
Ever written a Python program that works perfectly in your editor but fails the moment you try to run it elsewhere? This is where learning how to run python file in the terminal becomes a game-changer, helping you understand what really happens when your code executes.
This blog is written for beginners who want a clear, practical guide to run python file in the terminal with confidence. You will learn the correct commands, common mistakes, and why using the terminal is a core skill for every Python developer.
Quick Answer
To run python file in terminal, open the terminal, navigate to the folder where your Python file is saved, and execute it using the python filename.py or python3 filename.py command depending on your system. This runs your script through the Python interpreter and displays the output directly in the terminal, making it a reliable way to test, debug, and execute Python programs across different operating systems.
Table of contents
- What Is The Terminal And What Is A Python File
- How To Run a Python File In Terminal
- Prerequisites
- Step-by-Step Instructions
- Why Run a Python File In Terminal
- Common Errors And Best Practices
- 💡 Did You Know?
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- Why does my terminal say Python is not recognized as a command?
- Should I use Python or python3 to run a Python file?
- Can I run a Python file without changing the folder in the terminal?
- Why does my Python file run but show no output in the terminal?
- Is running a Python file in a terminal important for real projects?
What Is The Terminal And What Is A Python File
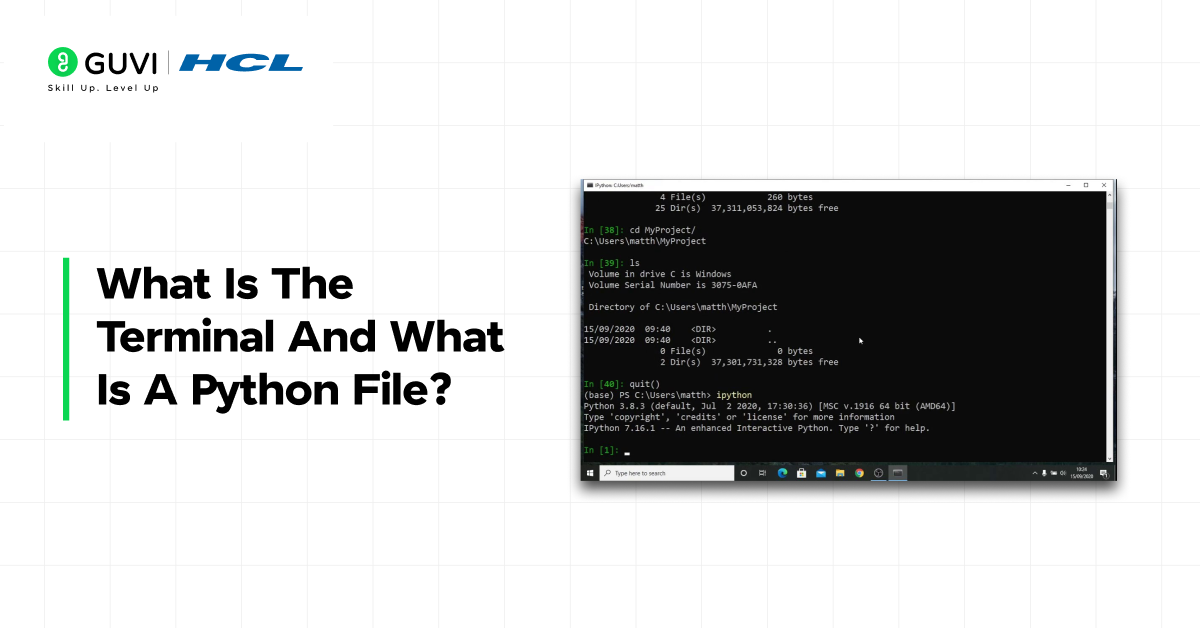
Before learning how to run python file in terminal, it is important to understand the basic components involved. Many beginners get confused not because Python is difficult, but because the terminal and Python files are not explained clearly in a simple format.
The terminal is where commands are executed, and a Python file contains the instructions that Python runs. Understanding both together makes executing Python programs straightforward.
Key Points
- Terminal – A text-based interface used to type commands and interact directly with the operating system
- Python File – A file with a .py extension that contains Python code written to perform tasks
- How They Work Together – The terminal sends the Python file to the Python interpreter for execution
Do check out HCL GUVI’s Python Hub to learn Python through structured tutorials, hands-on exercises, and real-world projects. It helps beginners strengthen fundamentals like running Python files in the terminal while building skills needed for professional Python development. The hub guides you from basic commands to practical Python applications step by step.
How To Run a Python File In Terminal

Running a Python file in the terminal is an essential skill for every beginner. In this section, we will cover everything you need to know before running a Python file, including the prerequisites, and then provide a clear, step-by-step guide to execute your Python program successfully in the terminal.
1. Prerequisites
Before running a Python file in the terminal, you need to ensure a few things are set up correctly. These prerequisites will help you avoid common errors and make the process smooth for beginners.
- Python Installed – Python must be installed on your system and added to your system path
- Terminal Access – You should know how to open Command Prompt on Windows or Terminal on macOS/Linux
- Python File Ready – Your .py file should be saved in a known location on your computer
- Basic Navigation Knowledge – You should be familiar with the cd command to move between folders in the terminal
2. Step-by-Step Instructions
Once the prerequisites are ready, you can follow these steps to run your Python file in the terminal:
1. Open the Terminal – Launch Command Prompt on Windows or Terminal on macOS/Linux. This is where you type the commands to execute your Python file.
2. Check Python Installation – Type python –version or python3 –version to ensure Python is installed correctly. If it shows the version number, you’re ready to proceed.
3. Navigate to Your Python File – Use the cd command to move to the folder containing your Python file. For example:
- Windows: cd Desktop\PythonProjects
- macOS/Linux: cd ~/PythonProjects
4. List Files in the Directory (Optional) – You can type dir on Windows or ls on macOS/Linux to confirm your Python file is in the folder.
5. Run the Python File – Type python filename.py or python3 filename.py (depending on your system) and press Enter. The Python interpreter will read and execute your code.
6. View the Output – Any results, messages, or errors from your program will appear directly in the terminal.
7. Fix Errors If Any – If you see errors, check for typos in the file name, incorrect Python version, or wrong folder path, then run the file again.
Do check out HCL GUVI’s Online IDE to learn Python and other programming languages directly in your browser without any setup. It helps beginners practice coding, run Python files in the terminal, and experiment with real-time projects easily. The IDE is designed to make coding simple, interactive, and accessible from anywhere.
Why Run a Python File In Terminal
Many beginners wonder why they should learn to run python file in the terminal when code editors can execute programs with a single click. The reason is simple: the terminal shows how Python programs actually run in real environments, without any hidden setup done by editors.
Running Python files in the terminal helps you understand execution flow, errors, and system behavior more clearly. It also prepares you for real-world development where scripts, applications, and automation tasks are executed from the command line.
- Real World Execution – Most production scripts and applications are run through the terminal
- Better Error Visibility – Errors and warnings are displayed clearly, making debugging easier
- Environment Awareness – You learn which Python version and environment your program is using
- Automation Friendly – Terminal execution is essential for automation and scheduled tasks
- Professional Skill – Knowing how to run a Python file in the terminal is expected of Python developers
Common Errors And Best Practices

When learning how to run python file in the terminal, beginners often face errors that feel confusing at first. Most of these issues are not caused by complex problems, but by small mistakes related to file location, commands, or Python setup. Understanding these common errors and following best practices can save a lot of time and frustration.
- Python Command Not Found – This usually means Python is not installed correctly or not added to the system path
- Wrong File Location – Running the command from the wrong folder causes the terminal to not find your Python file
- Incorrect File Name – Even a small typo or missing .py extension can prevent the file from running
- Using Python instead of python3 – Some systems require Python3 instead of python to run files
- Permission Issues – On macOS and Linux, a lack of permission can stop the file from executing
Following a few best practices helps avoid these problems and makes terminal usage smoother.
- Always Check Python Version – Confirm the Python version before running your file
- Use Clear File Names – Simple and meaningful file names reduce mistakes
- Know Your Folder Path – Always be sure of the directory where your file is saved
- Read Error Messages Carefully – Terminal errors usually explain exactly what went wrong
- Practice Regularly – The more you run python file in the terminal, the more confident you become
Do check out HCL GUVI’s Zen Class Python Course to learn Python through hands-on projects and real-world coding practice. It helps you strengthen fundamentals like running Python files from the terminal while also building job-ready development skills. This course bridges the gap between basic command-line usage and professional Python workflows.
💡 Did You Know?
- Python decides which interpreter runs your file based on the command (python vs python3), which is why the same file can behave differently on different systems.
- When you run a python file in terminal, the script name is stored internally as __main__, which is why code inside if __name__ == “__main__”: only runs during direct execution.
- Some Python editors automatically set environment variables for you, but the terminal does not, which is why code that works in an editor may fail in the terminal.
Conclusion
Learning how to run python file in the terminal is a small step that makes a big difference in how you understand Python. It helps you see how your code actually executes, how errors appear, and how Python behaves outside an editor.
Once you are comfortable running Python files from the terminal, debugging becomes easier and your workflow becomes more professional. This skill forms the foundation for automation, real-world projects, and working confidently with Python in any environment.
FAQs
1. Why does my terminal say Python is not recognized as a command?
This usually means Python is not installed properly or it was not added to the system path during installation.
2. Should I use Python or python3 to run a Python file?
On Windows, Python is commonly used, while on macOS and Linux, Python3 is often required to run Python files.
3. Can I run a Python file without changing the folder in the terminal?
Yes, you can run it by providing the full file path instead of navigating to the folder.
4. Why does my Python file run but show no output in the terminal?
Your program may not contain any print statements or visible output logic.
5. Is running a Python file in a terminal important for real projects?
Yes, most real-world Python scripts, automation tasks, and deployments rely on terminal-based execution.

























Did you enjoy this article?