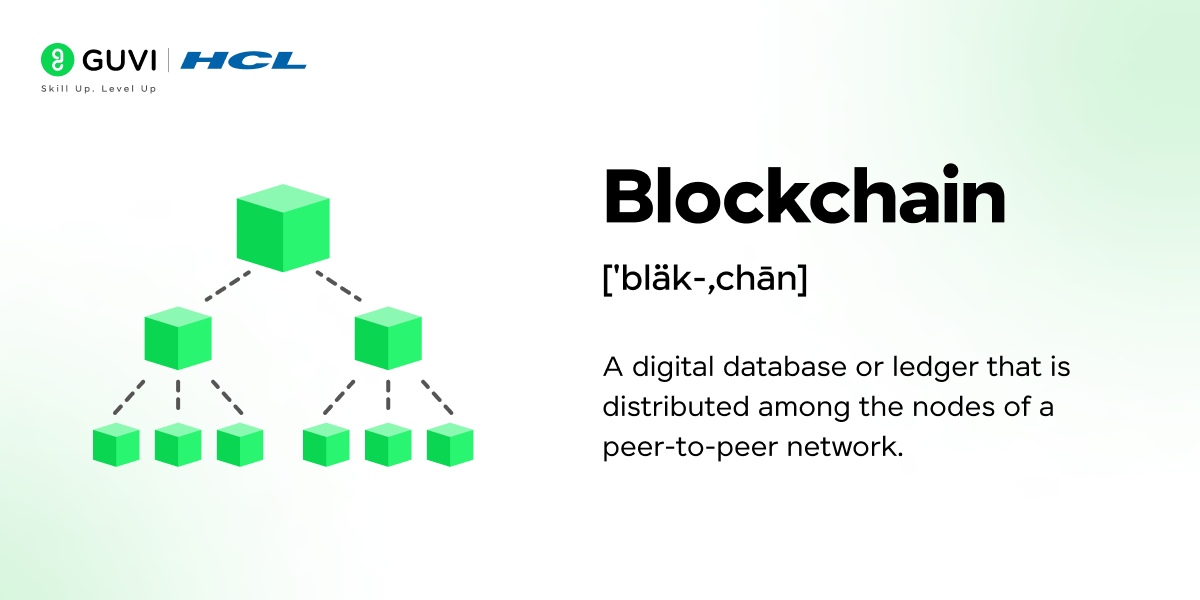
Blockchain is a decentralized, distributed ledger that records transactions across many computers. Each record, or “block,” is linked to the previous one, forming a chain of blocks. This structure ensures data transparency and immutability, making it secure and ideal for applications that require trust.
2. What’s the difference between Blockchain and a traditional database?
Unlike traditional databases, blockchain uses a decentralized approach where data is stored across multiple nodes, making it harder to alter or hack. Traditional databases rely on a central authority, while blockchain uses consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work (PoW) to validate transactions.
3. What is a Smart Contract?

A smart contract is a self-executing contract with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. It runs on a blockchain and automatically enforces the agreement’s terms when certain conditions are met, removing the need for intermediaries.
Also Read: Blockchain Developer Resume Guide: 11 Hot Tips to Make It Professional
4. Explain what Ethereum is and how it’s different from Bitcoin.
Ethereum is a decentralized platform that allows developers to build decentralized applications (DApps) using smart contracts. While Bitcoin primarily serves as digital currency, Ethereum enables programmable contracts and applications, making it more versatile for developers.
5. What is a DApp (Decentralized Application)?
A DApp is an application that operates on a decentralized network, typically a blockchain like Ethereum. Unlike traditional apps, DApps are open-source and run on a peer-to-peer network, making them more transparent and secure.
6. Coding Question: Write a simple Solidity function to add two numbers.
solidity
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
contract AddNumbers {
function add(uint a, uint b) public pure returns (uint) {
return a + b;
}
}7. Explain the role of a node in a blockchain network.
A node is a computer that participates in a blockchain network, validating transactions and maintaining a copy of the entire blockchain. Nodes contribute to the security and decentralization of the blockchain by participating in consensus and storing blockchain data.
Explore: Top 8 Blockchain Project Ideas For Students
Intermediate Level
8. What is consensus, and why is it essential in blockchain?
Consensus is a mechanism that ensures all nodes in a blockchain network agree on the validity of transactions. This agreement helps prevent fraud, double-spending and maintains trust in a decentralized network without a central authority.
9. Describe Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) and their differences.
PoW and PoS are two consensus mechanisms. PoW requires miners to solve complex puzzles to validate transactions, consuming significant energy. PoS, on the other hand, assigns validation rights based on the number of coins held by validators, making it more energy-efficient than PoW.
10. What are oracles in blockchain? Why are they important?
Oracles are services that fetch external data for smart contracts, enabling them to interact with real-world information. Since blockchains can’t access external data directly, oracles act as a bridge, allowing smart contracts to trigger actions based on real-world events.
11. What is a hash function, and how is it used in blockchain?
A hash function is an algorithm that takes an input and produces a fixed-size alphanumeric string, known as a hash. In blockchain, hashes are used to secure data and link blocks. Each block contains the hash of the previous block, creating an unbreakable chain.
Know More: Non-Coding Jobs in Blockchain: Exploring Opportunities Beyond Tech
12. Explain the concept of “Gas” in Ethereum.
Gas is a unit that measures the amount of computational work required to execute transactions or smart contracts on the Ethereum network. Users pay gas fees to incentivize miners to include their transactions in the blockchain.
13. Coding Question: Write a Solidity function to check if a number is even or odd.
solidity
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
contract CheckEvenOdd {
function isEven(uint number) public pure returns (bool) {
return number % 2 == 0;
}
}14. What is a Merkle Tree, and how does it work in blockchain?
A Merkle Tree is a binary tree where each leaf node represents a hash of data. It allows efficient verification of data integrity by combining hashes in pairs up to the root. This structure is commonly used in blockchains to verify large sets of transactions.
15. Explain the concept of sharding and how it improves blockchain scalability.
Sharding is a method that divides a blockchain network into smaller, manageable parts called “shards.” Each shard processes a subset of transactions, increasing the network’s throughput and scalability.
Advanced Level
16. What are zk-SNARKs, and how do they contribute to blockchain privacy?
zk-SNARKs (Zero-Knowledge Succinct Non-Interactive Argument of Knowledge) are cryptographic proofs that allow one party to prove knowledge of a value without revealing it. zk-SNARKs enhance privacy in blockchains by enabling confidential transactions.
17. How does a Lightning Network work, and what problem does it solve?
The Lightning Network is a second-layer solution for scaling Bitcoin transactions. It enables off-chain transactions, which are settled on the main blockchain only when needed, reducing congestion and enhancing transaction speed.
18. Explain the Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) concept in blockchain.
BFT is a property that allows a blockchain network to reach consensus even if some nodes act maliciously. BFT ensures that honest nodes can reach a consensus and prevent double-spending, crucial for blockchain security.
19. What is Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), and how does it work?
DPoS is a consensus mechanism where stakeholders elect a small number of trusted delegates to validate transactions. DPoS enhances network efficiency and speed, as fewer validators handle transactions compared to PoW or PoS.
20. Describe the term “51% attack” and its implications.
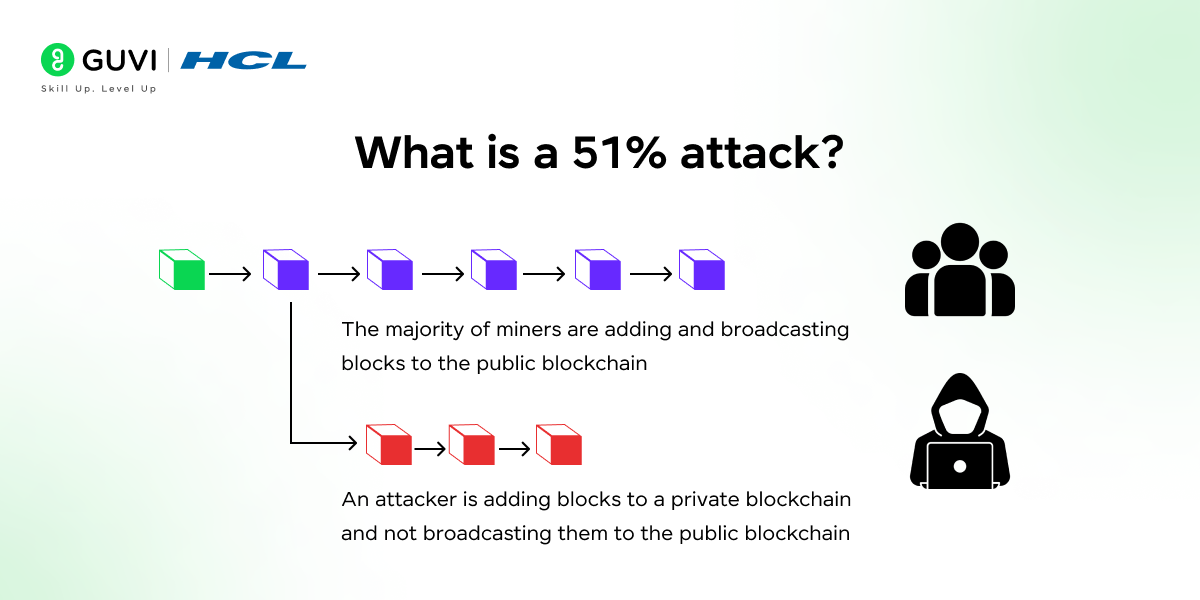
A 51% attack occurs when a single entity or group controls over 50% of a blockchain’s hashing power. This control allows them to alter the blockchain, double-spend, and invalidate transactions, threatening network security.
21. Coding Question: Write a Solidity function that checks if an address is a smart contract.
solidity
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
contract AddressChecker {
function isContract(address addr) public view returns (bool) {
uint32 size;
assembly { size := extcodesize(addr) }
return size > 0;
}
}22. What is a consensus algorithm? Explain one example in detail.
A consensus algorithm enables decentralized agreement on the blockchain’s state. Example: In PoW, miners compete to solve complex puzzles. The first to solve the puzzle adds a new block and is rewarded, securing the network against attacks.
23. Explain the concept of Interoperability in blockchain.
Interoperability allows different blockchain networks to communicate and share data. It enables the transfer of assets or information across multiple blockchains, creating a more connected ecosystem.
24. Describe what tokenomics is and its role in blockchain projects.
Tokenomics refers to the economic design of a blockchain project’s tokens, including supply, distribution, and incentive mechanisms. Good tokenomics ensures the sustainability and growth of a blockchain ecosystem.
25. Explain how Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) is used in blockchain.
ECC is a form of cryptography that secures blockchain transactions by generating public and private keys. Its efficiency and security make it ideal for blockchain applications, ensuring that transactions are tamper-proof.
26. What is Ethereum 2.0, and how does it aim to solve scalability issues?
Ethereum 2.0, also known as ETH2, is an upgrade to the Ethereum network focused on improving scalability, security, and sustainability. It replaces Proof of Work with Proof of Stake, introduces shard chains, and implements the Beacon Chain, which coordinates the network. These updates are expected to make Ethereum faster, more energy-efficient, and scalable.
27. What is Hyperledger, and how is it different from public blockchains like Ethereum?
Hyperledger is an open-source collaborative project aimed at advancing cross-industry blockchain technologies for business. Unlike public blockchains, Hyperledger is permissioned, meaning only authorized participants can access the network, making it suitable for enterprise use where privacy is crucial.
28. Explain the concept of a “sidechain” and give an example of its use case.
A sidechain is an independent blockchain connected to a main blockchain (parent chain) via a two-way peg. It allows assets to move between the main chain and the sidechain, offering enhanced scalability and new features. For example, the Liquid Network is a sidechain for Bitcoin, enabling faster and more confidential transactions.
29. What is a DAO (Decentralized Autonomous Organization), and how does it function?
A DAO is an organization represented by rules encoded as smart contracts on a blockchain. It’s governed by stakeholders rather than a centralized authority. Decisions within a DAO are made via voting mechanisms, allowing members to influence project developments transparently and democratically.
30. How does Cryptographic Hashing work, and why is it important in blockchain security?
Cryptographic hashing is the process of transforming data into a fixed-size hash value. Hashes are unique and irreversible, making them useful for securing transactions, ensuring data integrity, and linking blocks in a blockchain. This hashing process ensures that data within the blockchain remains unaltered and secure.
Bonus section: Scenario-Based Blockchain Interview Questions
The below scenario-based blockchain questions are designed to evaluate how well a candidate applies blockchain concepts to real-world problems. They focus on decision-making, system design, security, scalability, and practical implementation challenges commonly discussed in blockchain developer interviews.
1. How would you reduce high gas fees in a smart contract deployed on Ethereum during peak network usage?
High gas fees can be reduced by optimizing smart contract code, minimizing storage operations, removing unnecessary loops, and using efficient data structures. Deploying the application on Layer 2 solutions such as rollups or sidechains can significantly lower transaction costs. Another effective approach is batching transactions or moving non-critical logic off-chain.
2. A critical bug is found in a smart contract that is already deployed and handling user funds. What steps would you take?
If the contract supports upgradeability using proxy patterns, a fixed implementation can be deployed and linked to the proxy. If not, the contract should be paused immediately using a circuit breaker if available. Clear communication with users, security audits, and deploying a secure replacement contract help reduce potential losses.
3. How does blockchain prevent double-spending, and what practices ensure transaction finality?
Blockchain prevents double-spending through consensus mechanisms that validate each transaction before it is added to a block. Once recorded in the distributed ledger, altering transactions becomes extremely difficult. Requiring multiple confirmations further ensures transaction finality.
4. Which type of blockchain would you recommend for an organization that needs transparency along with data privacy?
A hybrid or consortium blockchain is well-suited for this requirement. It allows sensitive information to remain private among authorized participants while providing transparency where needed. Permissioned platforms such as Hyperledger Fabric offer strong access control and enterprise-grade performance.
5. How can slow transaction confirmation times in a blockchain application be improved?
Improving transaction speed involves choosing faster consensus mechanisms such as Proof of Stake or Byzantine Fault Tolerance. Adjusting block size and block time also helps. Layer 2 solutions and off-chain processing can significantly enhance scalability.
6. What measures can be taken to protect smart contracts from reentrancy attacks?
Reentrancy risks can be minimized by following the checks-effects-interactions pattern and updating contract state before external calls. Using reentrancy guards, avoiding calls to untrusted contracts, and leveraging audited libraries improves overall contract security.
7. What should be done if a user loses their private key and requests account recovery?
Private keys cannot be recovered in decentralized systems. To reduce future risks, developers can implement multisignature wallets, social recovery mechanisms, or hardware wallet integrations. Educating users on secure key storage is essential.
8. How should a blockchain application respond to a hard fork in the underlying network?
The development team should analyze the reason for the fork and select the chain that aligns with project goals and community support. Application components and smart contracts should be updated accordingly, and users must be informed about any impact on assets or transactions.
9. How can blockchain applications meet regulatory requirements without compromising decentralization?
Regulatory requirements can be handled at the application layer using identity verification, role-based access control, and audit trails. Permissioned or hybrid blockchain models help balance decentralization with compliance needs.
10. Which blockchain platform is best suited for building a supply chain tracking system and why?
Permissioned blockchains like Hyperledger Fabric are ideal for supply chain tracking. They offer scalability, privacy, controlled access, and efficient transaction processing across multiple organizations.
If you want to learn more about Blockchain and its implications in the real world, consider enrolling in HCL GUVI’s Certified Blockchain Professional Course which teaches everything you need and will also provide an industry-grade certificate!
💡 Did You Know?
- Many blockchain interview questions focus on real-world problem solving rather than just theory.
- Smart contract vulnerabilities are often caused by simple coding patterns, not the blockchain itself.
- Some interviewers test candidates with hypothetical network failures to see how they would maintain consensus and data integrity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, by understanding these foundational and advanced blockchain concepts, you’ll be well-prepared to answer a range of questions during a blockchain developer interview.
Interviewers will appreciate your depth of knowledge, from explaining basic terms like smart contracts and DApps to more complex concepts like zk-SNARKs and Ethereum 2.0. Studying these questions thoroughly will give you a confident edge, enabling you to discuss blockchain technology with clarity and insight.
Remember, continuous learning and practical application are key to staying ahead in this rapidly evolving field. Good luck with your interview journey!

































Did you enjoy this article?