
AI vs Machine Learning: A Simple Guide That Actually Makes Sense (2026)
Feb 12, 2026 5 Min Read 1572 Views
(Last Updated)
Confused about AI vs machine learning? You’re not alone. Despite 95 percent of senior leaders reporting their organizations are currently investing in AI, the difference between machine learning and artificial intelligence remains unclear to many.
Simply put, AI refers to the broad concept of machines carrying out tasks in ways that mimic human intelligence, while machine learning is actually a subset of AI that focuses on algorithms learning from data with minimal human intervention.
Throughout this guide, you’ll discover the fundamental differences between AI and ML in plain language. You’ll learn how AI encompasses a broader range of capabilities, while machine learning specifically deals with systems that identify patterns and make predictions based on data. Let’s begin!
Table of contents
- What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
- Types of tasks AI can perform
- Examples of AI in daily life
- What is Machine Learning (ML)?
- How machines learn from data
- Common ML algorithms
- AI vs Machine Learning
- Scope and purpose
- Data handling and learning approach
- Human intervention and adaptability
- Output and decision-making
- Use cases comparison
- How AI and ML Work Together in Real Life
- 1) AI systems powered by ML models
- 2) Examples: voice assistants, fraud detection, recommendation engines
- 3) Benefits of combining AI and ML
- Concluding Thoughts...
- FAQs
- Q1. What is the main difference between AI and machine learning?
- Q2. How do AI and machine learning work together in real-world applications?
- Q3. Can you give examples of AI and ML in everyday life?
- Q4. How does machine learning work?
- Q5. What are the benefits of combining AI and ML in business applications?
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Artificial intelligence refers to computer systems designed to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. Unlike traditional software that follows pre-programmed instructions, AI systems can reason, make decisions, solve problems, and even learn from experience.
Think of AI as a digital brain that can process information, recognize patterns, and take actions based on what it learns. As an umbrella term, AI encompasses multiple technologies working together to simulate human-like thinking and decision-making processes.
Types of tasks AI can perform
AI excels at various tasks that previously only humans could handle:
- Processing and analyzing data: AI can process massive amounts of information at incredible speeds, identifying patterns humans might miss.
- Decision-making: Modern AI systems can evaluate options and recommend or make decisions based on available data.
- Natural language processing: Understanding and generating human language, enabling technologies like translation and chatbots.
- Computer vision: Identifying objects, people, and situations in images and videos.
- Creative work: Generating original content, including text, images, and even music.
Examples of AI in daily life
AI has seamlessly integrated into our everyday routines:
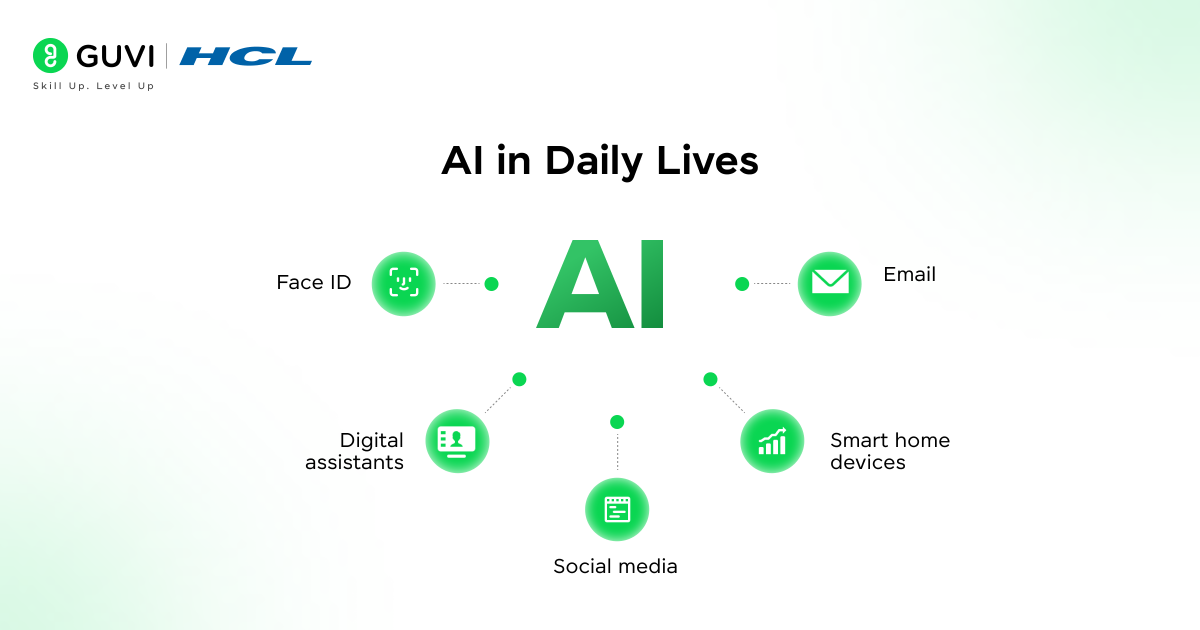
- Face ID: When you unlock your phone using facial recognition, AI analyzes thousands of invisible points on your face to verify your identity.
- Digital assistants: Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant use natural language processing to understand your commands and questions.
- Social media: AI personalizes your feeds based on past behavior and filters out inappropriate content.
- Smart home devices: From thermostats that learn your temperature preferences to refrigerators that track food inventory.
- Email: Spam filters and smart composition tools use AI to improve your communication.
As powerful as AI has become, it’s important to understand that current AI systems are designed for specific tasks rather than possessing general human-like intelligence. This distinction helps clarify how AI differs from machine learning, which we’ll explore next.
What is Machine Learning (ML)?
Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence. If AI is the broader concept of machines mimicking human intelligence, then ML is the application that allows systems to automatically learn and improve from experience.
Essentially, AI encompasses various approaches and algorithms with machine learning sitting under its umbrella. The relationship works this way: an “intelligent” computer uses AI to think like a human, whereas machine learning is how that computer system develops its intelligence.
How machines learn from data
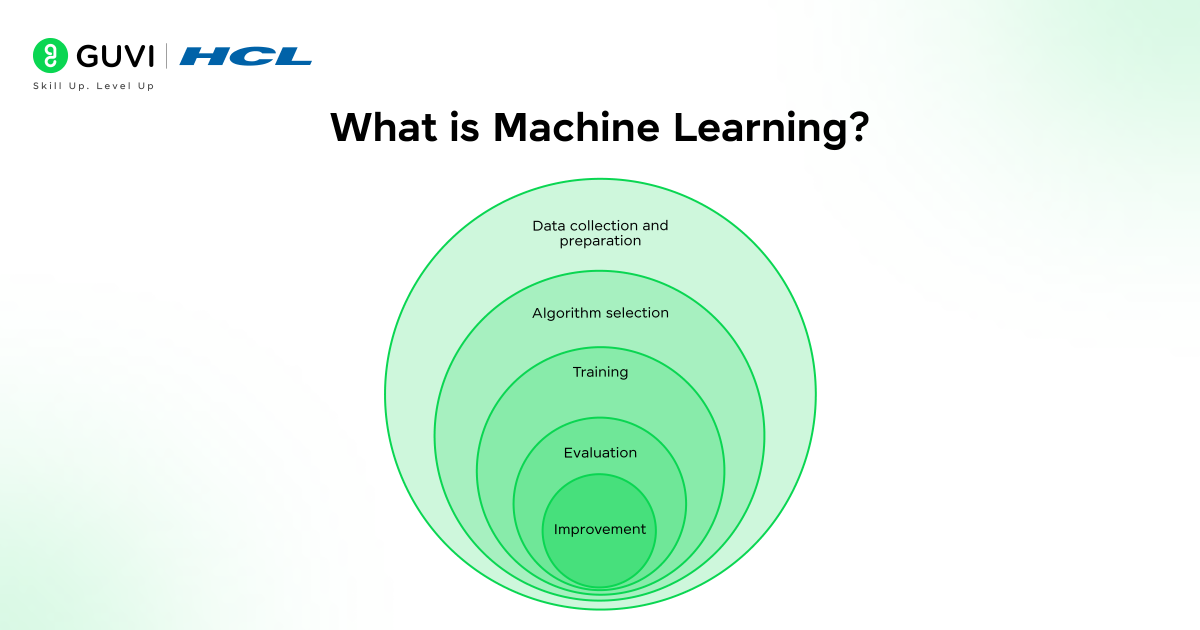
Machine learning starts with data—numbers, photos, text, or other information. This process follows several key steps:
- Data collection and preparation: Gathering relevant data that forms the foundation for learning
- Algorithm selection: Choosing appropriate algorithms based on the task
- Training: The algorithm learns patterns from the training data
- Evaluation: Testing accuracy using new data
- Improvement: Refining the model for better performance
Furthermore, ML models generally learn through three main approaches:
- Supervised learning: Algorithms learn from labeled examples, ideal for predicting outcomes when you know what to expect
- Unsupervised learning: Discovers patterns in unlabeled data without human guidance
- Reinforcement learning: Learns through trial and error, receiving feedback to determine if choices were correct
Common ML algorithms
Machine learning utilizes various algorithms to analyze data and make predictions:
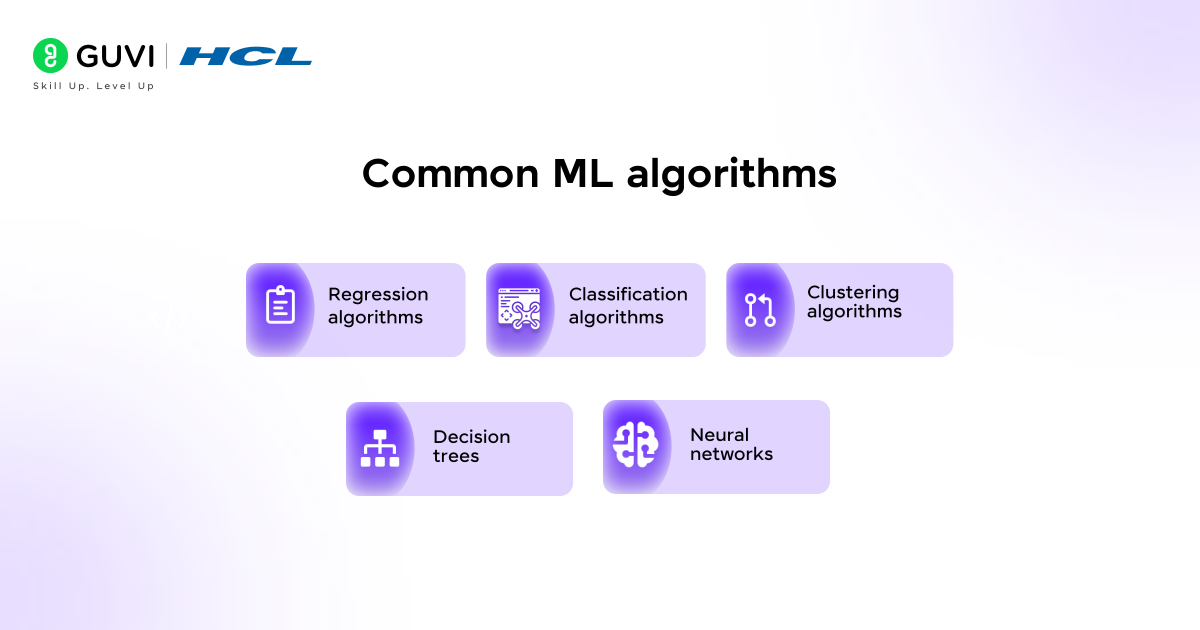
- Regression algorithms: Predict numerical values based on data relationships
- Classification algorithms: Assign data to preset categories
- Clustering algorithms: Divide data into similar groups
- Decision trees: Split data into homogeneous sets through branching decisions
- Neural networks: Process information through interconnected “neurons” to recognize patterns
The choice of algorithm depends on several factors, including data size, quality, and the specific problem you’re trying to solve.
AI vs Machine Learning
Understanding the dividing line between AI and machine learning helps clarify how these technologies work in practical terms. Though related, they differ in several fundamental ways.
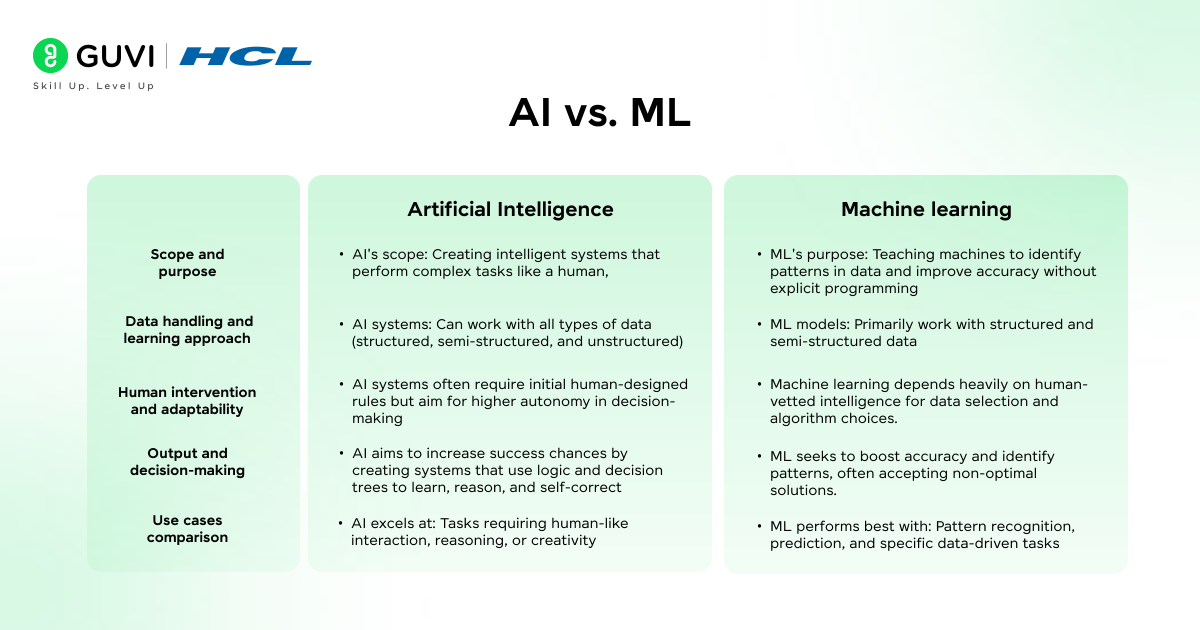
1. Scope and purpose
AI represents the broader concept, aiming to create systems that can simulate human intelligence and behavior. Meanwhile, machine learning functions as a subset of AI, focusing specifically on algorithms that learn from data. Consider this distinction:
- AI’s scope: Creating intelligent systems that perform complex tasks like a human, including reasoning, problem-solving, and planning
- ML’s purpose: Teaching machines to identify patterns in data and improve accuracy without explicit programming
2. Data handling and learning approach
The approaches to data and learning mark another significant difference:
- AI systems: Can work with all types of data (structured, semi-structured, and unstructured)
- ML models: Primarily work with structured and semi-structured data
Additionally, AI employs diverse strategies, including rule-based systems, neural networks, and machine learning itself. Conversely, ML focuses on statistical models and algorithms to extract knowledge from data autonomously.
3. Human intervention and adaptability
Human involvement varies considerably between these technologies:
AI systems often require initial human-designed rules but aim for higher autonomy in decision-making. On the other hand, machine learning depends heavily on human-vetted intelligence for data selection and algorithm choices.
Machine learning models typically need complete retraining to maintain accuracy when conditions change. However, newer adaptive AI systems can modify their behavior based on experiences without human input.
4. Output and decision-making
The decision-making processes reveal further distinctions:
AI aims to increase success chances by creating systems that use logic and decision trees to learn, reason, and self-correct. In contrast, ML seeks to boost accuracy and identify patterns, often accepting non-optimal solutions.
5. Use cases comparison
These technologies excel in different scenarios:
- AI excels at: Tasks requiring human-like interaction, reasoning, or creativity
- ML performs best with: Pattern recognition, prediction, and specific data-driven tasks
Both technologies continue evolving, with boundaries between them becoming increasingly fluid as development progresses.
Here are a couple of fascinating nuggets that show how AI and ML have shaped our world:
AI’s First Game Win (1951): The very first AI program was created in 1951 by Christopher Strachey, which successfully played a game of checkers on the Ferranti Mark I computer. This was decades before AI became a buzzword!
ML Powers Your Daily Choices: Netflix once revealed that its recommendation engine—driven by machine learning—saves the company over $1 billion annually by reducing subscription cancellations.
These facts highlight how AI and ML, though distinct, have been influencing human decisions for far longer than most people realize.
How AI and ML Work Together in Real Life
In today’s digital ecosystem, AI and machine learning combine forces to create powerful solutions that impact our daily lives. These once-theoretical technologies now drive practical applications that millions use every day.
1) AI systems powered by ML models
Modern AI systems rely on machine learning to deliver their functionality. While traditional AI assistants once used rule-based instructions with preprogrammed responses, today’s AI applications are almost entirely machine learning or foundation model-based.
The relationship works symbiotically—AI provides the framework for intelligent behavior, whereas ML models supply the data-driven learning capabilities that make systems truly adaptive.
2) Examples: voice assistants, fraud detection, recommendation engines
Voice assistants exemplify this partnership perfectly. These intelligent applications understand natural language commands through sophisticated ML algorithms that process speech and learn from interactions. Similarly, fraud detection systems use machine learning to analyze transaction patterns and identify suspicious activities, with anomaly detection models spotting fraudulent behaviors in real-time.
Additionally, recommendation engines—responsible for 35% of Amazon purchases—employ ML algorithms to process user data and suggest relevant products or content.
3) Benefits of combining AI and ML
The integration of these technologies creates several advantages. First, systems become more adaptive, storing previous interactions to improve future responses. Second, organizations experience efficiency gains, with some businesses reporting 50% reductions in call handling costs through AI-driven customer service.
Finally, personalization capabilities improve dramatically—McKinsey research indicates personalization can increase revenues by 5-15%, creating more engaging customer experiences.
Ready to go beyond theory? HCL GUVI’s Advanced AI & Machine Learning Course, co-designed with Intel and IIT‑M Pravartak, delivers a hands‑on, industry‑aligned curriculum covering Python, NLP, Generative AI, Deep Learning, and MLOps (LLMOps) and much more.
Concluding Thoughts…
Throughout this guide, we’ve clarified that AI represents the broader concept of machines performing tasks that mimic human intelligence. Machine learning, however, functions specifically as a subset of AI focused on algorithms that learn from data with minimal human guidance. The distinction matters because these technologies serve different purposes.
As these technologies evolve, their boundaries become increasingly fluid. For businesses and individuals alike, understanding the fundamentals of AI vs Machine Learning helps you navigate their growing influence in our lives. I hope this article has helped you understand the difference clearly and if you have any doubts, reach out to me in the comments section below. Good Luck!
FAQs
Q1. What is the main difference between AI and machine learning?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a broader concept that aims to create systems mimicking human intelligence, while machine learning (ML) is a subset of AI focused on algorithms that learn from data with minimal human intervention.
Q2. How do AI and machine learning work together in real-world applications?
AI provides the framework for intelligent behaviour, while ML supplies the data-driven learning capabilities. For example, voice assistants use AI for natural language understanding and ML algorithms to process speech and learn from interactions.
Q3. Can you give examples of AI and ML in everyday life?
AI is present in facial recognition systems and digital assistants like Siri or Alexa. ML is used in recommendation engines on streaming platforms and e-commerce sites, as well as in fraud detection systems for financial transactions.
Q4. How does machine learning work?
Machine learning works by analyzing large amounts of data to identify patterns and make predictions. It involves steps like data collection, algorithm selection, training the model on data, evaluating its performance, and continuous improvement.
Q5. What are the benefits of combining AI and ML in business applications?
Combining AI and ML can lead to more adaptive systems, improved efficiency (such as reducing call handling costs in customer service), and enhanced personalization capabilities, potentially increasing revenues and creating more engaging customer experiences.





























Did you enjoy this article?