
What are the Types of Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)
Sep 04, 2025 5 Min Read 1643 Views
(Last Updated)
Every software product, whether a mobile application or a huge enterprise system, follows a structured process to ensure the product meets user requirements and the business goals. This process is called the Software Development Life Cycle, providing a roadmap for planning, creating, testing, deploying, and maintaining software.
Over time, different types of SLDC models have been created to suit various project requirements. Some projects offer a flexible and continuous improvement, while some demand a strict structure and highly controlled process.
In the blog, you will get to know about SDLC, types of SDLC models, their advantages and disadvantages and also look closely at the methodologies of SDLC. By the end of this blog, you will be able to understand which is the best SLDC model for your software development, depending on your project requirements and goals.
Table of contents
- What is the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)?
- Phases of the Software Development Life Cycle
- Why Do Multiple SDLC Models Exist?
- What are the Different Types of SDLC Models?
- Waterfall Model in SDLC
- 2. Agile Model in SDLC
- Spiral Model in SDLC
- V-Model in SDLC
- Big Bang Model in SDLC
- Iterative Model in SDLC
- Incremental Model in SDLC
- Rapid Application Development (RAD) Model in SDLC
- Lean Model in SDLC
- DevOps Model in SDLC
- Comparison of SDLC Models
- SDLC Advantages and Disadvantages
- Advantages of SDLC:
- Disadvantages of SDLC:
- Final thoughts..
- FAQs
- Q1) What is the Software development life cycle in simple terms?
- Q2) Why is the Software development life cycle important?
- Q3) What are the most common types of SDLC?
- Q4) Which SDLC model is best?
- Q5) What is the difference between waterfall and agile SDLC models?
What is the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)?
The Software Development Life Cycle refers to the step-by-step process of creating software in the software industry. It is a series of planned activities that help in building and altering the software while also maintaining high quality throughout the project.
The phases of SDLC typically include planning, analysis, design, implementation, testing, deployment, and maintenance. However, different projects may require different approaches, which is where various SDLC models come into play.
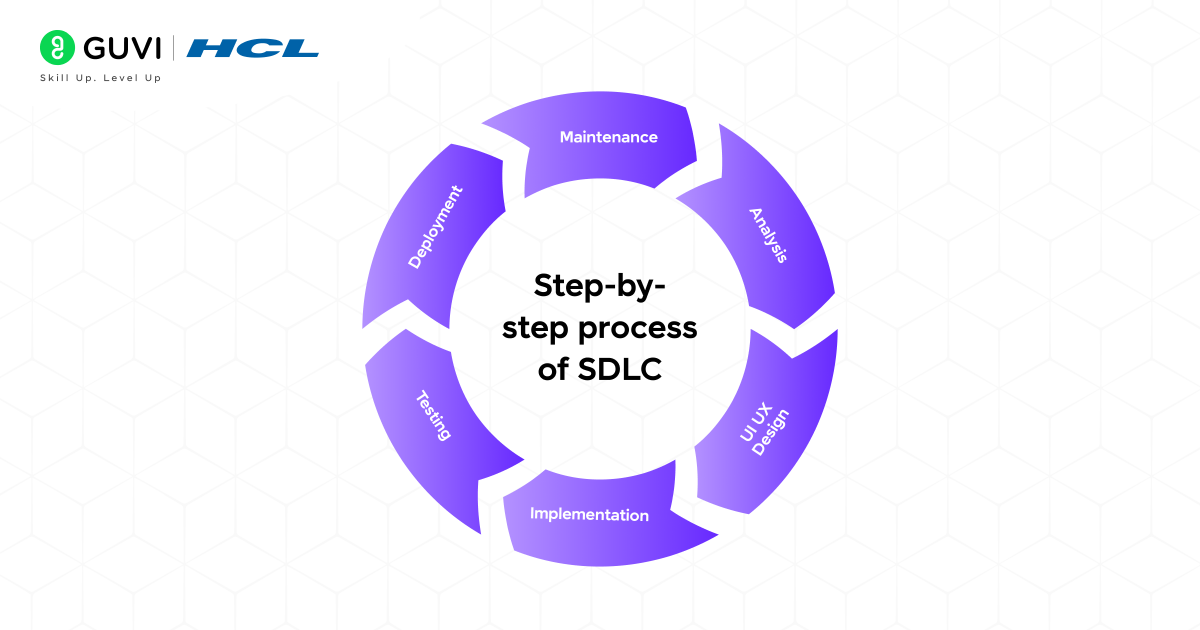
Phases of the Software Development Life Cycle
In software engineering models, SDLC provides a clear plan for each stage of building the product so that each stage of development is done efficiently within the time limit and also ensures the user requirements. Most Software development methodologies involve these common phases:
Planning: This is the foundation of Software Development, where they understand the scope and the feasibility of the project and also identify the resources needed, set timelines, and assess potential risks.
Requirement Analysis: This phase involves gathering a detailed requirement on what the software should do, who the end users and so on.
Design: During this specifications and blueprint of the product. This involves defining the architecture, tech stack, database, user interface layouts, and other components.
Development: In this phase, the software’s actual code is written. Every requirement that was reviewed and refined in earlier stages gets translated line by line into the chosen language, giving the specification concrete form.
Testing: Then comes the testing part, where QA Testers test the entire system thoroughly. This involves resolving any errors, bugs, and any other problems that might affect the core functionality of the software.
Deployment: After testing the software, it is deployed to the end users. It can be done in stages or all at once, depending upon the project’s needs.
Maintenance: Software needs ongoing maintenance to stay functional and efficient. Software updates, bug fixes, and feature additions are all part of this phase. This process makes sure the software is useful and relevant.
Why Do Multiple SDLC Models Exist?
Not every project has the same requirements, risks, or constraints. A safety-critical system requires a different approach than a small internal tool. This is the reason why multiple types is software development life cycle models exist. Every model has advantages and disadvantages depending on the requirements of the project.
Key factors influencing the choice include:
- Complexity of the project.
- Involvement of the customers.
- Budget and timeline constraints.
- Level of acceptable risk.
- Degree of customer involvement.
What are the Different Types of SDLC Models?
Here are some of the most commonly and widely used SDLC models with examples:
1. Waterfall Model in SDLC
The Waterfall model in SDLC is the traditional and the oldest methodology. This follows a linear and sequential software development, meaning each stage must be completed before moving to the next stage.
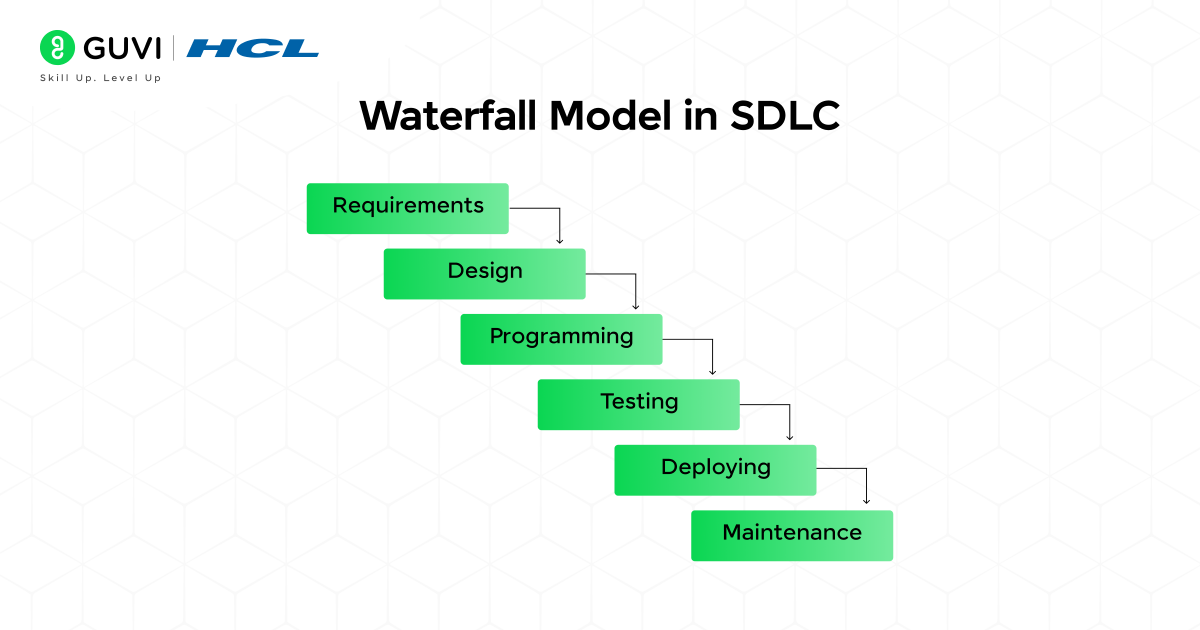
Advantages:
- Straightforward and easy to manage.
- Best for projects with fixed requirements.
- Works well with well-defined, smaller projects.
Disadvantages:
- Inflexible to changes once a phase is complete.
- Errors can become very hard to identify.
- Not ideal for dynamic or evolving projects.
2. Agile Model in SDLC
The Agile model in SDLC is the latest and fastest model, which emphasizes flexibility, collaboration, and adaptability. It divides the projects into smaller parts known as sprints. Each sprint is developed faster and is adaptable to make changes quickly.
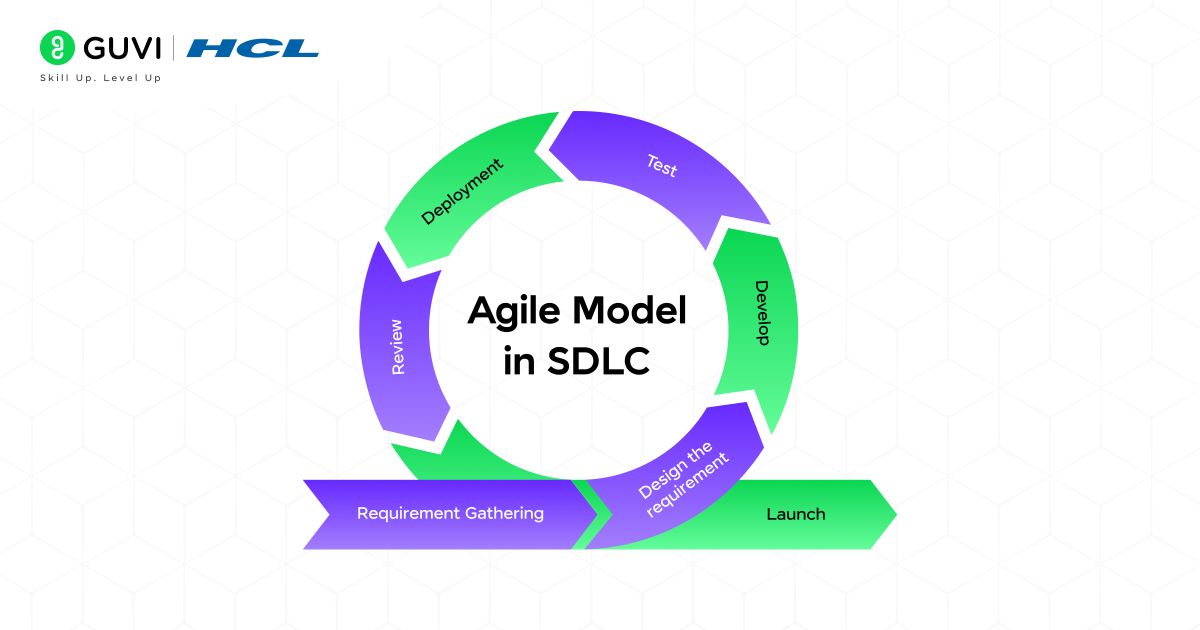
Advantages:
- Adapts quickly to changes.
- Encourages customer collaboration.
- Delivers functional software faster.
Disadvantages:
- Requires continuous stakeholder involvement.
- It can be difficult to estimate costs and timelines.
- Not ideal for projects needing strict documentation.
3. Spiral Model in SDLC
The spiral model in SDLC is a combination of the iterative and sequential linear development model. This model works in loops (spiral), with each loop consisting of planning, risk analysis, development and testing.
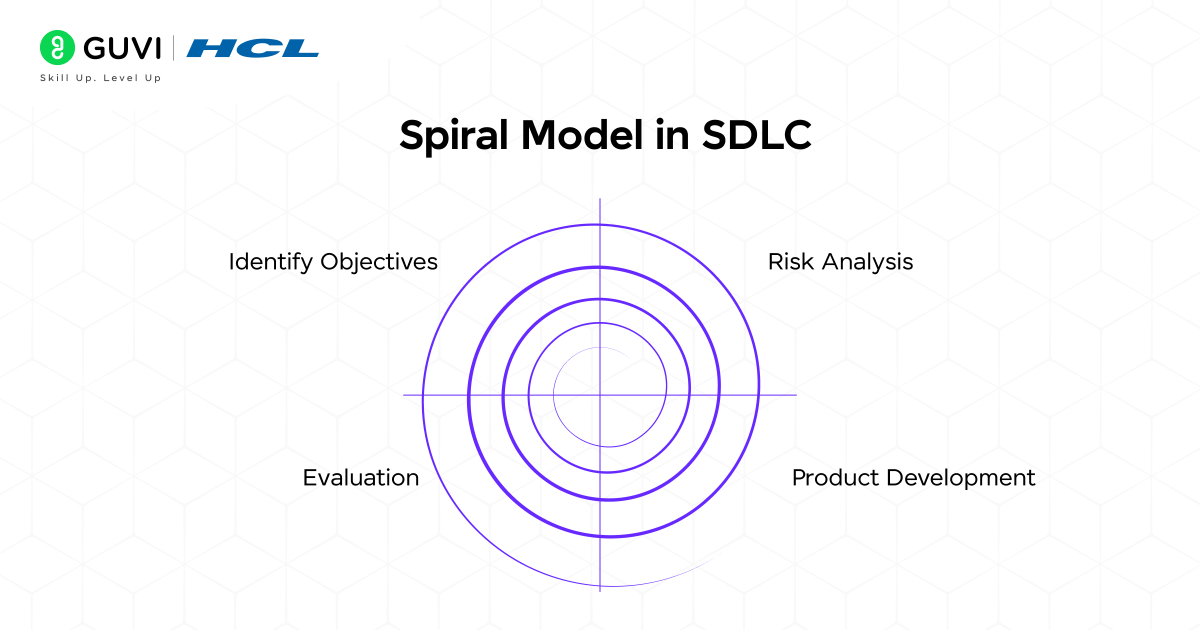
Advantages:
- A high amount of risk analysis is done
- Useful for large and complex systems.
- Incorporates user feedback at every stage.
Disadvantages:
- Projects are time-consuming.
- It can be very expensive.
- Requires expert project management.
4. V-Model in SDLC
The V-Model in SDLC is also known as the verification and validation model, where development and testing go concurrently. Meaning testing is required in every phase of the project.
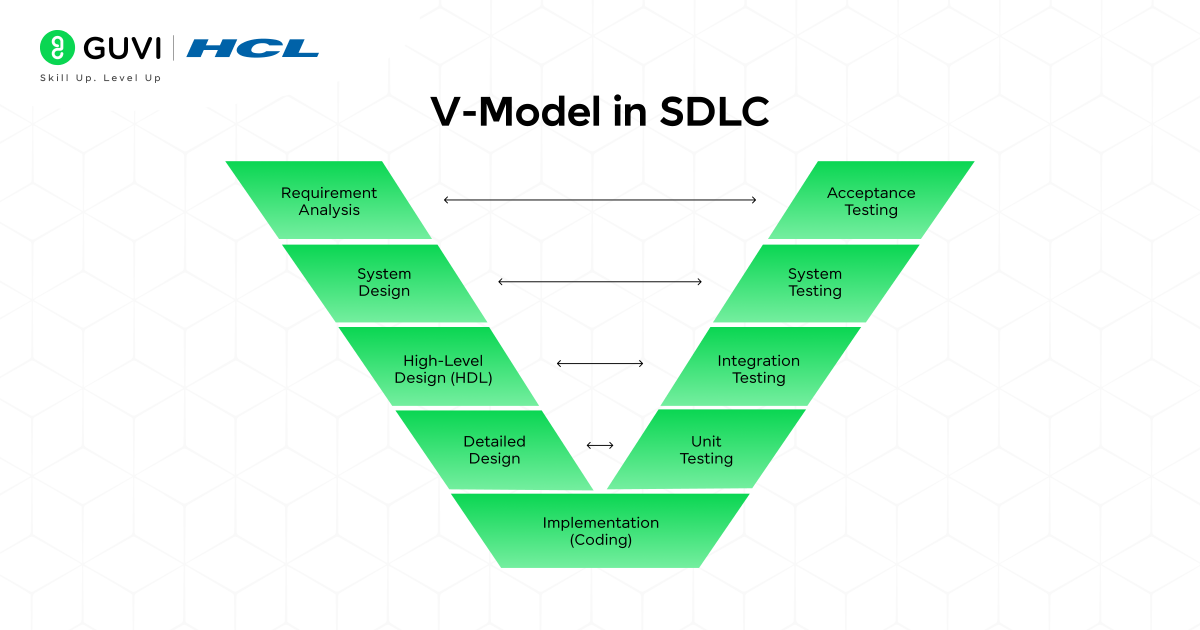
Advantages:
- High emphasis on testing and quality assurance.
- Progress can be tracked easily.
- Works well when requirements are clear.
Disadvantages:
- Inflexible to requirement changes.
- Heavily dependent on initial documentation.
- It is not recommended for object-oriented projects.
5. Big Bang Model in SDLC
The big bang model in SDLC is one of the simplest methodologies. It requires minimal planning and basic resources to begin the project. This model does not follow any techniques to build the software and is adaptable to quick changes.
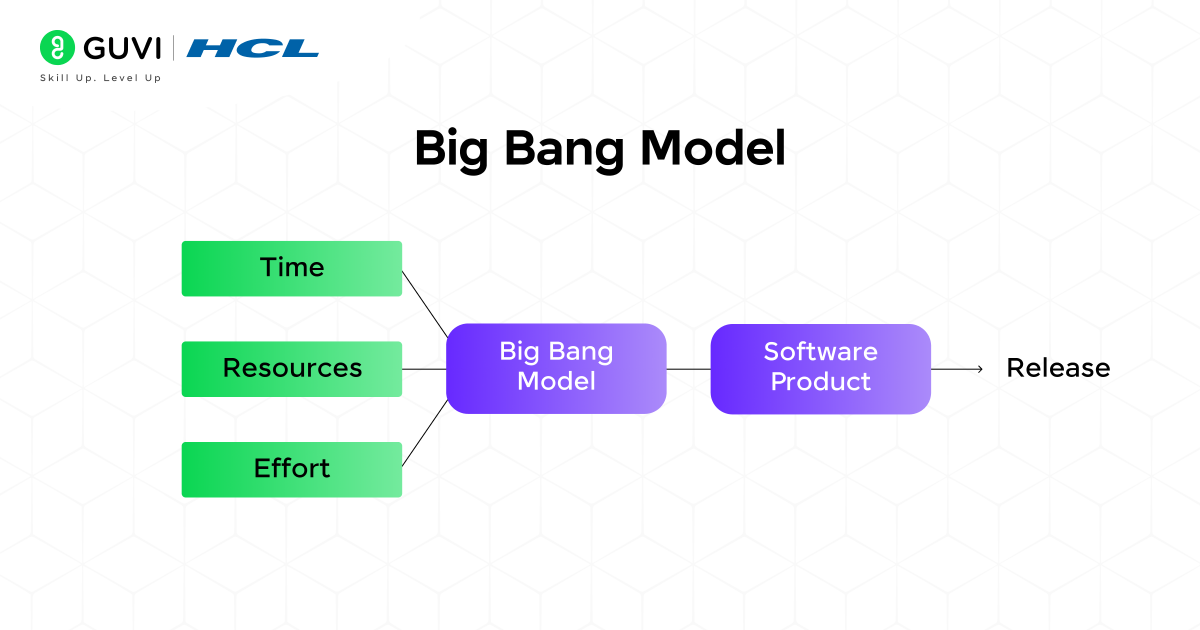
Advantages:
- Minimal planning overhead.
- Simple and quick for small projects.
- Few resources required.
Disadvantages:
- Not suitable for larger and complex projects
- Lack of structure often leads to rework.
- Risk is very high.
6. Iterative Model in SDLC
The Iterative model in SDLC delivers software in cycles. This SDLC model divides the project into smaller parts known as iterations, and these iterations produce a working version, which is improved in subsequent versions until the final product is ready.
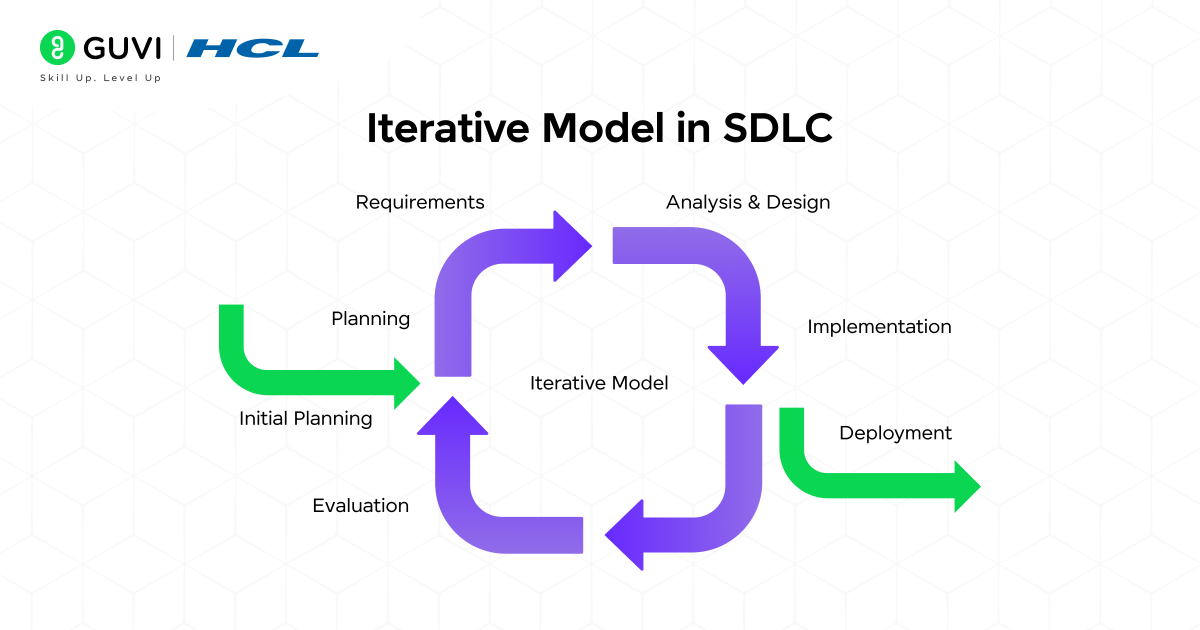
Advantages:
- Early delivery of working software.
- Allows continuous improvements.
- Adapts well to changing requirements.
Disadvantages:
- It can be expensive with multiple iterations.
- Requires proper planning and resources.
- Not the best choice for smaller projects
7. Incremental Model in SDLC
The Incremental model breaks down the system into smaller functional units or increments. Each increment adds more features, and the final product is developed through repeated cycles.
Advantages:
- Delivers working functionality early.
- Easier testing and debugging.
- Flexible to customer feedback and evolving requirements.
Disadvantages:
- Total cost may be higher than expected.
- System architecture must be well planned from the start.
- May not be suitable for all types of applications.
8. Rapid Application Development (RAD) Model in SDLC
RAD is focused on rapid prototyping and quick feedback over long drawn-out development cycles. It encourages user involvement and reusability of components.
Advantages:
- Faster development and delivery.
- Encourages user feedback and involvement.
- Reduces development time through reusable components.
Disadvantages:
- Not suitable for large-scale or complex projects.
- Requires skilled and experienced developers.
- Poor design can lead to software instability.
9. Lean Model in SDLC
Inspired by lean manufacturing principles, the Lean model focuses on delivering value with minimal waste. It encourages efficiency, continuous improvement, and respect for the team.
Advantages:
- Efficient use of time and resources.
- Emphasizes quality and simplicity.
- Empowers teams to make decisions.
Disadvantages:
- Requires a cultural shift in the organization.
- May not work well with rigid hierarchies.
- Risk of under-documentation.
10. DevOps Model in SDLC
DevOps integrates software development (Dev) with IT operations (Ops) to shorten the development lifecycle and improve software quality. It emphasizes automation, continuous integration (CI), continuous delivery (CD), and constant monitoring.
Advantages:
- Faster and more reliable software delivery.
- Enhances collaboration across teams.
- Automation reduces manual errors.
Disadvantages:
- Requires significant changes in culture and tools.
- High initial setup effort for automation and CI/CD pipelines.
- Security can be a challenge if not handled correctly.
Comparison of SDLC Models
| Model | Flexibility | Risk Management | Best For |
| Waterfall | Low | Low | Small, fixed projects |
| Agile | High | Medium | Dynamic, evolving projects |
| Spiral | Medium | High | Complex, high-risk projects |
| V-Model | Low | Medium | Safety-critical software |
| Big Bang | Very High | Very Low | Small prototypes |
| Iterative | Medium | Medium | Large projects with evolving needs |
| Incremental | Medium | Medium | Medium to large projects |
| RAD | High | Low | Quick delivery with user feedback |
| Lean | High | Medium | Efficient, value-driven projects |
| DevOps | High | High | Continuous delivery & automation |
More than 70% of companies today do not rely on a single SDLC model. Instead, they adopt a hybrid approach, combining methods like Agile, DevOps, or Iterative to achieve the right balance between flexibility, speed, and control for their projects.
SDLC Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages of SDLC:
- Structured Process – A clearly indicated step-by-step process will keep the project organized and manageable.
- Detailed documentation – It is helpful to have detailed documentation of all requirements, designs, and tests so there are no miscommunications.
- Risk Reduction – Model methods such as Spiral and Agile decrease risks, since feedback and testing are continuous.
- Involvement of the clients – Ensures that the final product aligns with business needs and user expectations.
Disadvantages of SDLC:
- Rigid and inflexible – Some models (like Waterfall or V-Model) don’t handle changes well once development begins.
- Time-Consuming Documentation – Some models require time-consuming documentation, which can slow down the progress in fast-moving projects.
- High Costs in Some Models – Models like Spiral may become costly due to risk analysis and iterations.
- Dependency on Requirements – If the requirements at the start of the project are not clear, then the entire project can be impacted.
If you are curious about software development and want to become a software developer, then grab the opportunity to learn with HCL GUVI’s IITM Pravartak and MongoDB Certified Online AI Software Development Course. The NSDC-endorsed course gives you a globally recognized certificate to add to your résumé, which is a significant advantage that will help you stand out in the competitive employment market.
Final thoughts..
The software development life cycle is an essential aspect of building software. Each step of SDLC is about enabling you to build projects, and with traditional models such as the Waterfall model to modern flexible models like the Agile and Iterative approaches, each model has pros and cons that serve different project goals. The V-Model emphasizes testing and quality, while the Spiral model is centered around risk and risk assessment. The Big Bang model, on the other hand, can work well in small experimental projects.
A “one-size-fits-all” solution does not exist. The most appropriate SDLC model will depend on factors like project complexity, budget, risk and customer involvement. Many organizations will even utilize multiple models to meet the needs for structure, adaptability, and delivery of project goals.
FAQs
Q1) What is the Software development life cycle in simple terms?
It is a process where the software is built. It is a step-by-step process that helps software developers to develop and alter the software according to the business needs and from the clients feedback.
Q2) Why is the Software development life cycle important?
Because it offers a proper and structured approach to software development, the SDLC is important because it ensures high quality, efficiency, and alignment with business objectives. Proper documentation can help create the application faster and more efficiently.
Q3) What are the most common types of SDLC?
The most common and widely used SDLC model types are waterfall, agile, big bang, V model, spiral, and Iterative model.
Q4) Which SDLC model is best?
Every SDLC model is unique and has its own advantages and disadvantages. Depending on the needs of the projects, you can choose which SDLC model suits you best.
Q5) What is the difference between waterfall and agile SDLC models?
The main difference is that the waterfall model is sequential, while the agile model is incremental and iterative. Also, the waterfall model delivers the product at the end of SDLC, whereas the agile model is released during the initial phase of development to get client feedback.



































Did you enjoy this article?