
Use ReactJS to Fetch and Display Data from API – 5 Simple Steps
Mar 21, 2024 5 Min Read 72716 Views
(Last Updated)
In this blog, we’ll learn how to fetch and display data from APIs and use it in a ReactJS app. There are multiple ways to fetch data in a React application, and we’ll walk you through those methods. With the help of APIs, we can fetch the data from servers and display it in our application. Let’s first understand what an API is.
API stands for “Application Programming Interface”, which is a method of communication between different applications. ReactJS is an open-source JavaScript-based library developed by Facebook used to create web applications’ user interfaces. As ReactJS is dynamic in nature, we can get the data using APIs and display it in our application.
To render some data in our front end, we either need a backend to store our data and then make use of the data, or we can simply use APIs to have some mock data while building an application.
When we use APIs, we don’t need a backend and are also not required to build anything from scratch. Mostly, we use the REST API or the GraphQL API to access the data added to the server. Before we get into depth, we should understand how an API works.
Table of contents
- How does an API work?
- Methods to Fetch and Display Data from API:
- Using JavaScript Fetch API
- Step 1. Create a React Application
- Step 2. Change your Project Directory
- Step 3. Access the API Endpoint
- Step 4. Import the useState() Hook and Set it to Hold Data
- Step 5. Create a FetchInfo() Callback Function to Fetch and Store Data
- Output
- Using Axios Library
- Step 1. Create a React Application
- Step 2. Change your Project Directory
- Step 3. Install the Axios Library with npm or yarn
- Step 4. Access the API Endpoint
- Step 5. Import the Axios and useState() Hook and Set it to Hold Data
- Step 6. Create a FetchInfo() Callback Function to Fetch and Store Data
- Output:
- Summing Up
- FAQs
- Q1. How to fetch data from API and display in JS?
- Q2. How to display and extract JSON data from an API?
- Q3. What is a fetch API in JavaScript?
How does an API work?
The workings of an API are very easy to understand. Here’s an example, say we want to build a new application but don’t have our own backend. Now, to display the news in our application, we need some third-party APIs to access their backend server and display the data in our app.
Now, there are three things we must have noted: an application, a server, and an API. Most times, the API is in between the app and server because whenever the client requests the data, the API makes a GET request to the server and sends that back to the application for display.
If you would like to explore ReactJS through a Self-paced course, try GUVI’s ReactJS Self-paced certification course.
Methods to Fetch and Display Data from API:
We commonly use a Web API called REST, or REpresentational State Transfer API, which consists of HTTP methods to fetch data from the server and display it in the application. A REST API has several methods, which are discussed further below:
- GET: This method is used to fetch data from a server endpoint.
- POST: This method is used to post the data to a server endpoint.
- DELETE: This method is used to delete the data from a server endpoint.
- PUT: This method is used to update or modify the data from a server endpoint.
Now as you have understood all the methods of the API, we can now move on to how the data is fetched from the server. To fetch the data, we use the GET method.
The different ways of Fetching the data in a React application are given below:
- Using React Hooks
- Using JavaScript Fetch API
- Using async/await
- Using Axios library
- Using React query
For now, we’ll only discuss the two ways of fetching data i.e., using JavaScript Fetch API and using Axios library API.
Here are the 6 Essential Prerequisites For Learning ReactJS you must know in order to be proficient in ReactJS.
Using JavaScript Fetch API
The JavaScript Fetch API is an inbuilt browser’s native API that gives an easy interface to fetch the data from the network. The simplest way to use fetch() is by taking one argument and the path from where the data is to be fetched and then returning a promise in a JSON object.
In this example, we are going to use mock data provided freely by JSONplaceholder in JSON format. We are going to use the user’s endpoint from that API i.e., https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users.
See the below steps to implement and use Fetch API to fetch the data in a react app.

Step 1. Create a React Application
npx create-react-app demoStep 2. Change your Project Directory
cd demoStep 3. Access the API Endpoint
Now, as done in the above method 1, where we’ll also access the API endpoint and store it in a const variable so that we can use it anytime and anywhere.
const url = “https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users”;Step 4. Import the useState() Hook and Set it to Hold Data
import React, { useState } from 'react';
const [data, setData] = useState([])Step 5. Create a FetchInfo() Callback Function to Fetch and Store Data
We will create a callback function that will store the user’s data and then use the useEffect() hook to make the function run every time the page loads. Now we get the data from the API using the fetch() method in the data variable.
const fetchInfo = () => {
return fetch(url)
.then((res) => res.json())
.then((d) => setData(d))
}
useEffect(() => {
fetchInfo();
}, [])Now your App.js file should look like the below:
import "./App.css";
import React, { useState, useEffect } from "react";
function App() {
const url = "https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users";
const [data, setData] = useState([]);
const fetchInfo = () => {
return fetch(url)
.then((res) => res.json())
.then((d) => setData(d))
}
useEffect(() => {
fetchInfo();
}, []);
return (
<div className="App">
<h1 style={{ color: "green" }}>using JavaScript inbuilt FETCH API</h1>
<center>
{data.map((dataObj, index) => {
return (
<div
style={{
width: "15em",
backgroundColor: "#35D841",
padding: 2,
borderRadius: 10,
marginBlock: 10,
}}
>
<p style={{ fontSize: 20, color: 'white' }}>{dataObj.name}</p>
</div>
);
})}
</center>
</div>
);
}
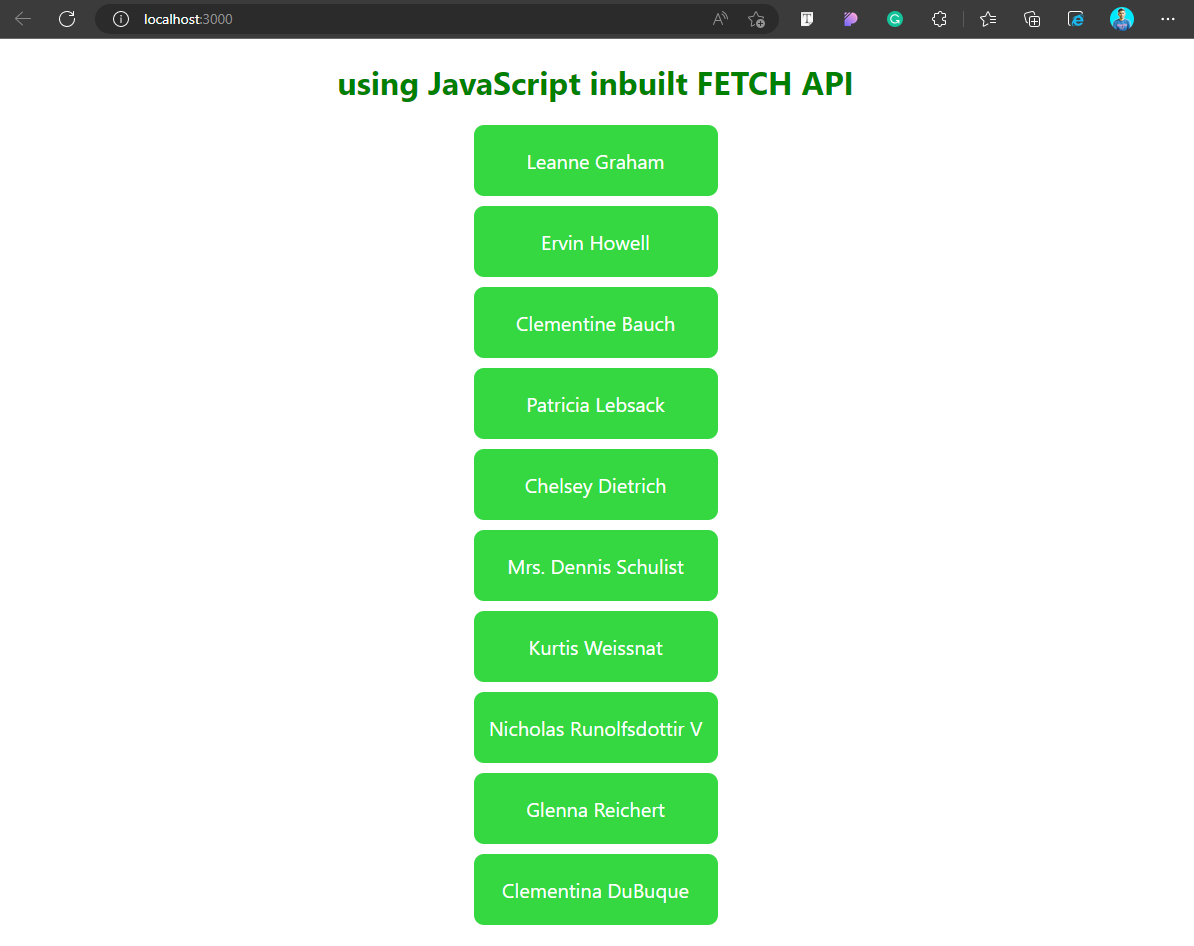
export default App;Output
The output for the above example is as follows:
Using Axios Library
Axios is an online HTTP library running on node.js that allows us to make various HTTP requests to a given server endpoint. If we see it working, then it uses the http module on the server side, whereas it uses XMLHttpRequests on the browser side. For this example, we are going to use the GET method to fetch and display the data in our React application. Here we don’t need to convert the result into a JSON object; it already comes as a JSON object.
See the below steps for the installation of the Axios library and the fetching process of the data in a react app.
Step 1. Create a React Application
The first thing to do is create a React application from scratch using the below npx command. Write or copy/paste the following to create a react app in your desired directory and name the project of your choice. For this example, we have created a project called “demo.”
npx create-react-app demoStep 2. Change your Project Directory
Once the project is created, change the directory to where the app folder is created.
cd demoStep 3. Install the Axios Library with npm or yarn
For using the axios library, we need to install that and we can do that using two ways i.e, either install using NPM or Yarn. Install it with any one of your choice or requirements.
npm install axiosOr
yarn add axiosStep 4. Access the API Endpoint
Now, as done in the above method 1, where we’ll also access the API endpoint and store it in a const variable so that we can use it anytime and anywhere.
const url = “https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users”;Step 5. Import the Axios and useState() Hook and Set it to Hold Data
Import the installed axios library to the App.js file and also the useState() hook to hold the data in a variable.
import React, { useState } from 'react';
import axios from 'axios';
const [data, setData] = useState([])Step 6. Create a FetchInfo() Callback Function to Fetch and Store Data
In this method also, we will create a callback function that will store the user’s data and then use the useEffect() hook to make the function run every time the page loads.
const fetchInfo = () => {
return axios.get(url)
.then((response) => setUser(response.data));
}
useEffect(() => {
fetchInfo();
}, [])Now your App.js file should look like below:
import "./App.css";
import React, { useState, useEffect } from "react";
import axios from "axios";
function App() {
const url = "https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users";
const [data, setData] = useState([]);
const fetchInfo = () => {
return axios.get(url).then((res) => setData(res.data));
};
useEffect(() => {
fetchInfo();
}, []);
return (
<div className="App">
<h1 style={{ color: "green" }}>using Axios Library to Fetch Data</h1>
<center>
{data.map((dataObj, index) => {
return (
<div
style={{
width: "15em",
backgroundColor: "#CD8FFD",
padding: 2,
borderRadius: 10,
marginBlock: 10,
}}
>
<p style={{ fontSize: 20, color: 'white' }}>{dataObj.name}</p>
</div>
);
})}
</center>
</div>
);
}
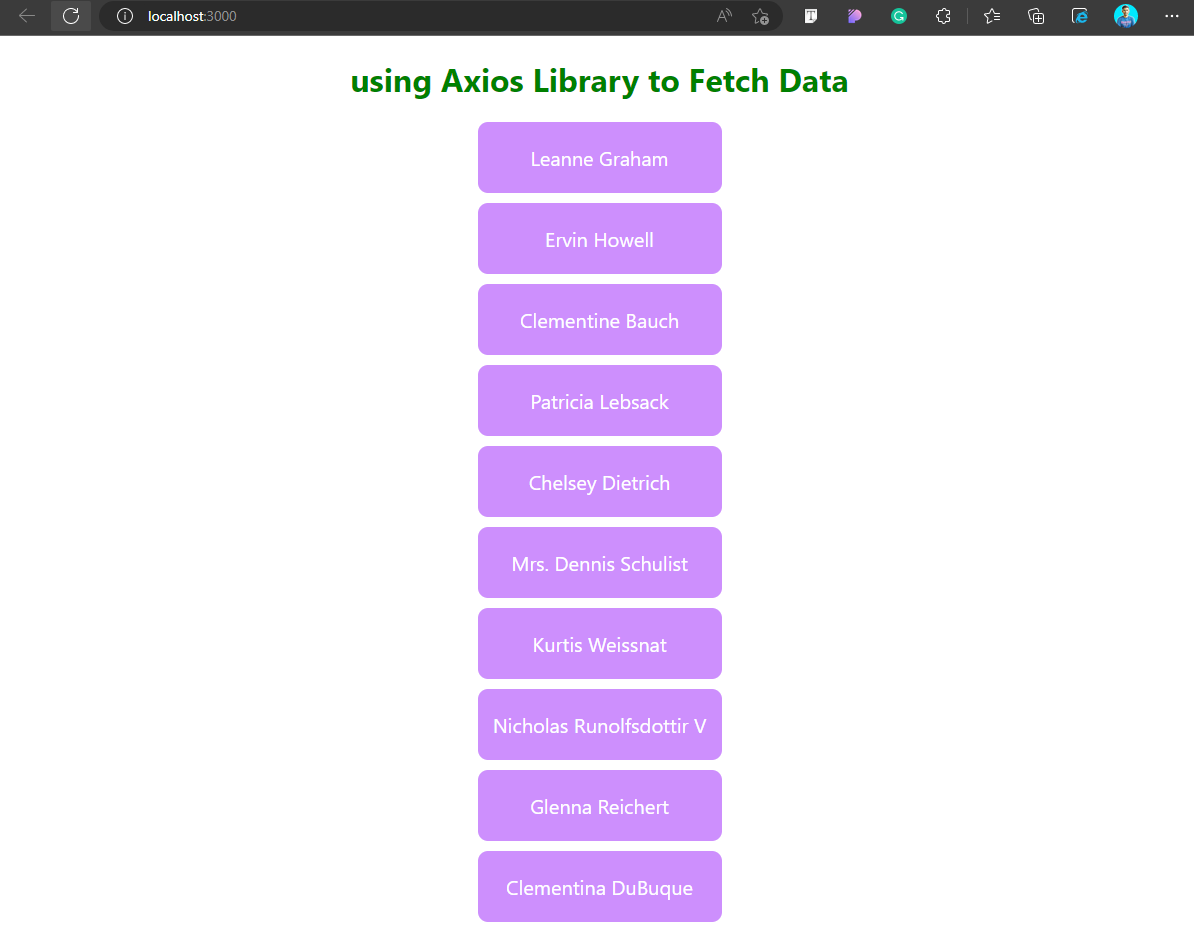
export default App;Output:
The output for the above example is as follows:
Before diving into the last section, ensure you’re solid on full-stack development essentials like front-end frameworks, back-end technologies, and database management. If you are looking for a detailed Full-Stack Development career program, you can join GUVI’s Full Stack Development Career Program with placement assistance. You will be able to master the MERN stack (MongoDB, Express.js, React, and Node.js) and build real-life projects.
Summing Up
In this blog, we learned how to fetch data using an API in a React.js application. We hope you get a very good understanding of how an API works, how to fetch data from an API, and the different ways of fetching data using an API. Additionally, we learned how to use the inbuilt JavaScript Fetch API to fetch data and also saw how to use the Axios library, which is a better alternative to the inbuilt Fetch API.
FAQs
Q1. How to fetch data from API and display in JS?
Ans.To fetch data from an API and display it in JS, you need to define a const data and store it in JSON by await response. json() method. When we get the data from API by fetch() method in the data variable; pass it to the function which will show the data fetched.
Q2. How to display and extract JSON data from an API?
Ans. To get JSON from a REST API endpoint, you must send an HTTP GET request to the REST API server and provide an Accept: application/json request header. The Accept: application/json header tells the REST API server that the API client expects to receive data in JSON format.

Q3. What is a fetch API in JavaScript?
Ans. The Fetch API is a modern interface that allows you to make HTTP requests to servers from web browsers. If you have worked with XMLHttpRequest (XHR) object, the Fetch API can perform all the tasks as the XHR object does. In addition, the Fetch API is much simpler and cleaner.























[…] this blog, we are going to use an existing react app project. Read the blog to know more about how to create a new react application using create-react-app […]
[…] our previous blog we have already discussed How to Fetch and Display data using API so we are not going to discuss that again here in […]
[…] Before moving on to learning about react props, make sure to create a react application project so that we can use props. We have already explained how to create a new react application in one of our blog. Learn more. […]